Abstract
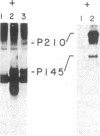
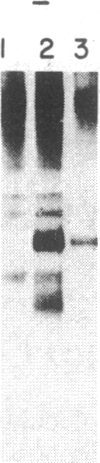
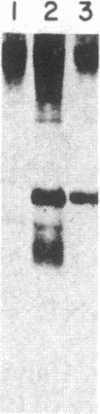
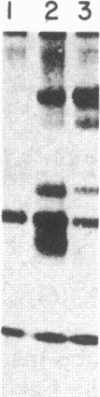
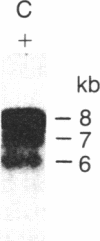
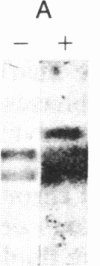
The consistent cytogenetic translocation of chronic myelogenous leukemia (the Philadelphia chromosome, Ph1) has been observed in cells of multiple hematopoietic lineages. This translocation creates a chimeric gene composed of breakpoint-cluster-region (bcr) sequences from chromosome 22 fused to a portion of the abl oncogene on chromosome 9. The resulting gene product (P210c-abl) resembles the transforming protein of the Abelson murine leukemia virus in its structure and tyrosine kinase activity. P210c-abl is expressed in Ph1-positive cell lines of myeloid lineage and in clinical specimens with myeloid predominance. We show here that Epstein-Barr virus-transformed B-lymphocyte lines that retain Ph1 can express P210c-abl. The level of expression in these B-cell lines is generally lower and more variable than that observed for myeloid lines. Protein expression is not related to amplification of the abl gene but to variation in the level of bcr-abl mRNA produced from a single Ph1 template.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartram C. R., de Klein A., Hagemeijer A., van Agthoven T., Geurts van Kessel A., Bootsma D., Grosveld G., Ferguson-Smith M. A., Davies T., Stone M. Translocation of c-ab1 oncogene correlates with the presence of a Philadelphia chromosome in chronic myelocytic leukaemia. Nature. 1983 Nov 17;306(5940):277–280. doi: 10.1038/306277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champlin R. E., Golde D. W. Chronic myelogenous leukemia: recent advances. Blood. 1985 May;65(5):1039–1047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. J., Groudine M. T. Rearrangement and amplification of c-abl sequences in the human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell line K-562. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4813–4817. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. J., Kubonishi I., Miyoshi I., Groudine M. T. Altered transcription of the c-abl oncogene in K-562 and other chronic myelogenous leukemia cells. Science. 1984 Jul 6;225(4657):72–74. doi: 10.1126/science.6587568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Konopka J. B., Witte O. N. Activation of the c-abl oncogene by viral transduction or chromosomal translocation generates altered c-abl proteins with similar in vitro kinase properties. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):204–213. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fialkow P. J., Martin P. J., Najfeld V., Penfold G. K., Jacobson R. J., Hansen J. A. Evidence for a multistep pathogenesis of chronic myelogenous leukemia. Blood. 1981 Jul;58(1):158–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gale R. P., Canaani E. An 8-kilobase abl RNA transcript in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5648–5652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson W. Protease-facilitated transfer of high-molecular-weight proteins during electrotransfer to nitrocellulose. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90147-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff S. P., Gilboa E., Witte O. N., Baltimore D. Structure of the Abelson murine leukemia virus genome and the homologous cellular gene: studies with cloned viral DNA. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):777–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90554-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groffen J., Stephenson J. R., Heisterkamp N., de Klein A., Bartram C. R., Grosveld G. Philadelphia chromosomal breakpoints are clustered within a limited region, bcr, on chromosome 22. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):93–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90077-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heisterkamp N., Stam K., Groffen J., de Klein A., Grosveld G. Structural organization of the bcr gene and its role in the Ph' translocation. 1985 Jun 27-Jul 3Nature. 315(6022):758–761. doi: 10.1038/315758a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heisterkamp N., Stephenson J. R., Groffen J., Hansen P. F., de Klein A., Bartram C. R., Grosveld G. Localization of the c-ab1 oncogene adjacent to a translocation break point in chronic myelocytic leukaemia. Nature. 1983 Nov 17;306(5940):239–242. doi: 10.1038/306239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Klein E. Evolution of tumours and the impact of molecular oncology. Nature. 1985 May 16;315(6016):190–195. doi: 10.1038/315190a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloetzer W., Kurzrock R., Smith L., Talpaz M., Spiller M., Gutterman J., Arlinghaus R. The human cellular abl gene product in the chronic myelogenous leukemia cell line K562 has an associated tyrosine protein kinase activity. Virology. 1985 Jan 30;140(2):230–238. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90361-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konopka J. B., Davis R. L., Watanabe S. M., Ponticelli A. S., Schiff-Maker L., Rosenberg N., Witte O. N. Only site-directed antibodies reactive with the highly conserved src-homologous region of the v-abl protein neutralize kinase activity. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):223–232. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.223-232.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konopka J. B., Watanabe S. M., Singer J. W., Collins S. J., Witte O. N. Cell lines and clinical isolates derived from Ph1-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia patients express c-abl proteins with a common structural alteration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1810–1814. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konopka J. B., Watanabe S. M., Witte O. N. An alteration of the human c-abl protein in K562 leukemia cells unmasks associated tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1035–1042. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90438-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konopka J. B., Witte O. N. Detection of c-abl tyrosine kinase activity in vitro permits direct comparison of normal and altered abl gene products. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3116–3123. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozzio C. B., Lozzio B. B. Human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell-line with positive Philadelphia chromosome. Blood. 1975 Mar;45(3):321–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin P. J., Najfeld V., Fialkow P. J. B-lymphoid cell involvement in chronic myelogenous leukemia: implications for the pathogenesis of the disease. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1982 Aug;6(4):359–368. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(82)90092-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitta M., Kato Y., Strife A., Wachter M., Fried J., Perez A., Jhanwar S., Duigou-Osterndorf R., Chaganti R. S., Clarkson B. Incidence of involvement of the B and T lymphocyte lineages in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Blood. 1985 Nov;66(5):1053–1061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce J. H., Di Fiore P. P., Aaronson S. A., Potter M., Pumphrey J., Scott A., Ihle J. N. Neoplastic transformation of mast cells by Abelson-MuLV: abrogation of IL-3 dependence by a nonautocrine mechanism. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):685–693. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80049-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley J. D. Chromosome abnormalities in human leukemia. Annu Rev Genet. 1980;14:17–39. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.14.120180.000313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley J. D. Letter: A new consistent chromosomal abnormality in chronic myelogenous leukaemia identified by quinacrine fluorescence and Giemsa staining. Nature. 1973 Jun 1;243(5405):290–293. doi: 10.1038/243290a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff-Maker L., Burns M. C., Konopka J. B., Clark S., Witte O. N., Rosenberg N. Monoclonal antibodies specific for v-abl- and c-abl-encoded molecules. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):1182–1186. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.1182-1186.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. C., Sonenshein G. E., Bothwell A., Gefter M. L. Multiple expression of Ig lambda-chain encoding RNA species in murine plasmacytoma cells. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2104–2108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selden J. R., Emanuel B. S., Wang E., Cannizzaro L., Palumbo A., Erikson J., Nowell P. C., Rovera G., Croce C. M. Amplified C lambda and c-abl genes are on the same marker chromosome in K562 leukemia cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7289–7292. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shtivelman E., Lifshitz B., Gale R. P., Canaani E. Fused transcript of abl and bcr genes in chronic myelogenous leukaemia. Nature. 1985 Jun 13;315(6020):550–554. doi: 10.1038/315550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stam K., Heisterkamp N., Grosveld G., de Klein A., Verma R. S., Coleman M., Dosik H., Groffen J. Evidence of a new chimeric bcr/c-abl mRNA in patients with chronic myelocytic leukemia and the Philadelphia chromosome. N Engl J Med. 1985 Dec 5;313(23):1429–1433. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198512053132301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitlock C. A., Witte O. N. The complexity of virus--cell interactions in Abelson virus infection of lymphoid and other hematopoietic cells. Adv Immunol. 1985;37:73–98. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60338-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitlock C. A., Ziegler S. F., Witte O. N. Progression of the transformed phenotype in clonal lines of Abelson virus-infected lymphocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;3(4):596–604. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.4.596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf D., Harris N., Rotter V. Reconstitution of p53 expression in a nonproducer Ab-MuLV-transformed cell line by transfection of a functional p53 gene. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):119–126. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90532-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]