Abstract
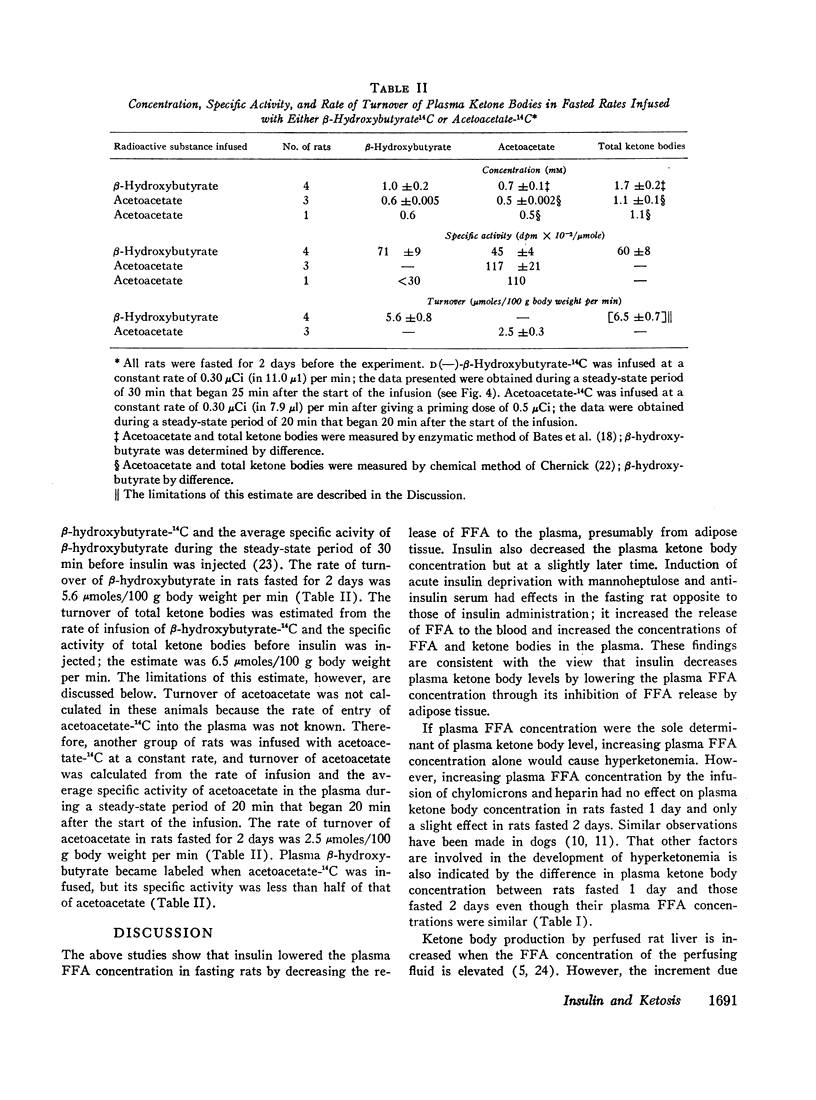
The metabolism of FFA and ketone bodies was studied in fasted rats by infusing at a constant rate tracer amounts of FFA-3H, β-hydroxybutyrate-14C or acetoacetate-14C for periods up to 2 hr. Blood that was removed for analyses was replaced by continuous transfusion. The rates of turnover of FFA, β-hydroxybutyrate, and acetoacetate in rats fasted for 2 days were, respectively, 3.2, 5.6, and 2.5 μmoles/100 g body weight per min.
