Abstract
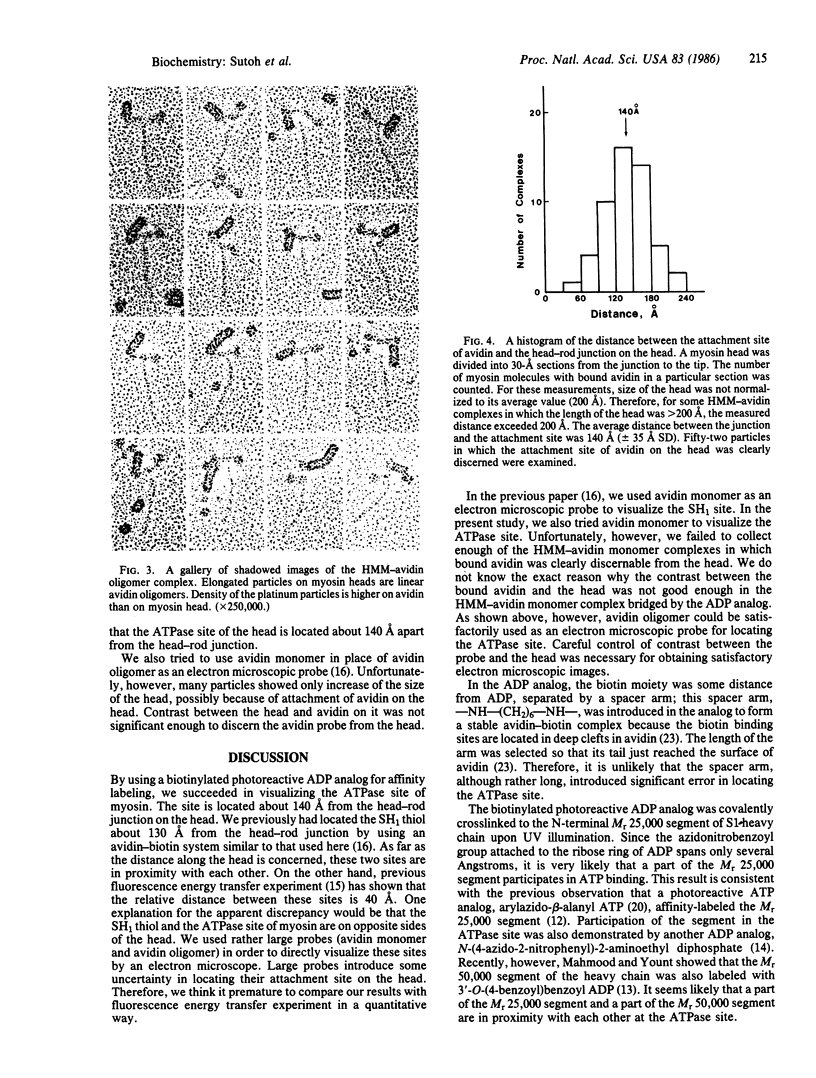
An ADP analog carrying a biotin moiety and a photoreactive group was synthesized. In the presence of vanadate ion (Vi), the analog was tightly trapped into the ATPase site of heavy meromyosin (HMM) or myosin subfragment 1 (S1) in an ADP analog/ATPase site molar ratio of 1:1. UV illumination on the HMM (or S1)-Vi-ADP analog complex resulted in covalent incorporation of the analog into the ATPase site. About 15% of the trapped analog was crosslinked to HMM or S1. Mapping of the crosslinking site of the analog showed that the N-terminal Mr 25,000 segment of the heavy chain participated in binding the ADP analog. The biotin moiety of the analog covalently incorporated into the ATPase site was visualized in electron microscopy by attaching an avidin oligomer. Rotary-shadowed images of the HMM-avidin complex revealed that the crosslinked ADP analog was located about 140 A from the head-rod junction on the head. The result indicates that the ATPase site of myosin is about 140 A apart from the head-rod junction along the head.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amos L. A., Huxley H. E., Holmes K. C., Goody R. S., Taylor K. A. Structural evidence that myosin heads may interact with two sites on F-actin. Nature. 1982 Sep 30;299(5882):467–469. doi: 10.1038/299467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botts J., Takashi R., Torgerson P., Hozumi T., Muhlrad A., Mornet D., Morales M. F. On the mechanism of energy transduction in myosin subfragment 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2060–2064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott A., Offer G. Shape and flexibility of the myosin molecule. J Mol Biol. 1978 Aug 25;123(4):505–519. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90204-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodno C. C. Inhibition of myosin ATPase by vanadate ion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2620–2624. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N. M., Konieczny L., Toms E. J., Valentine R. C. The use of bifunctional biotinyl compounds to determine the arrangement of subunits in avidin. Biochem J. 1971 Dec;125(3):781–791. doi: 10.1042/bj1250781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillory R. J., Jeng S. J. Arylazido nucleotide analogs in a photoaffinity approach to receptor site labeling. Methods Enzymol. 1977;46:259–288. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(77)46029-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. V., Roberts M. F., Dennis E. A., Allison W. S. Photoactivated heterobifunctional cross-linking reagents which demonstrate the aggregation state of phospholipase A2. Biochemistry. 1977 Dec 13;16(25):5650–5654. doi: 10.1021/bi00644a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg M., Mosbach K. Preparation of analogues of ATP, ADP and AMP suitable for binding to matrices and the enzymic interconversion of ATP and ADP in solid phase. Eur J Biochem. 1975 May 6;53(2):481–486. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04089.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahmood R., Yount R. G. Photochemical probes of the active site of myosin. Irradiation of trapped 3'-O-(4-benzoyl)benzoyladenosine 5'-triphosphate labels the 50-kilodalton heavy chain tryptic peptide. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):12956–12959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. B., Huxley H. E., DeRosier D. J. Three-dimensional reconstruction of F-actin, thin filaments and decorated thin filaments. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jun 14;50(2):279–295. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90192-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mornet D., Bertrand R. U., Pantel P., Audemard E., Kassab R. Proteolytic approach to structure and function of actin recognition site in myosin heads. Biochemistry. 1981 Apr 14;20(8):2110–2120. doi: 10.1021/bi00511a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mornet D., Pantel P., Audemard E., Kassab R. The limited tryptic cleavage of chymotryptic S-1: an approach to the characterization of the actin site in myosin heads. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Aug 13;89(3):925–932. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91867-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto Y., Yount R. G. Identification of an active site peptide of skeletal myosin after photoaffinity labeling with N-(4-azido-2-nitrophenyl)-2-aminoethyl diphosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1575–1579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onishi H., Wakabayashi T. Electron microscopic studies of myosin molecules from chicken gizzard muscle I: the formation of the intramolecular loop in the myosin tail. J Biochem. 