Abstract
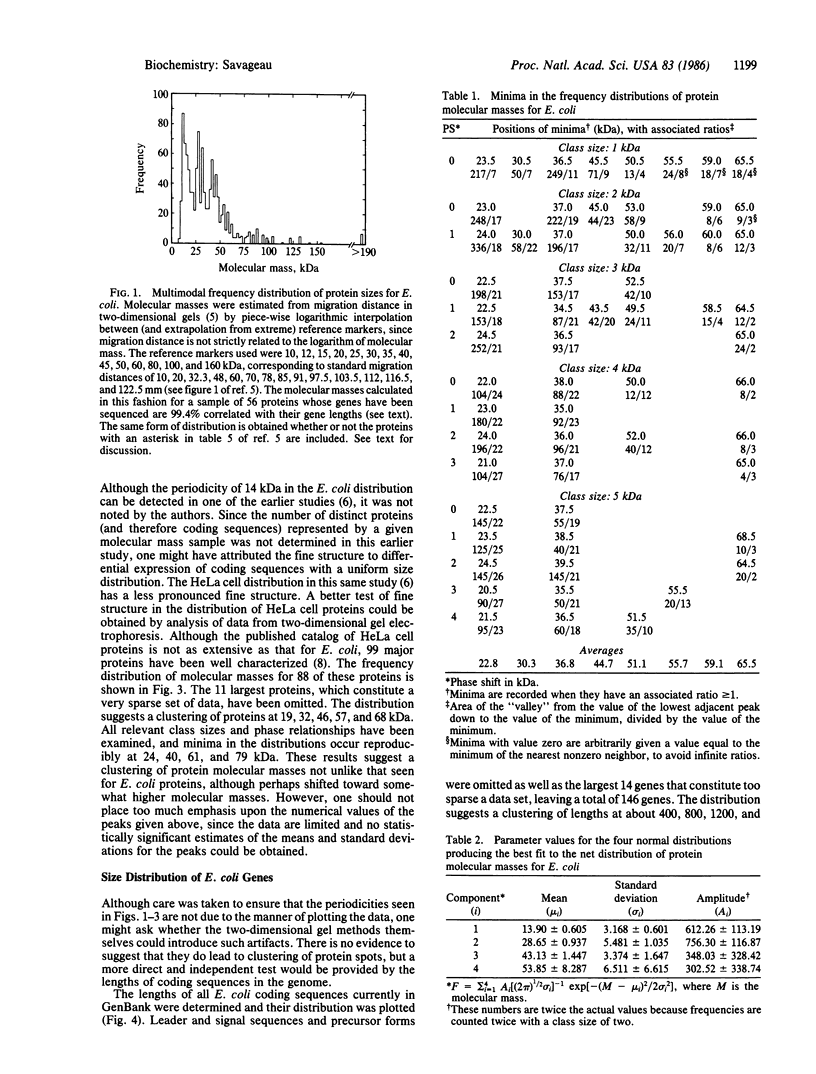
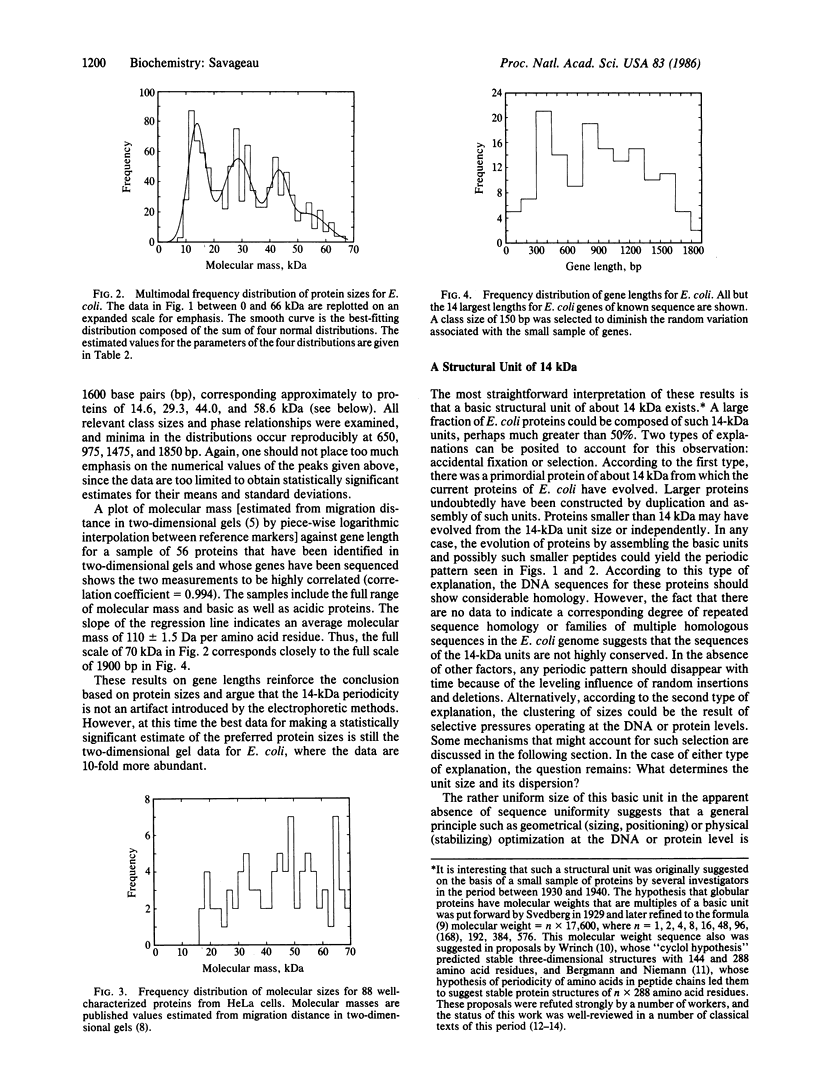
Initial attempts to correlate the distribution of gene density (number of gene loci per unit length on the linkage map) with the distribution of lengths of coding sequences have led to the observation that 46% of approximately 1000 sampled proteins in Escherichia coli have molecular masses of n X 14,000 +/- 2500 daltons (n = 1, 2, ...). This clustering around multiples of 14,000 contrasts with the 36% one would expect in these ranges if the sizes were uniformly distributed. The entire distribution is well fit by a sum of normal or lognormal distributions located at multiples of 14,000, which suggests that the percentage of E. coli proteins governed by the underlying sizing mechanism is much greater than 50%. Clustering of protein molecular sizes around multiples of a unit size also is suggested by the distribution of well-characterized HeLa cell proteins. The distribution of gene lengths for E. coli suggests regular clustering, which implies that the clustering of protein molecular masses is not an artifact of the molecular mass measurement by gel electrophoresis. These observations suggest the existence of a fundamental structural unit. The rather uniform size of this structural unit (without any apparent sequence homology) suggests that a general principle such as geometrical or physical optimization at the DNA or protein level is responsible. This suggestion is discussed in relation to experimental evidence for the domain structure of proteins and to existing hypotheses that attempt to account for these domains. Microevolution would appear to be accommodated by incremental changes within this fundamental unit, whereas macroevolution would appear to involve "quantum" changes to the next stable size of protein.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 7. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Jun;47(2):180–230. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.2.180-230.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann B. J., Low K. B., Taylor A. L. Recalibrated linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Mar;40(1):116–167. doi: 10.1128/br.40.1.116-167.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake C. C. Exons encode protein functional units. Nature. 1979 Feb 22;277(5698):598–598. doi: 10.1038/277598a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake C. Exons--present from the beginning? Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):535–537. doi: 10.1038/306535a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brändeén C. I. Relation between structure and function of alpha/beta-proteins. Q Rev Biophys. 1980 Aug;13(3):317–338. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500001712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne L. A., Skinner J. D. Avian erythrocyte chromatin degradation: the progressive exposure of the dinucleosomal repeat by bovine-pancreatic-DNAase-I-armed probes and free DNAase-I. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):665–673. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M., Cunningham B. A., Gall W. E., Gottlieb P. D., Rutishauser U., Waxdal M. J. The covalent structure of an entire gammaG immunoglobulin molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 May;63(1):78–85. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.1.78. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M., Gall W. E. The antibody problem. Annu Rev Biochem. 1969;38:415–466. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.38.070169.002215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert W. Genes-in-pieces revisited. Science. 1985 May 17;228(4701):823–824. doi: 10.1126/science.4001923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert W. Why genes in pieces? Nature. 1978 Feb 9;271(5645):501–501. doi: 10.1038/271501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Go M. Correlation of DNA exonic regions with protein structural units in haemoglobin. Nature. 1981 May 7;291(5810):90–92. doi: 10.1038/291090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Go M. Modular structural units, exons, and function in chicken lysozyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1964–1968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. E. Tertiary structure of Escherichia coli beta-D-galactosidase. J Mol Biol. 1969 Dec 28;46(3):441–446. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90187-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith J. D. Visualization of prokaryotic DNA in a regularly condensed chromatin-like fiber. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):563–567. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill R. L., Delaney R., Fellows R. E., Lebovitz H. E. The evolutionary origins of the immunoglobulins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Dec;56(6):1762–1769. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.6.1762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo T. Immunoglobulin genes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:499–528. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.002435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood L., Steinmetz M., Malissen B. Genes of the major histocompatibility complex of the mouse. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:529–568. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.002525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jurka J., Savageau M. A. Gene density over the chromosome of Escherichia coli: frequency distribution, spatial clustering, and symmetry. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):806–811. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.806-811.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karplus M., Weaver D. L. Protein-folding dynamics. Nature. 1976 Apr 1;260(5550):404–406. doi: 10.1038/260404a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiehn E. D., Holland J. J. Size distrbution of polypeptide chains in cells. Nature. 1970 May 9;226(5245):544–545. doi: 10.1038/226544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malissen M., Minard K., Mjolsness S., Kronenberg M., Goverman J., Hunkapiller T., Prystowsky M. B., Yoshikai Y., Fitch F., Mak T. W. Mouse T cell antigen receptor: structure and organization of constant and joining gene segments encoding the beta polypeptide. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1101–1110. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90444-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., Vaughn V., Phillips T. A., Bloch P. L. Gene-protein index of Escherichia coli K-12. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Jun;47(2):231–284. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.2.231-284.