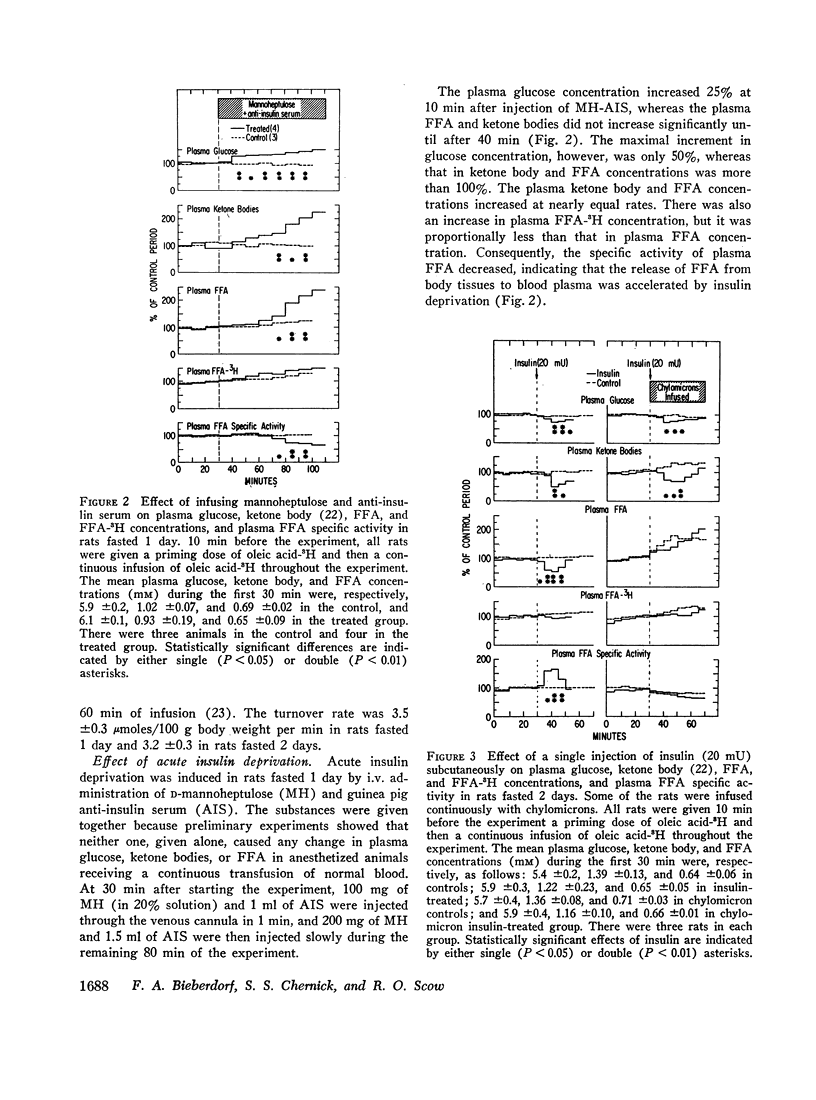
Infusion of mannoheptulose with anti-insulin serum increased plasma glucose, FFA, and ketone body concentrations and decreased the specific activity of plasma FFA. Injection of insulin (20 mU i.v.) decreased almost simultaneously plasma glucose, FFA, and ketone body concentrations and increased the specific activity of FFA, but it did not affect the plasma concentration of FFA-3H. The findings indicate that insulin deprivation increased and insulin injection decreased the release of FFA from body tissues in fasting rats.