1982 Sep;92(3):871–879. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shotton D. M., Burke B. E., Branton D. The molecular structure of human erythrocyte spectrin. Biophysical and electron microscopic studies. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jun 25;131(2):303–329. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90078-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slayter H. S., Lowey S. Substructure of the myosin molecule as visualized by electron microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Oct;58(4):1611–1618. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.4.1611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutoh K. An actin-binding site on the 20K fragment of myosin subfragment 1. Biochemistry. 1982 Sep 14;21(19):4800–4804. doi: 10.1021/bi00262a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutoh K. Identification of myosin-binding sites on the actin sequence. Biochemistry. 1982 Jul 20;21(15):3654–3661. doi: 10.1021/bi00258a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutoh K. Mapping of actin-binding sites on the heavy chain of myosin subfragment 1. Biochemistry. 1983 Mar 29;22(7):1579–1585. doi: 10.1021/bi00276a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutoh K., Yamamoto K., Wakabayashi T. Electron microscopic visualization of the SH1 thiol of myosin by the use of an avidin-biotin system. J Mol Biol. 1984 Sep 15;178(2):323–339. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90147-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szilagyi L., Balint M., Sreter F. A., Gergely J. Photoaffinity labelling with an ATP analog of the N-terminal peptide of myosin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Apr 13;87(3):936–945. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)92047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao T., Lamkin M. Excitation energy transfer studies on the proximity between SH1 and the adenosinetriphosphatase site in myosin subfragment 1. Biochemistry. 1981 Aug 18;20(17):5051–5055. doi: 10.1021/bi00520a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor K. A., Amos L. A. A new model for the geometry of the binding of myosin crossbridges to muscle thin filaments. J Mol Biol. 1981 Apr 5;147(2):297–324. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90442-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoshima C., Wakabayashi T. Three-dimensional image analysis of the complex of thin filaments and myosin molecules from skeletal muscle. I. Tilt angle of myosin subfragment-1 in the rigor complex. J Biochem. 1979 Dec;86(6):1887–1890. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoshima C., Wakabayashi T. Three-dimensional image analysis of the complex of thin filaments and myosin molecules from skeletal muscle. IV. Reconstitution from minimal- and high-dose images of the actin-tropomyosin-myosin subfragment-1 complex. J Biochem. 1985 Jan;97(1):219–243. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoshima C., Wakabayashi T. Three-dimensional image analysis of the complex of thin filaments and myosin molecules from skeletal muscle. V. Assignment of actin in the actin-tropomyosin-myosin subfragment-1 complex. J Biochem. 1985 Jan;97(1):245–263. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler J. M., Branton D. Rotary shadowing of extended molecules dried from glycerol. J Ultrastruct Res. 1980 May;71(2):95–102. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(80)90098-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakabayashi T., Toyoshima C. Three-dimensional image analysis of the complex of thin filaments and myosin molecules from skeletal muscle. II. The multi-domain structure of actin-myosin S1 complex. J Biochem. 1981 Sep;90(3):683–701. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeds A. G., Taylor R. S. Separation of subfragment-1 isoenzymes from rabbit skeletal muscle myosin. Nature. 1975 Sep 4;257(5521):54–56. doi: 10.1038/257054a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Sekine T. Interaction of myosin subfragment-1 with actin. III. Effect of cleavage of the subfragment-1 heavy chain on its interaction with actin. J Biochem. 1979 Dec;86(6):1869–1881. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Sekine T. Interactions of ATP analogues, N6-[(6-aminohexyl) Carbamoylmethyl] ATP and its dinitrophenyl derivative, with the active site of myosin. J Biochem. 1982 Nov;92(5):1519–1525. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]