Abstract
We have isolated five cDNA clones for rat liver catalase (hydrogen peroxide:hydrogen peroxide oxidoreductase, EC 1.11.1.6). These clones overlapped with each other and covered the entire length of the mRNA, which had been estimated to be 2.4 kilobases long by blot hybridization analysis of electrophoretically fractionated RNA. Nucleotide sequencing was carried out on these five clones and the composite nucleotide sequence of catalase cDNA was determined. The 5' noncoding region contained 83 bases and was followed by 1581 bases of an open reading frame that encoded 527 amino acids. The 3' noncoding region was 831 bases long and contained long repeats of the unit AC. The amino acid sequence deduced from the nucleotide sequence of the cDNAs showed about 90% homology with the reported primary structure of bovine liver catalase. The molecular weight of rat liver catalase was calculated to be 59,758 from the predicted amino acid sequence. The amino acid residues in contact with the heme group are completely identical for bovine liver and rat liver catalases. The amino acid sequence at the COOH terminus was confirmed by the results of carboxypeptidase P treatment of the protein purified from rat liver in the presence of leupeptin. Rat liver catalase has no cleavable signal peptide for translocation of the enzyme into peroxisomes.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Crane D., Holmes R., Masters C. Proteolytic modification of mouse liver catalase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Feb 26;104(4):1567–1572. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91430-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doi Y., Nishida T. Microheterogeneity and physical properties of human lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5840–5846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii-Kuriyama Y., Taniguchi T., Mizukami Y., Sakai M., Tashiro Y., Muramatsu M. Construction and identification of a hybrid plasmid containing DNA sequence complementary to phenobarbital-inducible cytochrome P-450 messenger RNA from rat liver. J Biochem. 1981 Jun;89(6):1869–1879. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiki Y., Rachubinski R. A., Mortensen R. M., Lazarow P. B. Synthesis of 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase of rat liver peroxisomes on free polyribosomes as a larger precursor. Induction of thiolase mRNA activity by clofibrate. Biochem J. 1985 Mar 15;226(3):697–704. doi: 10.1042/bj2260697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuta S., Hashimoto T., Miura S., Mori M., Tatibana M. Cell-free synthesis of the enzymes of peroxisomal beta-oxidation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Mar 30;105(2):639–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91482-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuta S., Miyazawa S., Hashimoto T. Biosynthesis of enzymes of peroxisomal beta-oxidation. J Biochem. 1982 Aug;92(2):319–326. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman B. M., Blobel G. Biogenesis of peroxisomes: intracellular site of synthesis of catalase and uricase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5066–5070. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes R. S., Masters C. J. Species specific features of the distribution and multiplicity of mammalian liver catalase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Jan;148(1):217–223. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90134-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. L., Masters C. J. On the nature and characteristics of the multiple forms of catalase in mouse liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Jul;169(1):7–21. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90311-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. L., Masters C. J. On the synthesis and degradation of the multiple forms of catalase in mouse liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Apr 2;161(2):601–609. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90343-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi-Torii K., Hayashi S., Nakamoto H., Nakamura S. Properties of Aspergillus niger catalase. J Biochem. 1982 Nov;92(5):1449–1456. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korneluk R. G., Quan F., Lewis W. H., Guise K. S., Willard H. F., Holmes M. T., Gravel R. A. Isolation of human fibroblast catalase cDNA clones. Sequence of clones derived from spliced and unspliced mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13819–13823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Grez M., Hauser H., Lindenmaier W., Schütz G. 5'-Terminal sequences of eucaryotic mRNA can be cloned with high efficiency. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 25;9(10):2251–2266. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.10.2251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mainferme F., Wattiaux R. Effect of lysosomes on rat-liver catalase. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Oct;127(2):343–346. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06877.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