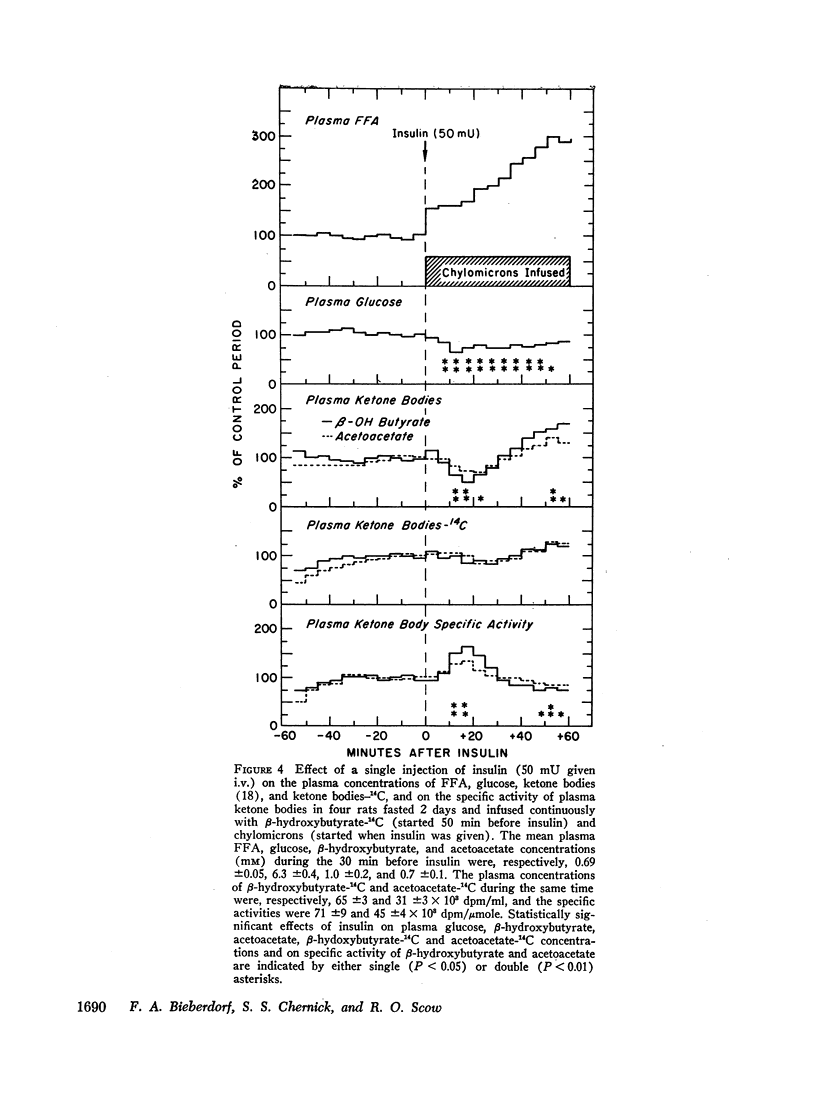
The plasma FFA concentration in fasting rats was increased by infusing chylomicrons and heparin, but this had very little effect on either plasma ketone body or glucose concentrations. Insulin injection (20 mU i.v.) lowered the plasma ketone body concentration in these animals. Studies using β-hydroxybutyrate-14C showed that insulin (50 mU i.v.) decreased ketogenesis in the presence of a sustained high plasma FFA concentration and had no effect on uptake of circulating ketone bodies.
The results indicate that plasma FFA concentration is not the sole determinant of plasma ketone body concentration and that insulin can suppress ketone body production through some means other than lowering plasma FFA concentration.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARMIN J., GRANT R. T., WRIGHT P. H. Experimental diabetes in rats produced by parenteral administration of antiinsulin serum. J Physiol. 1960 Aug;153:146–165. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEATTY C. H., MARCO A., PETERSON R. D., BOCEK R. M., WEST E. S. Acetoacetic acid metabolism by skeletal muscle fibers from control and diabetic rats. J Biol Chem. 1960 Oct;235:2774–2777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEATTY C. H., PETERSON R. D., BOCEK R. M., WEST E. S. Acetoacetate and glucose uptake by diaphragm and skeletal muscle from from control and diabetic rats. J Biol Chem. 1959 Jan;234(1):11–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERGMAN E. N., KON K., KATZ M. L. QUANTITATIVE MEASUREMENTS OF ACETOACETATE METABOLISM AND OXIDATION IN SHEEP. Am J Physiol. 1963 Oct;205:658–662. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1963.205.4.658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRESSLER R. The biochemistry of ketosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 Mar 5;104:735–752. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb17705.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates M. W., Krebs H. A., Williamson D. H. Turnover rates of ketone bodies in normal, starved and alloxan-diabetic rats. Biochem J. 1968 Dec;110(4):655–661. doi: 10.1042/bj1100655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crespin S. R., Greenough W. B., 3rd, Steinberg D. Stimulation of insulin secretion by infusion of free fatty acids. J Clin Invest. 1969 Oct;48(10):1934–1943. doi: 10.1172/JCI106160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLE V. P., MEINERTZ H. Microdetermination of long-chain fatty acids in plasma and tissues. J Biol Chem. 1960 Sep;235:2595–2599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain J. N., Scow R. O. Effect of hypophysectomy on lipid metabolism in pancreatectomized rats. Endocrinology. 1965 Sep;77(3):547–552. doi: 10.1210/endo-77-3-547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster D. W. Studies in the ketosis of fasting. J Clin Invest. 1967 Aug;46(8):1283–1296. doi: 10.1172/JCI105621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimberg M., Weinstein I., Kohout M. The effects of glucagon, dibutyryl cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate, and concentration of free fatty acid on hepatic lipid metabolism. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 10;244(19):5131–5139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacev V. P., Scow R. O. Effect of hormones on fatty acid release by rat adipose tissue in vivo. Am J Physiol. 