Abstract
When myosin subfragment 1 derivatives in which the reactive sulfhydryl SH1 has been blocked react with N,N'-p-phenylenedimaleimide or 5,5'-dithiobis(2-nitrobenzoic acid), the reactive sulfhydryl group SH2 of the 20-kDa domain is crosslinked with a thiol of the 50-kDa domain of the heavy chain. The crosslink induces the stable trapping of a significant amount of Mg2+-nucleotide in the ATPase site.
Full text
PDF

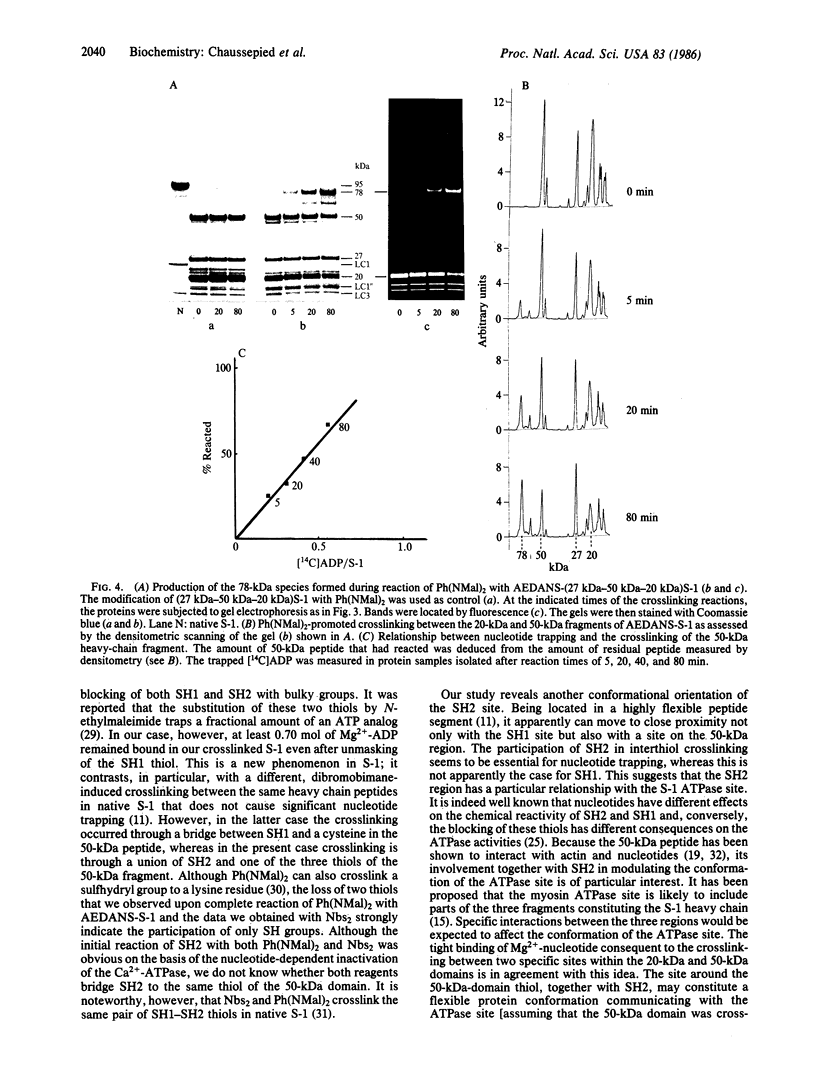

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ando T., Duke J. A., Tonomura Y., Morales M. F. Spectroscopic isolation of ES complexes of myosin subfragment-1 ATPase by fluorescence quenching. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Nov 16;109(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91557-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botts J., Takashi R., Torgerson P., Hozumi T., Muhlrad A., Mornet D., Morales M. F. On the mechanism of energy transduction in myosin subfragment 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2060–2064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke M., Reisler E. Effect of nucleotide binding on the proximity of the essential sulfhydryl groups of myosin. Chemical probing of movement of residues during conformational transitions. Biochemistry. 1977 Dec 13;16(25):5559–5563. doi: 10.1021/bi00644a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalovich J. M., Greene L. E., Eisenberg E. Crosslinked myosin subfragment 1: a stable analogue of the subfragment-1.ATP complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):4909–4913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.4909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalbey R. E., Wells J. A., Yount R. G. Trapping of transition metal-nucleotide complexes in myosin subfragment 1 by cross-linking thiols; divalent transition metal probes of the active site. Biochemistry. 1983 Jan 18;22(2):490–496. doi: 10.1021/bi00271a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg E., Kielley W. W. Troponin-tropomyosin complex. Column chromatographic separation and activity of the three, active troponin components with and without tropomyosin present. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 10;249(15):4742–4748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elzinga M., Phelan J. J. F-actin is intermolecularly crosslinked by N,N'-p-phenylenedimaleimide through lysine-191 and cysteine-374. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6599–6602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley A. F., Simmons R. M. Proposed mechanism of force generation in striated muscle. Nature. 1971 Oct 22;233(5321):533–538. doi: 10.1038/233533a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunz P. A., Walser J. T., Watterson J. G., Schaub M. C. Isolation of cyanogen bromide and tryptic peptides containing the essential thiol groups from isolated myosin heads. FEBS Lett. 1977 Nov 1;83(1):137–140. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80658-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahmood R., Yount R. G. Photochemical probes of the active site of myosin. Irradiation of trapped 3'-O-(4-benzoyl)benzoyladenosine 5'-triphosphate labels the 50-kilodalton heavy chain tryptic peptide. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):12956–12959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mornet D., Bertrand R., Pantel P., Audemard E., Kassab R. Structure of the actin-myosin interface. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):301–306. doi: 10.1038/292301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mornet D., Pantel P., Audemard E., Kassab R. Involvement of an arginyl residue in the catalytic activity of myosin heads. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Oct 15;100(2):421–431. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb04185.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mornet D., Pantel P., Audemard E., Kassab R. The limited tryptic cleavage of chymotryptic S-1: an approach to the characterization of the actin site in myosin heads. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Aug 13;89(3):925–932. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91867-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mornet D., Ue K., Morales M. F. Proteolysis and the domain organization of myosin subfragment 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):736–739. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mornet D., Ue K., Morales M. F. Stabilization of a primary loop in myosin subfragment 1 with a fluorescent crosslinker. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1658–1662. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offer G., Moos C., Starr R. A new protein of the thick filaments of vertebrate skeletal myofibrils. Extractions, purification and characterization. J Mol Biol. 1973 Mar 15;74(4):653–676. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto Y., Sekine T. A streamlined method of subfragment one preparation from myosin. J Biochem. 1985 Oct;98(4):1143–1145. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope B. J., Wagner P. D., Weeds A. G. Heterogeneity of myosin heavy chains in subfragment-1 isoenzymes rabbit skeletal myosin. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jan 25;109(3):470–473. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisler E., Burke M., Harrington W. F. Cooperative role of two sulfhydryl groups in myosin adenosine triphosphatase. Biochemistry. 1974 May 7;13(10):2014–2022. doi: 10.1021/bi00707a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisler E. Sulfhydryl modification and labeling of myosin. Methods Enzymol. 1982;85(Pt B):84–93. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)85012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein L. A., Chock P. B., Eisenberg E. Mechanism of the actomyosin ATPase: effect of actin on the ATP hydrolysis step. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1346–1350. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takashi R., Duke J., Ue K., Morales M. F. Defining the "fast-reacting" thiols of myosin by reaction with 1, 5 IAEDANS. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Jul;175(1):279–283. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90509-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor E. W. Mechanism of actomyosin ATPase and the problem of muscle contraction. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1979;6(2):103–164. doi: 10.3109/10409237909102562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeds A. G., Taylor R. S. Separation of subfragment-1 isoenzymes from rabbit skeletal muscle myosin. Nature. 1975 Sep 4;257(5521):54–56. doi: 10.1038/257054a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. A., Sheldon M., Yount R. G. Magnesium nucleotide is stoichiometrically trapped at the active site of myosin and its active proteolytic fragments by thiol cross-linking reagents. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1598–1602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. A., Yount R. G. Active site trapping of nucleotides by crosslinking two sulfhydryls in myosin subfragment 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4966–4970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. A., Yount R. G. Chemical modification of myosin by active-site trapping of metal-nucleotides with thiol crosslinking reagents. Methods Enzymol. 1982;85(Pt B):93–116. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)85013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. A., Yount R. G. Reaction of 5,5'-dithiobis(2-nitrobenzoic acid) with myosin subfragment one: evidence for formation of a single protein disulfide with trapping of metal nucleotide at the active site. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 15;19(8):1711–1717. doi: 10.1021/bi00549a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Sekine T. Interactions of ATP analogues, N6-[(6-aminohexyl) Carbamoylmethyl] ATP and its dinitrophenyl derivative, with the active site of myosin. J Biochem. 1982 Nov;92(5):1519–1525. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]