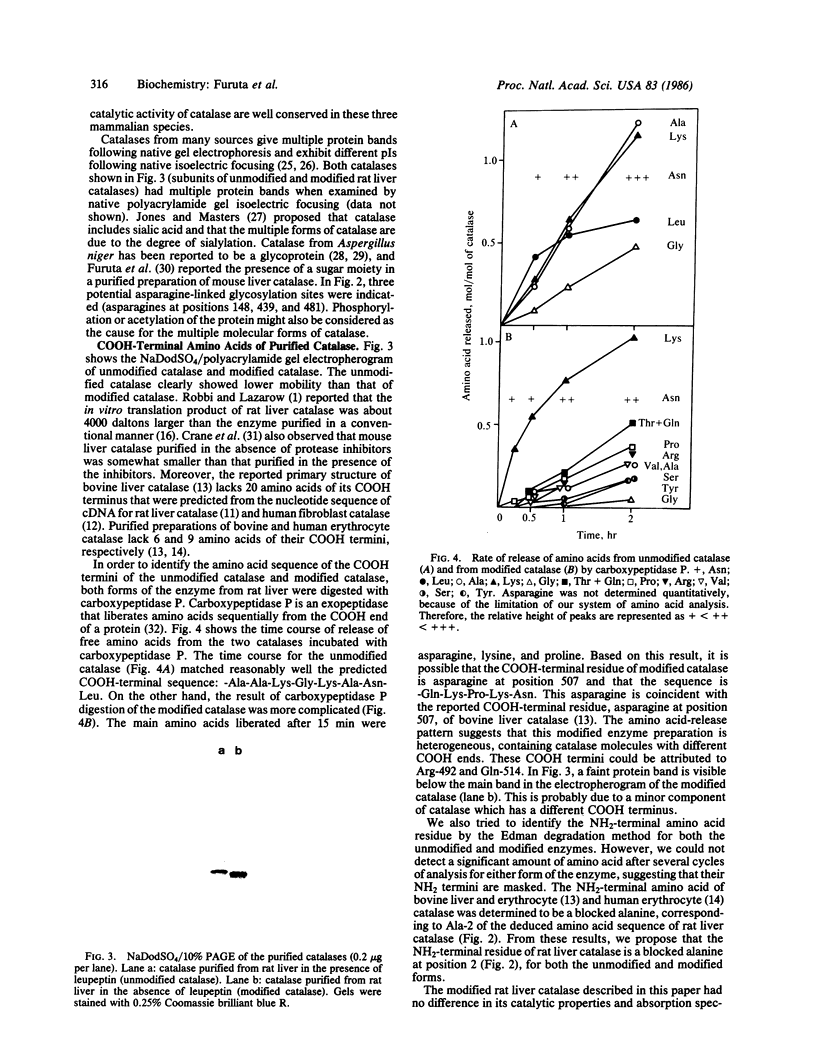
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura S., Mori M., Takiguchi M., Tatibana M., Furuta S., Miyazawa S., Hashimoto T. Biosynthesis and intracellular transport of enzymes of peroxisomal beta-oxidation. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6397–6402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murthy M. R., Reid T. J., 3rd, Sicignano A., Tanaka N., Rossmann M. G. Structure of beef liver catalase. J Mol Biol. 1981 Oct 25;152(2):465–499. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90254-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osumi T., Ishii N., Hijikata M., Kamijo K., Ozasa H., Furuta S., Miyazawa S., Kondo K., Inoue K., Kagamiyama H. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of the cDNA for rat peroxisomal enoyl-CoA: hydratase-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase bifunctional enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 25;260(15):8905–8910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osumi T., Ozasa H., Hashimoto T. Molecular cloning of cDNA for rat acyl-CoA oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2031–2034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osumi T., Ozasa H., Miyazawa S., Hashimoto T. Molecular cloning of cDNA for rat liver catalase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jul 31;122(2):831–837. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80109-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozasa H., Miyazawa S., Osumi T. Biosynthesis of carnitine octanoyltransferase and carnitine palmitoyltransferase. J Biochem. 1983 Aug;94(2):543–549. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRICE V. E., STERLING W. R., TARANTOLA V. A., HARTLEY R. W., Jr, RECHCIGL M., Jr The kinetics of catalase synthesis and destruction in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1962 Nov;237:3468–3475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rachubinski R. A., Fujiki Y., Mortensen R. M., Lazarow P. B. Acyl-Coa oxidase and hydratase-dehydrogenase, two enzymes of the peroxisomal beta-oxidation system, are synthesized on free polysomes of clofibrate-treated rat liver. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):2241–2246. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.2241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbi M., Lazarow P. B. Synthesis of catalase in two cell-free protein-synthesizing systems and in rat liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4344–4348. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder W. A., Shelton J. R., Shelton J. B., Apell G., Evans L., Bonaventura J., Fang R. S. The partial amino acid sequence of human erythrocyte catalase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Mar;214(1):422–424. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90045-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder W. A., Shelton J. R., Shelton J. B., Robberson B., Apell G., Fang R. S., Bonaventura J. The complete amino acid sequence of bovine liver catalase and the partial sequence of bovine erythrocyte catalase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Mar;214(1):397–421. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90044-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman B. P., Hultin H. O. Effect of deglycosylation on the stability of Aspergillus niger catalase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Dec;212(2):385–392. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90379-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama S., Oobayashi A., Tanabe O., Sugawara S., Araki E. Production and some properties of a new type of acid carboxypeptidase of Penicillium molds. Appl Microbiol. 1974 May;27(5):953–960. doi: 10.1128/am.27.5.953-960.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]