1966 Jun;210(6):1199–1208. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.210.6.1199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs H. A., Wallace P. G., Hems R., Freedland R. A. Rates of ketone-body formation in the perfused rat liver. Biochem J. 1969 May;112(5):595–600. doi: 10.1042/bj1120595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison L. L., Seyffert W. A., Jr, Unger R. H., Barker B. Effect on plasma free fatty acids on plasma glucagon and serum insulin concentrations. Metabolism. 1968 Apr;17(4):301–304. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(68)90097-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen O. E., Morgan A. P., Kemp H. G., Sullivan J. M., Herrera M. G., Cahill G. F., Jr Brain metabolism during fasting. J Clin Invest. 1967 Oct;46(10):1589–1595. doi: 10.1172/JCI105650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penhos J. C., Wu C. H., Lemberg A., Daunas J., Brodoff B., Sodero A., Levine R. The effect of insulin on the metabolism of lipids and on urea formation by the perfused rat liver. Metabolism. 1968 Mar;17(3):246–259. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(68)90127-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBINSON D. S. THE CLEARING FACTOR LIPASE AND ITS ACTION IN THE TRANSPORT OF FATTY ACIDS BETWEEN THE BLOOD AND TISSUES. Adv Lipid Res. 1963;1:133–182. doi: 10.1016/b978-1-4831-9937-5.50010-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCOW R. O., CHERNICK S. S. Hormonal control of protein and fat metabolism in the pancreatectomized rat. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1960;16:497–545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMON E., SCOW R. O., CHERNICK S. S. Effects of D-mannoheptulose and D- edoheptulose on blood glucose and ketone bodies in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1961 Dec;201:1073–1077. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.201.6.1073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STADIE W. C. Ketogenesis. Diabetes. 1958 May-Jun;7(3):173–180. doi: 10.2337/diab.7.3.173b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEELE R., WALL J. S., DE BODO R. C., ALTSZULER N. Measurement of size and turnover rate of body glucose pool by the isotope dilution method. Am J Physiol. 1956 Sep;187(1):15–24. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1956.187.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scow R. O., Stein Y., Stein O. Incorporation of dietary lecithin and lysolecithin into lymph chylomicrons in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1967 Nov 10;242(21):4919–4924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Harken D. R., Dixon C. W., Heimberg M. Hepatic lipid metabolism in experimental diabetes. V. The effect of concentration of oleate on metabolism of triglycerides and on ketogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1969 May 10;244(9):2278–2285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson D. H., Bates M. W., Krebs H. A. Activity and intracellular distribution of enzymes of ketone-body metabolism in rat liver. Biochem J. 1968 Jul;108(3):353–361. doi: 10.1042/bj1080353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