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnes J. R., Seidman J. G. Structure of wild-type and mutant mouse beta 2-microglobulin genes. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):661–669. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90182-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettijohn D. E. Structure and properties of the bacterial nucleoid. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):667–669. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90269-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. S. The anatomy and taxonomy of protein structure. Adv Protein Chem. 1981;34:167–339. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60520-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakano H., Rogers J. H., Hüppi K., Brack C., Traunecker A., Maki R., Wall R., Tonegawa S. Domains and the hinge region of an immunoglobulin heavy chain are encoded in separate DNA segments. Nature. 1979 Feb 22;277(5698):627–633. doi: 10.1038/277627a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer S. S., Cohen J. E. The size distributions of proteins, mRNA, and nuclear RNA. J Mol Evol. 1980 Mar;15(1):37–57. doi: 10.1007/BF01732582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S., Russell D. W. The LDL receptor gene: a mosaic of exons shared with different proteins. Science. 1985 May 17;228(4701):815–822. doi: 10.1126/science.2988123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tainer J. A., Getzoff E. D., Alexander H., Houghten R. A., Olson A. J., Lerner R. A., Hendrickson W. A. The reactivity of anti-peptide antibodies is a function of the atomic mobility of sites in a protein. Nature. 1984 Nov 8;312(5990):127–134. doi: 10.1038/312127a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westhof E., Altschuh D., Moras D., Bloomer A. C., Mondragon A., Klug A., Van Regenmortel M. H. Correlation between segmental mobility and the location of antigenic determinants in proteins. Nature. 1984 Sep 13;311(5982):123–126. doi: 10.1038/311123a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetlaufer D. B. Folding of protein fragments. Adv Protein Chem. 1981;34:61–92. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60518-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetlaufer D. B. Nucleation, rapid folding, and globular intrachain regions in proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):697–701. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. F., Gagnon J. Neuronal cell Thy-1 glycoprotein: homology with immunoglobulin. Science. 1982 May 14;216(4547):696–703. doi: 10.1126/science.6177036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. P., Athey B. D., Muglia L. J., Schappe R. S., Gough A. H., Langmore J. P. Chromatin fibers are left-handed double helices with diameter and mass per unit length that depend on linker length. Biophys J. 1986 Jan;49(1):233–248. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83637-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodcock C. L., Frado L. L., Rattner J. B. The higher-order structure of chromatin: evidence for a helical ribbon arrangement. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 1):42–52. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worcel A., Strogatz S., Riley D. Structure of chromatin and the linking number of DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1461–1465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


