Abstract
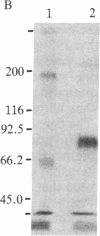
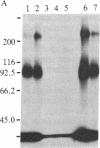
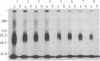
We have developed a method to immunoprecipitate rat nerve growth factor (NGF) receptor proteins and have applied the method to detect NGF receptor molecules in the rat brain. Crosslinking 125I-labeled NGF to either PC12 cells or cultured rat sympathetic neurons yielded two radiolabeled molecules (90 kDa and 220 kDa) that were immunoprecipitated by monoclonal antibody 192-IgG. Further, 192-IgG precipitated two radiolabeled proteins, with the expected sizes (80 kDa and 210 kDa) of noncrosslinked NGF receptor components, from among numerous surface-iodinated PC12 cell proteins. These results demonstrate the specific immunoprecipitation of NGF receptor molecules by 192-IgG. We applied the 125I-NGF crosslinking and 192-IgG-mediated immunoprecipitation procedures to plasma membrane preparations of the following areas of rat brain: medial septum, cerebellum, brainstem, hippocampus, cerebral cortex, thalamus, and olfactory bulb. NGF receptor molecules of the same molecular masses as the peripheral receptor components were consistently detected in all of these regions and in preparations from whole brains. Removal of the peripheral sympathetic innervation of the brain did not eliminate these NGF receptor proteins, indicating that the receptor is endogenous to central nervous system tissues. We also observed retrograde transport of 125I-labeled 192-IgG from the parietal cortex to the nucleus basalis and from the hippocampus to the nucleus of the diagonal band of Broca and the medial septal nucleus. These findings demonstrate the presence in brain of NGF receptor molecules indistinguishable from those of the peripheral nervous system.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bocchini V., Angeletti P. U. The nerve growth factor: purification as a 30,000-molecular-weight protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Oct;64(2):787–794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.2.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray D. Surface movements during the growth of single explanted neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Apr;65(4):905–910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.4.905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buxser S. E., Watson L., Johnson G. L. A comparison of binding properties and structure of NGF receptor on PC12 pheochromocytoma and A875 melanoma cells. J Cell Biochem. 1983;22(4):219–233. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240220404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buxser S., Puma P., Johnson G. L. Properties of the nerve growth factor receptor. Relationship between receptor structure and affinity. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1917–1926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler C. E., Parsons L. M., Hosang M., Shooter E. M. A monoclonal antibody modulates the interaction of nerve growth factor with PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):6882–6889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler L. P., Chandler C. E., Hosang M., Shooter E. M. A monoclonal antibody which inhibits epidermal growth factor binding has opposite effects on the biological action of epidermal growth factor in different cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3360–3367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costrini N. V., Bradshaw R. A. Binding characteristics and apparent molecular size of detergent solubilized nerve growth factor receptor of sympathetic ganglia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3242–3245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiStefano P. S., Schweitzer J. B., Taniuchi M., Johnson E. M., Jr Selective destruction of nerve growth factor receptor-bearing cells in vitro using a hybrid toxin composed of ricin A chain and a monoclonal antibody against the nerve growth factor receptor. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):1107–1114. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.1107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edvinsson L. Neurogenic mechanisms in the cerebrovascular bed. Autonomic nerves, amine receptors and their effects on cerebral blood flow. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1975;427:1–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnahn H., Hefti F., Heumann R., Schwab M. E., Thoenen H. NGF-mediated increase of choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) in the neonatal rat forebrain: evidence for a physiological role of NGF in the brain? Brain Res. 1983 Jul;285(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(83)90107-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grob P. M., Berlot C. H., Bothwell M. A. Affinity labeling and partial purification of nerve growth factor receptors from rat pheochromocytoma and human melanoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6819–6823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grob P. M., Ross A. H., Koprowski H., Bothwell M. Characterization of the human melanoma nerve growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):8044–8049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hefti F., Dravid A., Hartikka J. Chronic intraventricular injections of nerve growth factor elevate hippocampal choline acetyltransferase activity in adult rats with partial septo-hippocampal lesions. Brain Res. 1984 Feb 20;293(2):305–311. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)91237-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hefti F., Hartikka J., Eckenstein F., Gnahn H., Heumann R., Schwab M. Nerve growth factor increases choline acetyltransferase but not survival or fiber outgrowth of cultured fetal septal cholinergic neurons. Neuroscience. 1985 Jan;14(1):55–68. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90163-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honegger P., Lenoir D. Nerve growth factor (NGF) stimulation of cholinergic telencephalic neurons in aggregating cell cultures. Brain Res. 1982 Feb;255(2):229–238. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(82)90023-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosang M., Shooter E. M. Molecular characteristics of nerve growth factor receptors on PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):655–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard A. L., Cohn Z. A. The enzymatic iodination of the red cell membrane. J Cell Biol. 1972 Nov;55(2):390–405. doi: 10.1083/jcb.55.2.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. M., Jr, O'Brien F., Werbitt R. Modification and characterization of the permanent sympathectomy produced by the administration of guanethidine to newborn rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1976 May;37(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(76)90006-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korsching S., Auburger G., Heumann R., Scott J., Thoenen H. Levels of nerve growth factor and its mRNA in the central nervous system of the rat correlate with cholinergic innervation. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1389–1393. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03791.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann J., Nagy J. I., Atmadia S., Fibiger H. C. The nucleus basalis magnocellularis: the origin of a cholinergic projection to the neocortex of the rat. Neuroscience. 1980;5(7):1161–1174. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90195-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchalonis J. J. An enzymic method for the trace iodination of immunoglobulins and other proteins. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(2):299–305. doi: 10.1042/bj1130299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massague J., Guillette B. J., Czech M. P., Morgan C. J., Bradshaw R. A. Identification of a nerve growth factor receptor protein in sympathetic ganglia membranes by affinity labeling. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 25;256(18):9419–9424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley W. C., Rutkowski J. L., Tennekoon G. I., Buchanan K., Johnston M. V. Choline acetyltransferase activity in striatum of neonatal rats increased by nerve growth factor. Science. 1985 Jul 19;229(4710):284–287. doi: 10.1126/science.2861660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puma P., Buxser S. E., Watson L., Kelleher D. J., Johnson G. L. Purification of the receptor for nerve growth factor from A875 melanoma cells by affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3370–3375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler M., Schwab M. E. Specific retrograde transport of nerve growth factor (NGF) from neocortex to nucleus basalis in the rat. Brain Res. 1984 May 21;300(1):33–39. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)91338-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelton D. L., Reichardt L. F. Expression of the beta-nerve growth factor gene correlates with the density of sympathetic innervation in effector organs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7951–7955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szutowicz A., Frazier W. A., Bradshaw R. A. Subcellular localization of nerve growth factor receptors. Developmental correlations in chick embryo brain. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 10;251(5):1524–1528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szutowicz A., Frazier W. A., Bradshaw R. A. Subcellular localization of nerve growth factor receptors. Thirteen-day chick embryo brain. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 10;251(5):1516–1523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniuchi M., Johnson E. M., Jr Characterization of the binding properties and retrograde axonal transport of a monoclonal antibody directed against the rat nerve growth factor receptor. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):1100–1106. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.1100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoenen H., Barde Y. A. Physiology of nerve growth factor. Physiol Rev. 1980 Oct;60(4):1284–1335. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1980.60.4.1284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyss J. M., Swanson L. W., Cowan W. M. A study of subcortical afferents to the hippocampal formation in the rat. Neuroscience. 1979;4(4):463–476. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(79)90124-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann A., Sutter A., Shooter E. M. Monoclonal antibodies against beta nerve growth factor and their effects on receptor binding and biological activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4611–4615. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]