Abstract
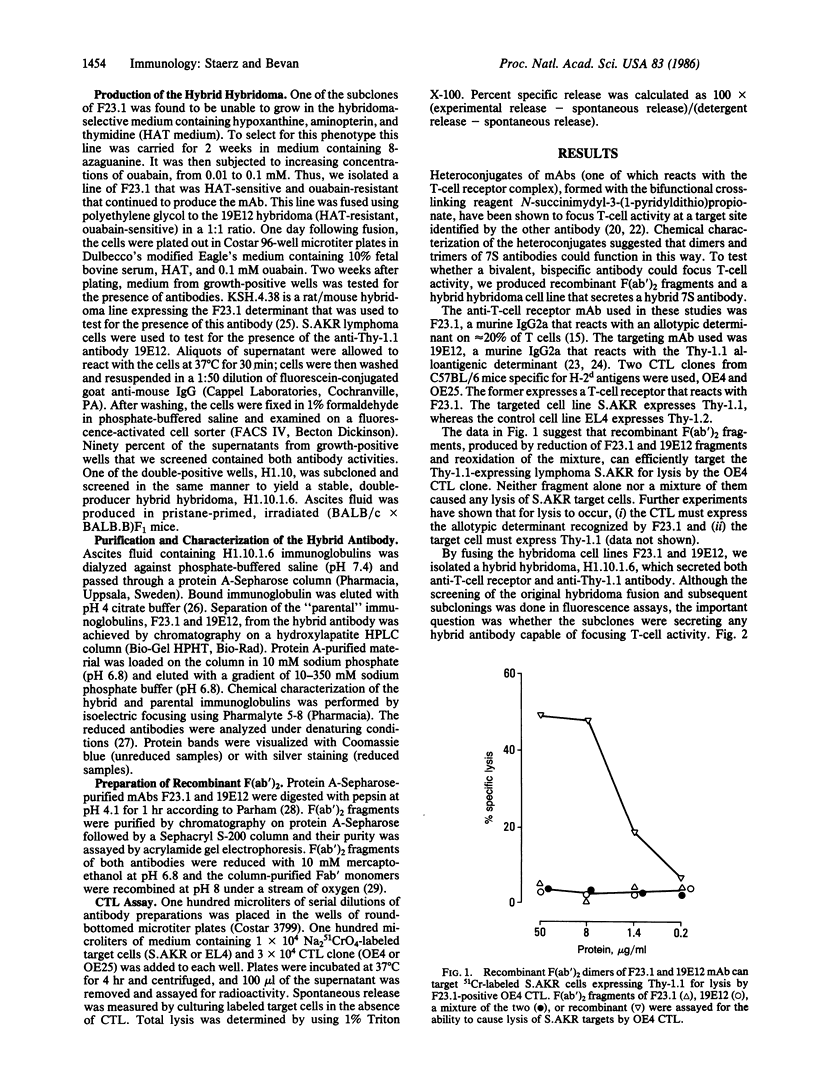
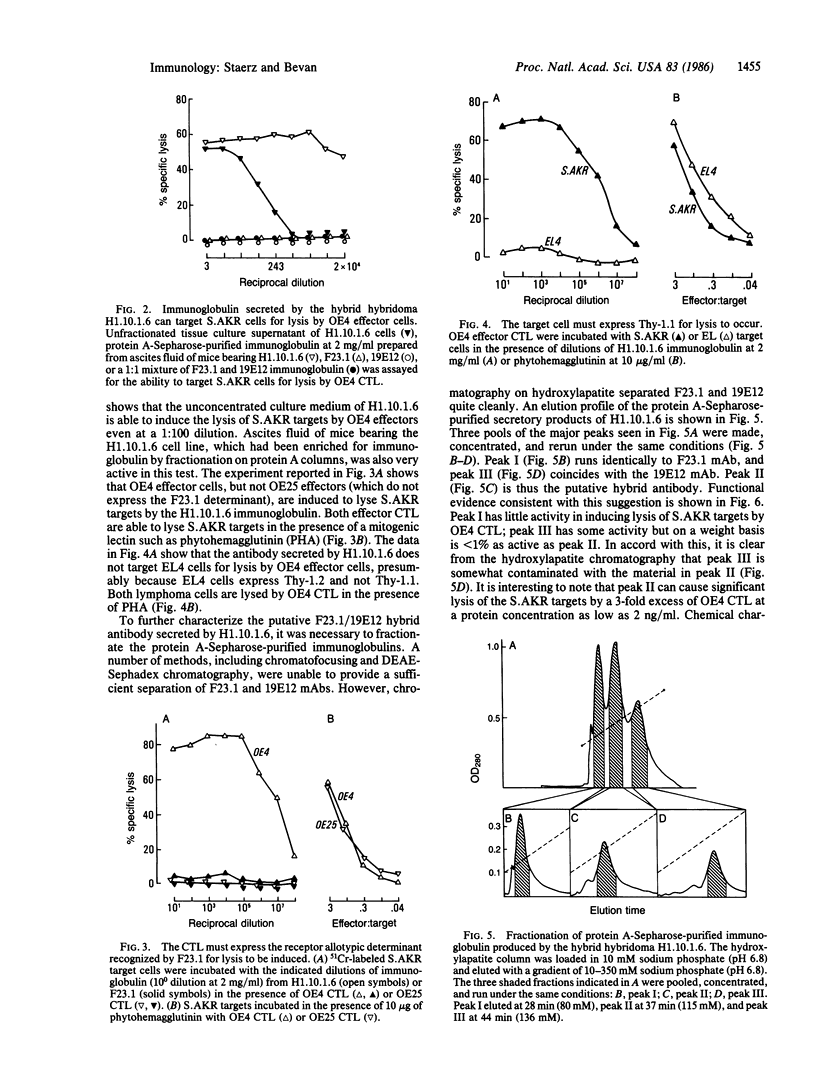
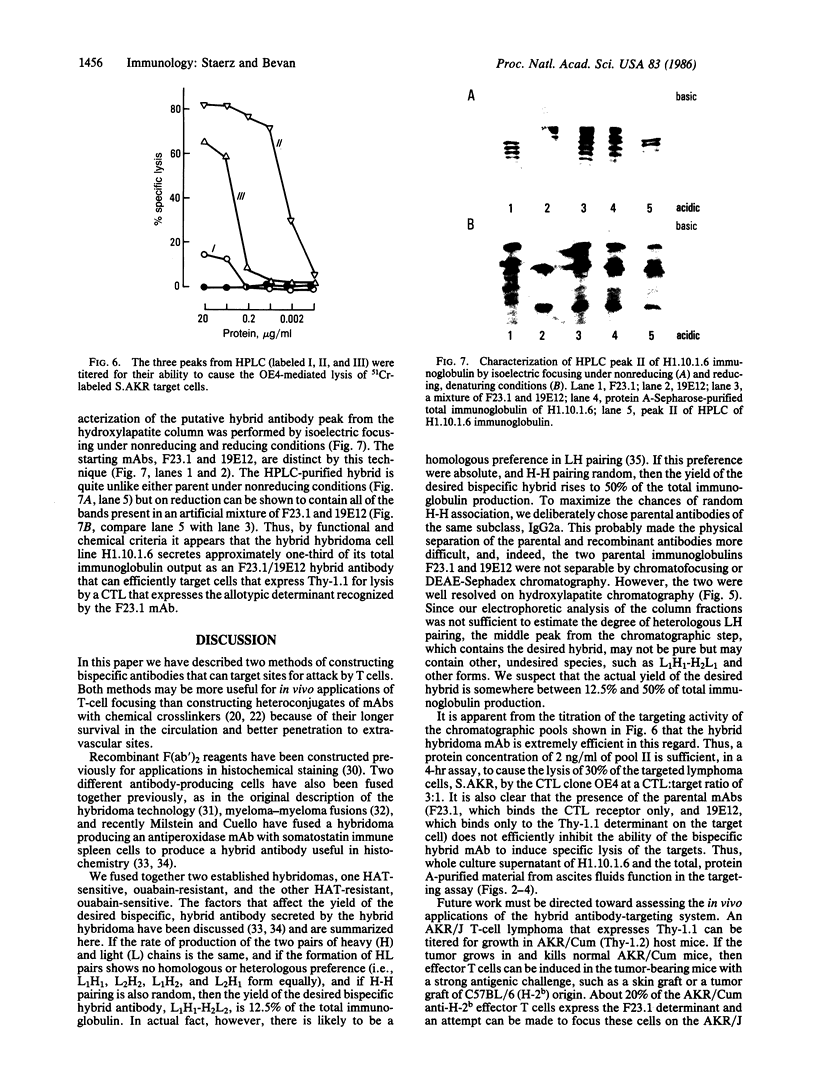
Previous studies have shown that heteroconjugates of monoclonal antibodies in which one of the component antibodies is directed at the T-cell receptor and the other is directed against any chosen site can focus effector T cells to function at the targeted site. We report here the production of a hybrid hybridoma cell line, H1.10.1.6, which secretes large amounts of a bispecific hybrid antibody of the IgG2a class, that can focus T-cell activity. The parental hybridoma lines for the secondary fusion were F23.1, which secretes an antibody specific for an allotypic determinant on the T-cell receptor of most mouse strains, and 19E12, secreting an anti-Thy-1.1 antibody. The bispecific hybrid antibody was partially purified by hydroxylapatite chromatography and characterized by isoelectric focusing. It efficiently targets Thy-1.1-expressing tumor cells for lysis by F23.1 receptor-positive cytotoxic T-cell clones in vitro. Such hybrid antibodies produced by hybrid hybridoma cell lines may have application in the therapeutic targeting of tumors or sites of viral infections for attack by T cells.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison J. P., McIntyre B. W., Bloch D. Tumor-specific antigen of murine T-lymphoma defined with monoclonal antibody. J Immunol. 1982 Nov;129(5):2293–2300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman Y., Stewart S. J., Levy S., Levy R. Biosynthesis, glycosylation, and in vitro translation of the human T cell antigen Leu-4. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):1876–1881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein I. D., Tam M. R., Nowinski R. C. Mouse leukemia: therapy with monoclonal antibodies against a thymus differentiation antigen. Science. 1980 Jan 4;207(4426):68–71. doi: 10.1126/science.6965328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigler R. D., Fisher D. E., Wang C. Y., Rinnooy Kan E. A., Kunkel H. G. Idiotype-like molecules on cells of a human T cell leukemia. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):1000–1005. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.1000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borst J., Coligan J. E., Oettgen H., Pessano S., Malin R., Terhorst C. The delta- and epsilon-chains of the human T3/T-cell receptor complex are distinct polypeptides. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):455–458. doi: 10.1038/312455a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boylston A. W., Cosford P. Growth of normal human T lymphocytes induced by monoclonal antibody to the T cell antigen receptor. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Jul;15(7):738–742. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien Y. H., Gascoigne N. R., Kavaler J., Lee N. E., Davis M. M. Somatic recombination in a murine T-cell receptor gene. Nature. 1984 May 24;309(5966):322–326. doi: 10.1038/309322a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien Y., Becker D. M., Lindsten T., Okamura M., Cohen D. I., Davis M. M. A third type of murine T-cell receptor gene. Nature. 1984 Nov 1;312(5989):31–35. doi: 10.1038/312031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crispe I. N., Bevan M. J., Staerz U. D. Selective activation of Lyt 2+ precursor T cells by ligation of the antigen receptor. Nature. 1985 Oct 17;317(6038):627–629. doi: 10.1038/317627a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Préval C., Fougereau M. Specific interaction between VH and VL regions of human monoclonal immunoglobulins. J Mol Biol. 1976 Apr 15;102(3):657–678. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90340-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ey P. L., Prowse S. J., Jenkin C. R. Isolation of pure IgG1, IgG2a and IgG2b immunoglobulins from mouse serum using protein A-sepharose. Immunochemistry. 1978 Jul;15(7):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haskins K., Hannum C., White J., Roehm N., Kubo R., Kappler J., Marrack P. The antigen-specific, major histocompatibility complex-restricted receptor on T cells. VI. An antibody to a receptor allotype. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):452–471. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haskins K., Kubo R., White J., Pigeon M., Kappler J., Marrack P. The major histocompatibility complex-restricted antigen receptor on T cells. I. Isolation with a monoclonal antibody. J Exp Med. 1983 Apr 1;157(4):1149–1169. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.4.1149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman R. W., Bluestone J. A., Leo O., Shaw S. Lysis of anti-T3-bearing murine hybridoma cells by human allospecific cytotoxic T cell clones and inhibition of that lysis by anti-T3 and anti-LFA-1 antibodies. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):5–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houston L. L., Nowinski R. C., Bernstein I. D. Specific in vivo localization of monoclonal antibodies directed against the Thy 1.1 antigen. J Immunol. 1980 Aug;125(2):837–843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hämmerling U., Aoki T., de Harven E., Boyse E. A., Old L. J. Use of hybrid antibody with anti-gamma-G and anti-ferritin specificities in locating cell surface antigens by electron microscopy. J Exp Med. 1968 Dec 1;128(6):1461–1473. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.6.1461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanagawa O., Chiller J. M. Lymphokine-mediated induction of cytolytic activity in a T cell hybridoma. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):397–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanellopoulos J. M., Wigglesworth N. M., Owen M. J., Crumpton M. J. Biosynthesis and molecular nature of the T3 antigen of human T lymphocytes. EMBO J. 1983;2(10):1807–1814. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01662.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kranz D. M., Tonegawa S., Eisen H. N. Attachment of an anti-receptor antibody to non-target cells renders them susceptible to lysis by a clone of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7922–7926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancki D. W., Ma D. I., Havran W. L., Fitch F. W. Cell surface structures involved in T cell activation. Immunol Rev. 1984 Oct;81:65–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1984.tb01105.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margulies D. H., Kuehl W. M., Scharff M. D. Somatic cell hybridization of mouse myeloma cells. Cell. 1976 Jul;8(3):405–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Fitzgerald K. A., Hussey R. E., Hodgdon J. C., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. Clonotypic structures involved in antigen-specific human T cell function. Relationship to the T3 molecular complex. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):705–719. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Hodgdon J. C., Hussey R. E., Protentis J. P., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. Antigen-like effects of monoclonal antibodies directed at receptors on human T cell clones. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):988–993. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milstein C., Cuello A. C. Hybrid hybridomas and their use in immunohistochemistry. Nature. 1983 Oct 6;305(5934):537–540. doi: 10.1038/305537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NISONOFF A., RIVERS M. M. Recombination of a mixture of univalent antibody fragments of different specificity. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 May;93:460–462. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90296-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parham P. On the fragmentation of monoclonal IgG1, IgG2a, and IgG2b from BALB/c mice. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):2895–2902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez P., Hoffman R. W., Shaw S., Bluestone J. A., Segal D. M. Specific targeting of cytotoxic T cells by anti-T3 linked to anti-target cell antibody. Nature. 1985 Jul 25;316(6026):354–356. doi: 10.1038/316354a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Kranz D. M., Takagaki Y., Hayday A. C., Eisen H. N., Tonegawa S. A third rearranged and expressed gene in a clone of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Nature. 1984 Nov 1;312(5989):36–40. doi: 10.1038/312036a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim G. K., Yagüe J., Nelson J., Marrack P., Palmer E., Augustin A., Kappler J. Primary structure of human T-cell receptor alpha-chain. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):771–775. doi: 10.1038/312771a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siu G., Kronenberg M., Strauss E., Haars R., Mak T. W., Hood L. The structure, rearrangement and expression of D beta gene segments of the murine T-cell antigen receptor. 1984 Sep 27-Oct 3Nature. 311(5984):344–350. doi: 10.1038/311344a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staerz U. D., Kanagawa O., Bevan M. J. Hybrid antibodies can target sites for attack by T cells. Nature. 1985 Apr 18;314(6012):628–631. doi: 10.1038/314628a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staerz U. D., Rammensee H. G., Benedetto J. D., Bevan M. J. Characterization of a murine monoclonal antibody specific for an allotypic determinant on T cell antigen receptor. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):3994–4000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




