Abstract
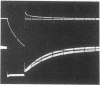
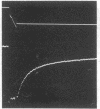
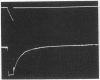
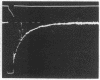
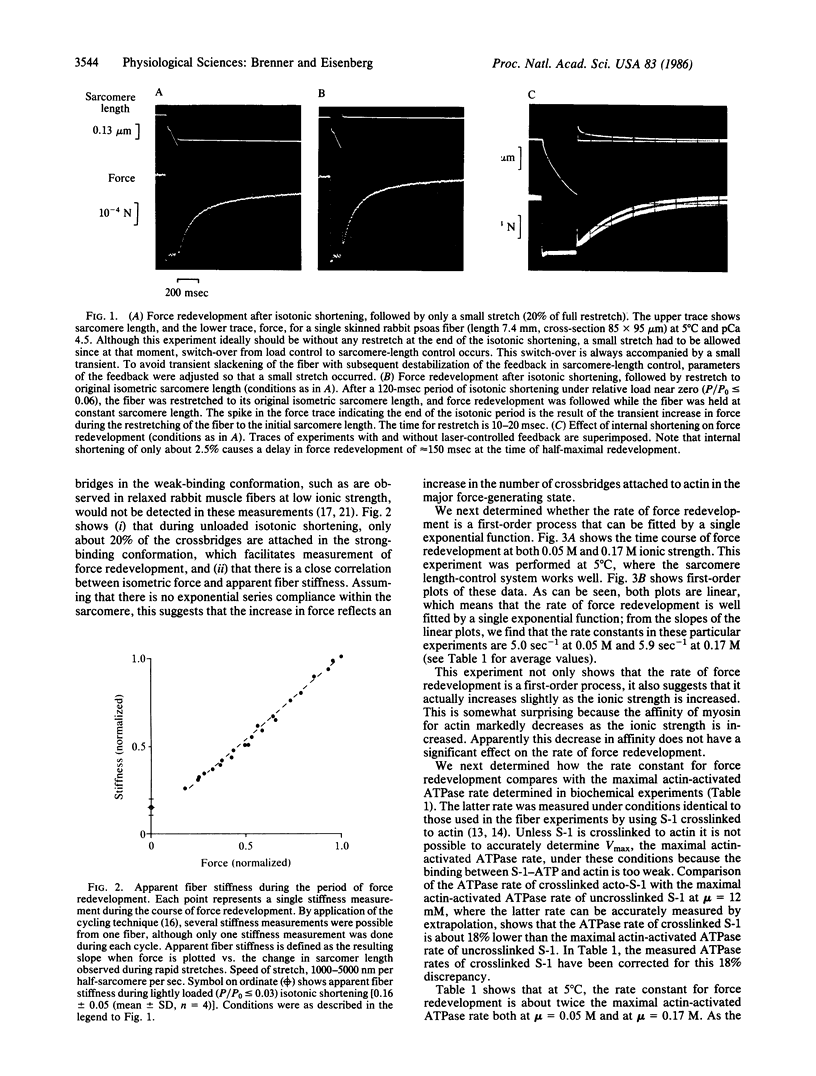
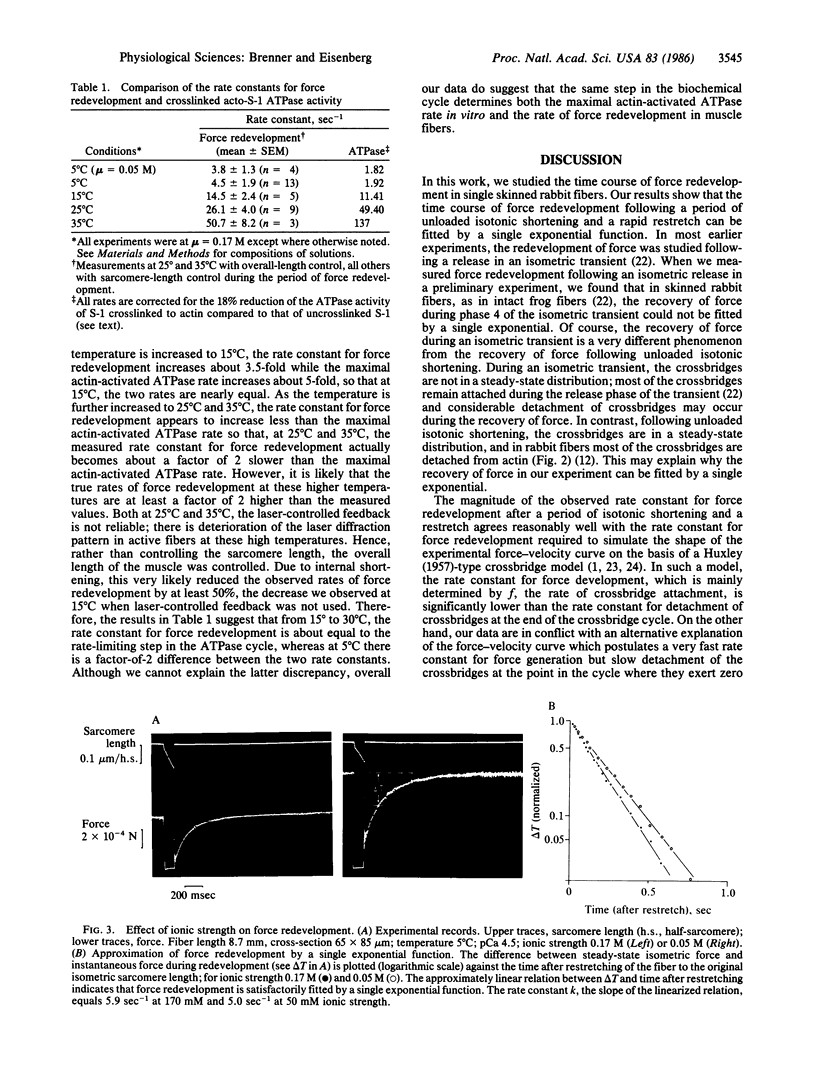
Crossbridge models of muscle contraction based on biochemical studies predict that there may be a relationship between the rate-limiting step in the actomyosin ATPase cycle in vitro and the rate of force development in vivo. In the present study, we measured the rate of force redevelopment in skinned rabbit muscle fibers following unloaded isotonic shortening and a rapid restretch. For comparison, ATPase activity was measured under identical conditions, using myosin subfragment-1 chemically crosslinked to actin. We found that the time course of force redevelopment is well fitted by a single exponential function, implying that force redevelopment is a first-order process, described by a single rate constant. The magnitude of this rate constant is in close agreement with the rate constant necessary to simulate the experimental force-velocity relation on the basis of a crossbridge model of the type proposed by A. F. Huxley in 1957. In addition, the observed close correlation between the rate constant for force redevelopment and the maximal actin-activated actomyosin ATPase rate under a variety of conditions suggests that the step that determines the rate of force generation in the crossbridge cycle may be the physiological equivalent of the rate-limiting step in the actomyosin ATPase cycle in solution.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brenner B., Schoenberg M., Chalovich J. M., Greene L. E., Eisenberg E. Evidence for cross-bridge attachment in relaxed muscle at low ionic strength. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7288–7291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. Technique for stabilizing the striation pattern in maximally calcium-activated skinned rabbit psoas fibers. Biophys J. 1983 Jan;41(1):99–102. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84411-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg E., Greene L. E. The relation of muscle biochemistry to muscle physiology. Annu Rev Physiol. 1980;42:293–309. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.42.030180.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg E., Hill T. L., Chen Y. Cross-bridge model of muscle contraction. Quantitative analysis. Biophys J. 1980 Feb;29(2):195–227. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85126-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg E., Hill T. L. Muscle contraction and free energy transduction in biological systems. Science. 1985 Mar 1;227(4690):999–1006. doi: 10.1126/science.3156404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg E., Moos C. The interaction of actin with myosin and heavy meromyosin in solution at low ionic strength. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jun 25;242(12):2945–2951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford L. E., Huxley A. F., Simmons R. M. Tension responses to sudden length change in stimulated frog muscle fibres near slack length. J Physiol. 1977 Jul;269(2):441–515. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths P. J., Kuhn H. J., Güth K., Rüegg J. C. Rate of isometric tension development in relation to calcium binding of skinned muscle fibres. Pflugers Arch. 1979 Nov;382(2):165–170. doi: 10.1007/BF00584218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILL A. V. The mechanics of active muscle. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1953 Mar 11;141(902):104–117. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1953.0027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY A. F. Muscle structure and theories of contraction. Prog Biophys Biophys Chem. 1957;7:255–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julian F. J., Morgan D. L. Variation of muscle stiffness with tension during tension transients and constant velocity shortening in the frog. J Physiol. 1981;319:193–203. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julian F. J., Sollins M. R. Variation of muscle stiffness with force at increasing speeds of shortening. J Gen Physiol. 1975 Sep;66(3):287–302. doi: 10.1085/jgp.66.3.287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moisescu D. G. Kinetics of reaction in calcium-activated skinned muscle fibres. Nature. 1976 Aug 12;262(5569):610–613. doi: 10.1038/262610a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mornet D., Bertrand R., Pantel P., Audemard E., Kassab R. Structure of the actin-myosin interface. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):301–306. doi: 10.1038/292301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld S. S., Taylor E. W. The ATPase mechanism of skeletal and smooth muscle acto-subfragment 1. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):11908–11919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenberg M., Brenner B., Chalovich J. M., Greene L. E., Eisenberg E. Cross-bridge attachment in relaxed muscle. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1984;170:269–284. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-4703-3_24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siemankowski R. F., Wiseman M. O., White H. D. ADP dissociation from actomyosin subfragment 1 is sufficiently slow to limit the unloaded shortening velocity in vertebrate muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):658–662. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein L. A., Chock P. B., Eisenberg E. The rate-limiting step in the actomyosin adenosinetriphosphatase cycle. Biochemistry. 1984 Mar 27;23(7):1555–1563. doi: 10.1021/bi00302a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein L. A., Greene L. E., Chock P. B., Eisenberg E. Rate-limiting step in the actomyosin adenosinetriphosphatase cycle: studies with myosin subfragment 1 cross-linked to actin. Biochemistry. 1985 Mar 12;24(6):1357–1363. doi: 10.1021/bi00327a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein L. A., Schwarz R. P., Jr, Chock P. B., Eisenberg E. Mechanism of actomyosin adenosine triphosphatase. Evidence that adenosine 5'-triphosphate hydrolysis can occur without dissociation of the actomyosin complex. Biochemistry. 1979 Sep 4;18(18):3895–3909. doi: 10.1021/bi00585a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor E. W. Mechanism of actomyosin ATPase and the problem of muscle contraction. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1979;6(2):103–164. doi: 10.3109/10409237909102562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]