Abstract
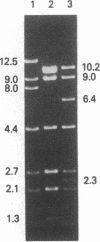
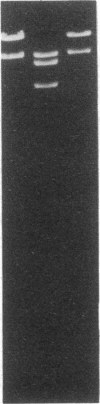
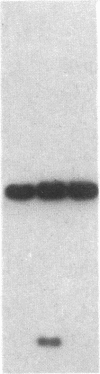
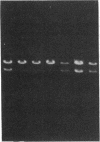
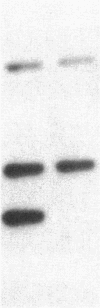
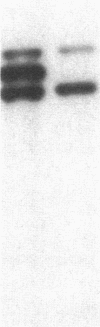
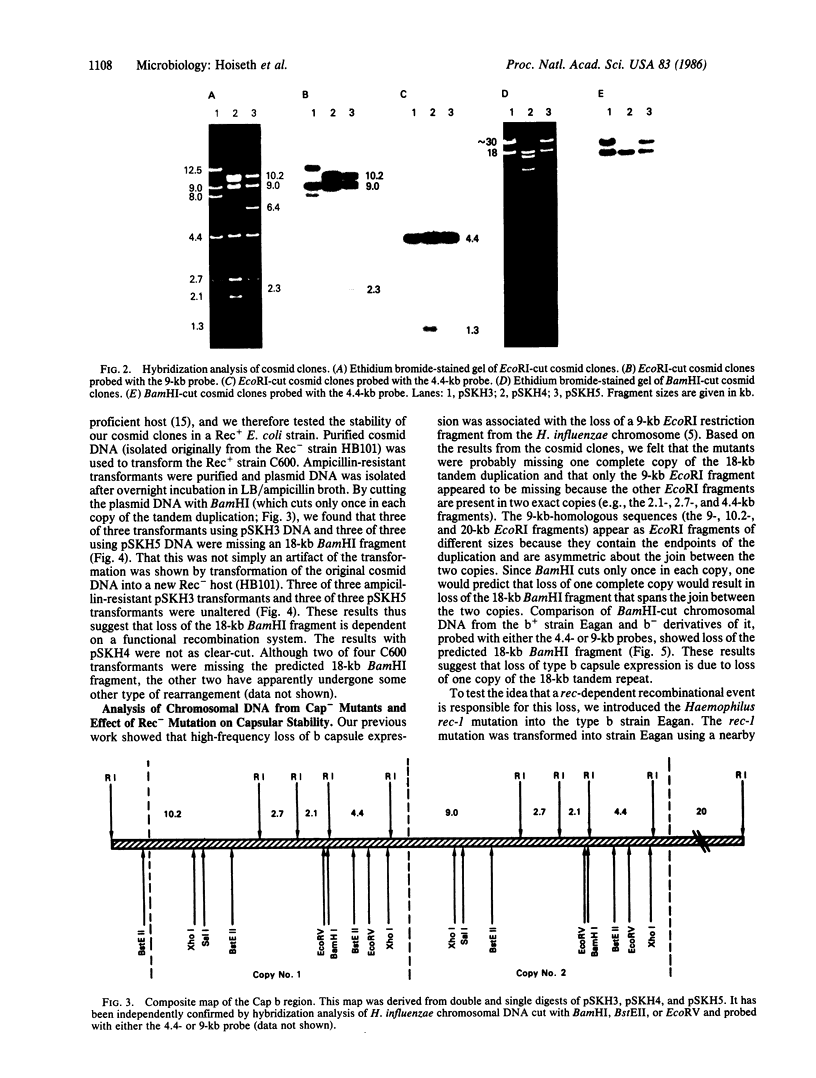
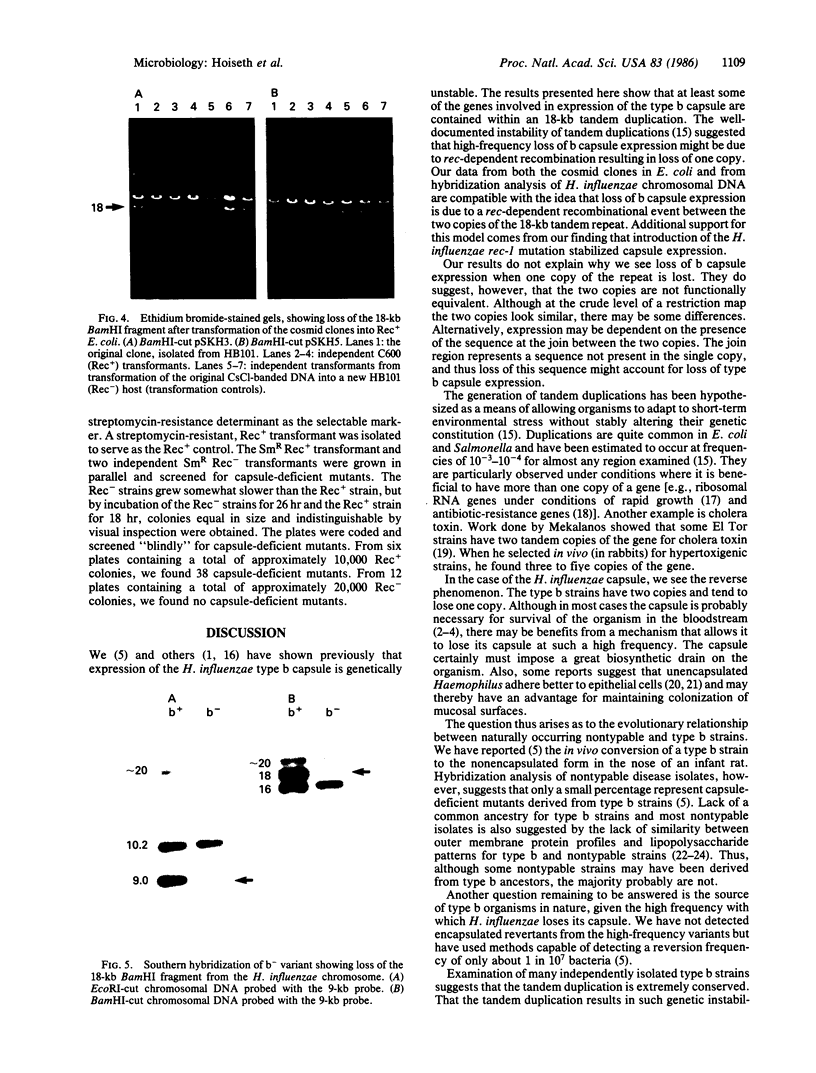
Encapsulated Haemophilus influenzae type b produce nonencapsulated variants at high frequency (0.1-0.3%). Cosmid cloning was used to investigate the genetic mechanism responsible for this instability. Analysis of three independently derived cosmid clones showed that the b+ parental strain contains an 18-kilobase tandem duplication of genes involved in type b capsule expression. Loss of one complete copy of the 18-kilobase tandem duplication occurred following transformation of the cosmid clones into Rec+, but not Rec-, Escherichia coli, and in H. influenzae strains that had spontaneously lost capsule expression. These results suggest that high-frequency loss of type b capsule expression is due to rec-dependent recombination between the two copies of the 18-kilobase tandem repeat. This is further supported by our finding that introduction of the H. influenzae rec-1 mutation stabilized type b capsule expression.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson P., Johnston R. B., Jr, Smith D. H. Human serum activities against Hemophilus influenzae, type b. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jan;51(1):31–38. doi: 10.1172/JCI106793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson P., Roth J. Spontaneous tandem genetic duplications in Salmonella typhimurium arise by unequal recombination between rRNA (rrn) cistrons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3113–3117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R. P., Roth J. R. Tandem genetic duplications in phage and bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:473–505. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.002353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barenkamp S. J., Munson R. S., Jr, Granoff D. M. Outer membrane protein and biotype analysis of pathogenic nontypable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):535–540. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.535-540.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catlin B. W., Bendler J. W., 3rd, Goodgal S. H. The type b capsulation locus of Haemophilus influenzae: map location and size. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 May;70(3):411–422. doi: 10.1099/00221287-70-3-411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catlin B. W. Haemophilus influenzae in cultures of cerebrospinal fluid. Noncapsulated variants typable by immunofluorescence. Am J Dis Child. 1970 Sep;120(3):203–210. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1970.02100080087005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto H., Rownd R. H. Transition of the R factor NR1 and Proteus mirabilis: level of drug resistance of nontransitioned and transitioned cells. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jul;123(1):56–68. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.1.56-68.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill W. E., Payne W. L., Crouch R. J., Davis V. M., English L. L., Ferreira J. L., Gemski P., Jagow J. A., Moseley S. L., Noah C. W. Genetic methods for the detection of microbial pathogens. Identification of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli by DNA colony hybridization: collaborative study. J Assoc Off Anal Chem. 1984 Jul-Aug;67(4):801–807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B., Collins J. A small cosmid for efficient cloning of large DNA fragments. Gene. 1980 Nov;11(3-4):291–298. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90069-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoiseth S. K., Connelly C. J., Moxon E. R. Genetics of spontaneous, high-frequency loss of b capsule expression in Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1985 Aug;49(2):389–395. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.2.389-395.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inzana T. J. Electrophoretic heterogeneity and interstrain variation of the lipopolysaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae. J Infect Dis. 1983 Sep;148(3):492–499. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.3.492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampe R. M., Mason E. O., Jr, Kaplan S. L., Umstead C. L., Yow M. D., Feigin R. D. Adherence of Haemophilus influenzae to buccal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):166–172. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.166-172.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb M. R., Smith D. H. Outer membrane protein composition in disease isolates of Haemophilus influenzae: pathogenic and epidemiological implications. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):709–717. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.709-717.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J. Duplication and amplification of toxin genes in Vibrio cholerae. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):253–263. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90228-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxon E. R., Deich R. A., Connelly C. Cloning of chromosomal DNA from Haemophilus influenzae. Its use for studying the expression of type b capsule and virulence. J Clin Invest. 1984 Feb;73(2):298–306. doi: 10.1172/JCI111214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxon E. R., Vaughn K. A. The type b capsular polysaccharide as a virulence determinant of Haemophilus influenzae: studies using clinical isolates and laboratory transformants. J Infect Dis. 1981 Apr;143(4):517–524. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.4.517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pichichero M. E. Adherence of Haemophilus influenzae to human buccal and pharyngeal epithelial cells: relationship to pilation. J Med Microbiol. 1984 Aug;18(1):107–116. doi: 10.1099/00222615-18-1-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow J. K., Boling M. E., Beattie K. L., Kimball R. F. A complex of recombination and repair genes in Haemophilus influenzae. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jul 21;68(2):361–378. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90218-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton A., Schneerson R., Kendall-Morris S., Robbins J. B. Differential complement resistance mediates virulence of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):95–104. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.95-104.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwahlen A., Winkelstein J. A., Moxon E. R. Surface determinants of Haemophilus influenzae pathogenicity: comparative virulence of capsular transformants in normal and complement-depleted rats. J Infect Dis. 1983 Sep;148(3):385–394. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.3.385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]