Abstract
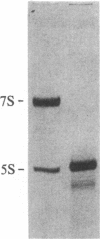
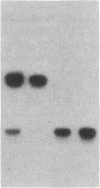
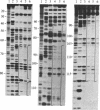
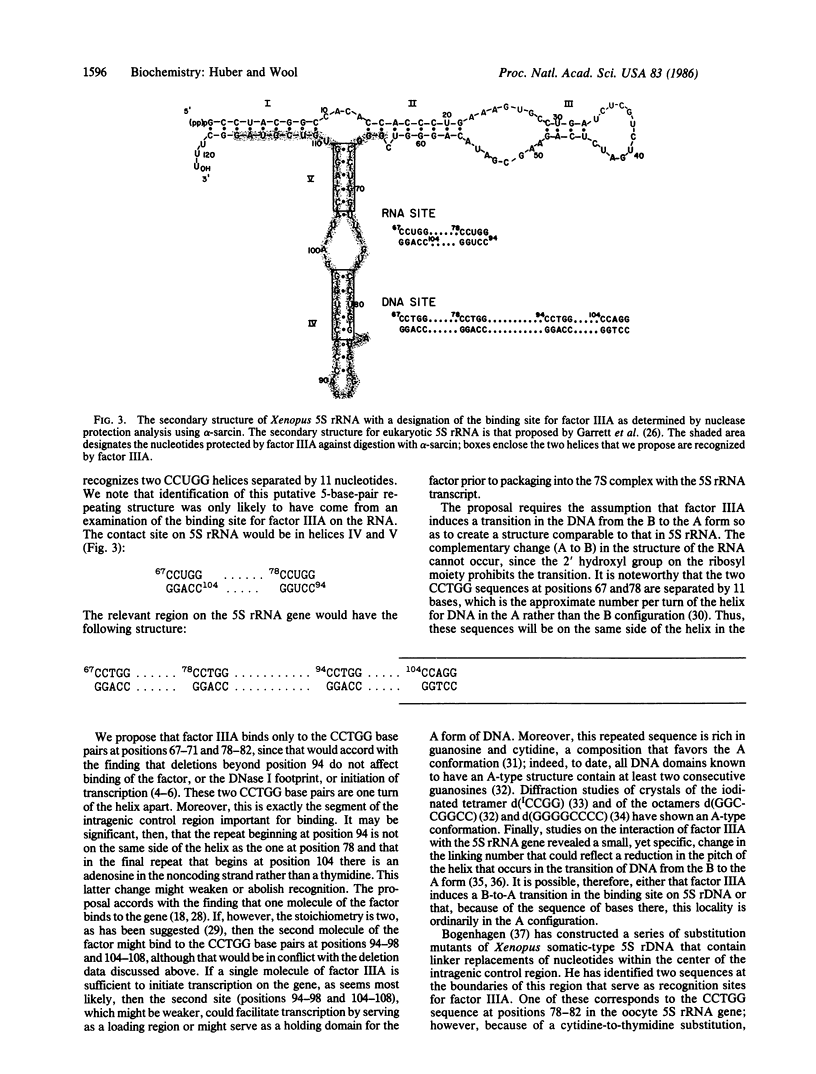
Transcription factor IIIA interacts specifically with an internal control region of Xenopus 5S ribosomal RNA genes and is also a component, along with 5S rRNA, of a 7S ribonucleoprotein particle present in previtellogenic oocytes. We have determined the region of the 5S rRNA in the 7S ribonucleoprotein complex that is protected by the transcription factor from digestion with the ribonuclease alpha-sarcin. The binding site for factor IIIA extends from nucleotide 64 through nucleotide 116; the protected region includes two CCUGG helices separated by 11 nucleotides. The same helices occur in the factor IIIA binding site in the 5S rRNA gene and may constitute a common structural feature recognized by the protein in the gene and in the gene product.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen J., Delihas N., Hanas J. S., Wu C. W. 5S RNA structure and interaction with transcription factor A. 1. Ribonuclease probe of the structure of 5S RNA from Xenopus laevis oocytes. Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 20;23(24):5752–5759. doi: 10.1021/bi00319a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen J., Delihas N., Hanas J. S., Wu C. W. 5S RNA structure and interaction with transcription factor A. 2. Ribonuclease probe of the 7S particle from Xenopus laevis immature oocytes and RNA exchange properties of the 7S particle. Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 20;23(24):5759–5766. doi: 10.1021/bi00319a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnott S., Selsing E. Letter: The structure of polydeoxyguanylic acid with polydeoxycytidylic acid. J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 15;88(2):551–552. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90502-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieker J. J., Roeder R. G. Physical properties and DNA-binding stoichiometry of a 5 S gene-specific transcription factor. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6158–6164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. Nucleotide sequences in Xenopus 5S DNA required for transcription termination. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90522-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Sakonju S., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: II. The 3' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F. The intragenic control region of the Xenopus 5 S RNA gene contains two factor A binding domains that must be aligned properly for efficient transcription initiation. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):6466–6471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Wormington W. M., Brown D. D. Stable transcription complexes of Xenopus 5S RNA genes: a means to maintain the differentiated state. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):413–421. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90359-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conner B. N., Takano T., Tanaka S., Itakura K., Dickerson R. E. The molecular structure of d(ICpCpGpG), a fragment of right-handed double helical A-DNA. Nature. 1982 Jan 28;295(5847):294–299. doi: 10.1038/295294a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis H., Wegnez M. Recherches biochimiques sur l'oogenése. 7. Synthése et maturation du RNA 5S dans les petitis oocytes de Xenopus laevis. Biochimie. 1973;55(9):1137–1151. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(73)80453-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H., Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Mapping adenines, guanines, and pyrimidines in RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2527–2538. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Huber P. W., Wool I. G. The ribonuclease activity of the cytotoxin alpha-sarcin. The characteristics of the enzymatic activity of alpha-sarcin with ribosomes and ribonucleic acids as substrates. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2662–2667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelke D. R., Ng S. Y., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. Specific interaction of a purified transcription factor with an internal control region of 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford P. J., Southern E. M. Different sequences for 5S RNA in kidney cells and ovaries of Xenopus laevis. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jan 3;241(105):7–12. doi: 10.1038/newbio241007a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanas J. S., Bogenhagen D. F., Wu C. W. Binding of Xenopus transcription factor A to 5S RNA and to single stranded DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2745–2758. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanas J. S., Bogenhagen D. F., Wu C. W. Cooperative model for the binding of Xenopus transcription factor A to the 5S RNA gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2142–2145. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanas J. S., Bogenhagen D. F., Wu C. W. DNA unwinding ability of Xenopus transcription factor A. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):1265–1276. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.1265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda B. M., Roeder R. G. Association of a 5S gene transcription factor with 5S RNA and altered levels of the factor during cell differentiation. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):119–126. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90160-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber P. W., Wool I. G. Nuclease protection analysis of ribonucleoprotein complexes: use of the cytotoxic ribonuclease alpha-sarcin to determine the binding sites for Escherichia coli ribosomal proteins L5, L18, and L25 on 5S rRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):322–326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Martin P. L., Roeder R. G. Transcription of class III genes: formation of preinitiation complexes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):740–748. doi: 10.1126/science.6356356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mairy M., Denis H. Recherches biochimiques sur l'oogenèse. I. Synthèse et accumulation du RNA pendant l'oogenèse du crapaud sud-africain Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1971 Feb;24(2):143–165. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(71)90092-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCall M., Brown T., Kennard O. The crystal structure of d(G-G-G-G-C-C-C-C). A model for poly(dG).poly(dC). J Mol Biol. 1985 Jun 5;183(3):385–396. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montoya J., Ojala D., Attardi G. Distinctive features of the 5'-terminal sequences of the human mitochondrial mRNAs. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):465–470. doi: 10.1038/290465a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peattie D. A., Douthwaite S., Garrett R. A., Noller H. F. A "bulged" double helix in a RNA-protein contact site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7331–7335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck L. J., Wang J. C. Sequence dependence of the helical repeat of DNA in solution. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):375–378. doi: 10.1038/292375a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Brown D. D. A specific transcription factor that can bind either the 5S RNA gene or 5S RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4170–4174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard B., Wegnez M. Isolation of a 7S particle from Xenopus laevis oocytes: a 5S RNA-protein complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):241–245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieler T., Erdmann V. A. Isolation and characterization of a 7 S RNP particle from mature Xenopus laevis oocytes. FEBS Lett. 1983 Jul 4;157(2):283–287. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80562-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds W. F., Gottesfeld J. M. 5S rRNA gene transcription factor IIIA alters the helical configuration of DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1862–1866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: I. The 5' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90384-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Brown D. D. Contact points between a positive transcription factor and the Xenopus 5S RNA gene. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):395–405. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90133-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Brown D. D., Engelke D., Ng S. Y., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. The binding of a transcription factor to deletion mutants of a 5S ribosomal RNA gene. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):665–669. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90429-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shastry B. S., Ng S. Y., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors involved in the transcription of class III genes in Xenopus laevis. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12979–12986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. R., Jackson I. J., Brown D. D. Domains of the positive transcription factor specific for the Xenopus 5S RNA gene. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):645–652. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90396-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. H., Fujii S., van Boom J. H., Rich A. Molecular structure of the octamer d(G-G-C-C-G-G-C-C): modified A-DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):3968–3972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.3968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegnez M., Denis H. Recherches biochimiques sur l'oogenése. 6. Propriétés du RNA 5 S présent dans les différents compartiments cellulaires des oocytes de Xenopus laevis. Biochimie. 1973;55(9):1129–1135. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(73)80452-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wormington W. M., Bogenhagen D. F., Jordan E., Brown D. D. A quantitative assay for Xenopus 5S RNA gene transcription in vitro. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):809–817. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90106-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]