Abstract
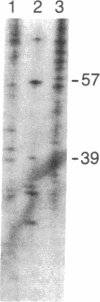
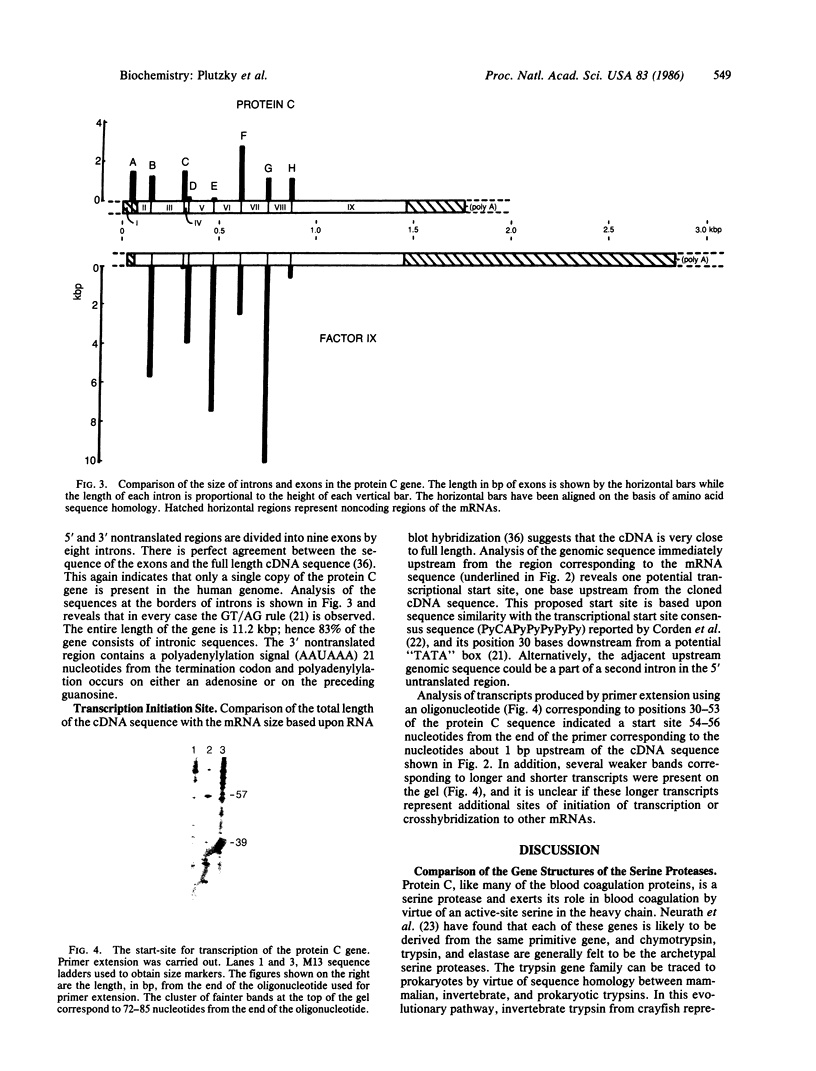
We have isolated overlapping phage genomic clones covering an area of 21 kilobases that encodes the human protein C gene. The gene is at least 11.2 kilobases long and is made up of nine exons and eight introns. Two regions homologous to epidermal growth factor and transforming growth factor are encoded by amino acids 46-91 and 92-136 and are precisely delimited by introns, as is a similar sequence in the genes for coagulation factor IX and tissue plasminogen activator. When homologous amino acids of factor IX and protein C are aligned, the positions of all eight introns correspond precisely, suggesting that these genes are the product of a relatively recent gene duplication. Nevertheless, the two genes are sufficiently distantly related that no nucleic acid homology remains in the intronic regions and that the size of the introns varies dramatically between the two genes. The similarity of the genes for factor IX and protein C suggests that they may be the most closely related members of the serine protease gene family involved in coagulation and fibrinolysis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anson D. S., Choo K. H., Rees D. J., Giannelli F., Gould K., Huddleston J. A., Brownlee G. G. The gene structure of human anti-haemophilic factor IX. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1053–1060. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01926.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckmann R. J., Schmidt R. J., Santerre R. F., Plutzky J., Crabtree G. R., Long G. L. The structure and evolution of a 461 amino acid human protein C precursor and its messenger RNA, based upon the DNA sequence of cloned human liver cDNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 25;13(14):5233–5247. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.14.5233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertina R. M., Broekmans A. W., van der Linden I. K., Mertens K. Protein C deficiency in a Dutch family with thrombotic disease. Thromb Haemost. 1982 Aug 24;48(1):1–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branson H. E., Katz J., Marble R., Griffin J. H. Inherited protein C deficiency and coumarin-responsive chronic relapsing purpura fulminans in a newborn infant. Lancet. 1983 Nov 19;2(8360):1165–1168. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91216-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Benoist C., O'Hare K., Gannon F., Chambon P. Ovalbumin gene: evidence for a leader sequence in mRNA and DNA sequences at the exon-intron boundaries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4853–4857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bányai L., Váradi A., Patthy L. Common evolutionary origin of the fibrin-binding structures of fibronectin and tissue-type plasminogen activator. FEBS Lett. 1983 Oct 31;163(1):37–41. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)81157-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comp P. C., Esmon C. T. Recurrent venous thromboembolism in patients with a partial deficiency of protein S. N Engl J Med. 1984 Dec 13;311(24):1525–1528. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198412133112401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corden J., Wasylyk B., Buchwalder A., Sassone-Corsi P., Kedinger C., Chambon P. Promoter sequences of eukaryotic protein-coding genes. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1406–1414. doi: 10.1126/science.6251548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabtree G. R., Kant J. A. Organization of the rat gamma-fibrinogen gene: alternative mRNA splice patterns produce the gamma A and gamma B (gamma ') chains of fibrinogen. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):159–166. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90415-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craik C. S., Rutter W. J., Fletterick R. Splice junctions: association with variation in protein structure. Science. 1983 Jun 10;220(4602):1125–1129. doi: 10.1126/science.6344214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T., Owen W. G. Identification of an endothelial cell cofactor for thrombin-catalyzed activation of protein C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2249–2252. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon N. L., Owen W. G., Esmon C. T. Isolation of a membrane-bound cofactor for thrombin-catalyzed activation of protein C. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):859–864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernlund P., Stenflo J. Amino acid sequence of the light chain of bovine protein C. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12170–12179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster D. C., Yoshitake S., Davie E. W. The nucleotide sequence of the gene for human protein C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4673–4677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster D., Davie E. W. Characterization of a cDNA coding for human protein C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4766–4770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory H., Preston B. M. The primary structure of human urogastrone. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1977;9(2):107–118. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1977.tb03470.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. H., Evatt B., Zimmerman T. S., Kleiss A. J., Wideman C. Deficiency of protein C in congenital thrombotic disease. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1370–1373. doi: 10.1172/JCI110385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisiel W., Canfield W. M., Ericsson L. H., Davie E. W. Anticoagulant properties of bovine plasma protein C following activation by thrombin. Biochemistry. 1977 Dec 27;16(26):5824–5831. doi: 10.1021/bi00645a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisiel W. Human plasma protein C: isolation, characterization, and mechanism of activation by alpha-thrombin. J Clin Invest. 1979 Sep;64(3):761–769. doi: 10.1172/JCI109521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marlar R. A., Griffin J. H. Deficiency of protein C inhibitor in combined factor V/VIII deficiency disease. J Clin Invest. 1980 Nov;66(5):1186–1189. doi: 10.1172/JCI109952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquardt H., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Twardzik D. R., De Larco J. E., Stephenson J. R., Todaro G. J. Transforming growth factors produced by retrovirus-transformed rodent fibroblasts and human melanoma cells: amino acid sequence homology with epidermal growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4684–4688. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath H. Evolution of proteolytic enzymes. Science. 1984 Apr 27;224(4647):350–357. doi: 10.1126/science.6369538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ny T., Elgh F., Lund B. The structure of the human tissue-type plasminogen activator gene: correlation of intron and exon structures to functional and structural domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5355–5359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakata Y., Curriden S., Lawrence D., Griffin J. H., Loskutoff D. J. Activated protein C stimulates the fibrinolytic activity of cultured endothelial cells and decreases antiactivator activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1121–1125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligsohn U., Berger A., Abend M., Rubin L., Attias D., Zivelin A., Rapaport S. I. Homozygous protein C deficiency manifested by massive venous thrombosis in the newborn. N Engl J Med. 1984 Mar 1;310(9):559–562. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198403013100904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. E., Summers M. D. The bidirectional transfer of DNA and RNA to nitrocellulose or diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):123–129. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenflo J. A new vitamin K-dependent protein. Purification from bovine plasma and preliminary characterization. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jan 25;251(2):355–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenflo J., Fernlund P. Amino acid sequence of the heavy chain of bovine protein C. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12180–12190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenflo J. Structure and function of protein C. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1984 Apr;10(2):109–121. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1004413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titani K., Sasagawa T., Woodbury R. G., Ericsson L. H., Dörsam H., Kraemer M., Neurath H., Zwilling R. Amino acid sequence of crayfish (Astacus fluviatilis) trypsin If. Biochemistry. 1983 Mar 15;22(6):1459–1465. doi: 10.1021/bi00275a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]