Abstract
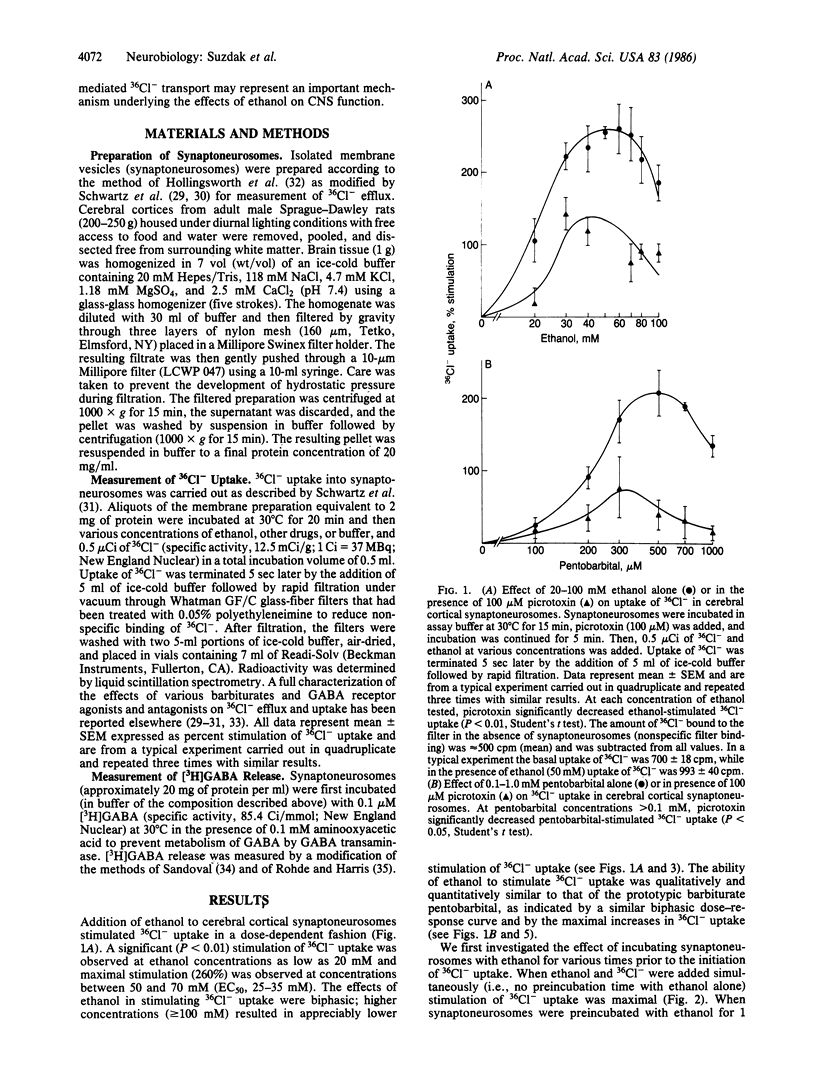
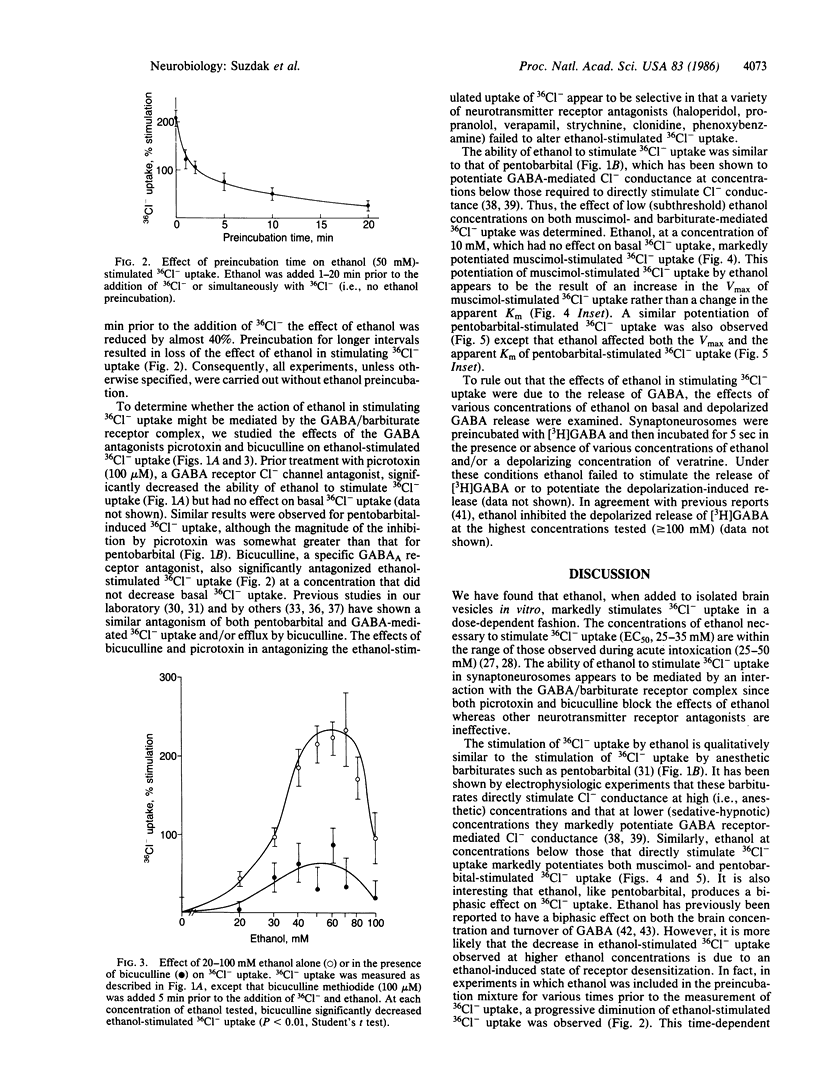
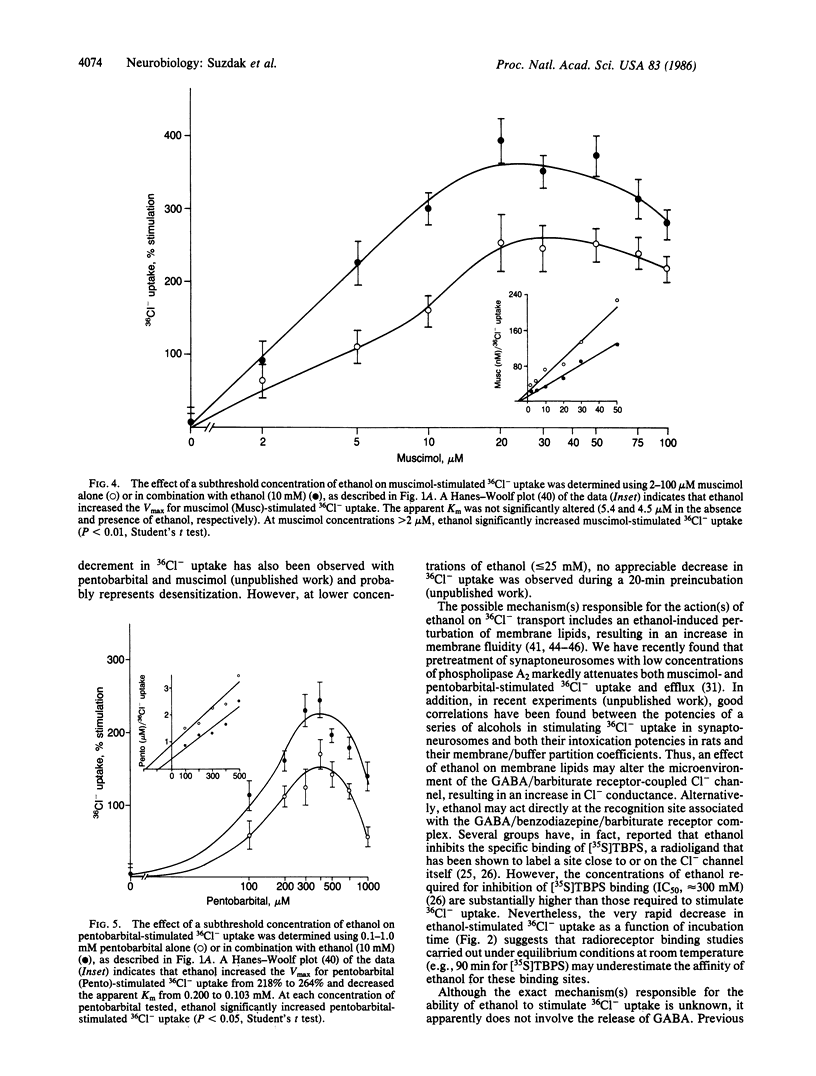
The effects of ethanol on Cl- uptake were studied using a cell-free subcellular preparation from brain that contains a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)/barbiturate receptor-sensitive Cl- transport system. In isolated vesicles prepared from rat cerebral cortex, ethanol, at concentrations that are present during acute intoxication (20-50 mM), stimulated 36Cl- uptake in a concentration-dependent and biphasic manner. The ethanol-stimulated uptake of 36Cl- was markedly inhibited by the GABA antagonists picrotoxin and bicuculline but not by a variety of other neurotransmitter receptor antagonists. The effects of ethanol in stimulating 36Cl- uptake in isolated brain vesicles were qualitatively and quantitatively similar to that of pentobarbital. Ethanol also markedly potentiated both muscimol- and pentobarbital-stimulated 36Cl- uptake at concentrations below those that directly stimulate 36Cl- uptake. Under our incubation conditions, ethanol did not release GABA, suggesting that it interacts with the postsynaptic GABA/barbiturate receptor complex. The ability of ethanol to stimulate GABA/barbiturate receptor-mediated Cl- transport may explain many of its pharmacological properties and provides a mechanism for the common psychopharmacological actions of ethanol, barbiturates, and benzodiazepines.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BELLEVILLE R. E., FRASER H. F. Tolerance to some effects of barbiturates. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1957 Aug;120(4):469–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker J. L., Ransom B. R. Amino acid pharmacology of mammalian central neurones grown in tissue culture. J Physiol. 1978 Jul;280:331–354. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker J. L., Ransom B. R. Pentobarbitone pharmacology of mammalian central neurones grown in tissue culture. J Physiol. 1978 Jul;280:355–372. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin J. H., Goldstein D. B. Effects of low concentrations of ethanol on the fluidity of spin-labeled erythrocyte and brain membranes. Mol Pharmacol. 1977 May;13(3):435–441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa E., Guidotti A., Mao C. C., Suria A. New concepts on the mechanism of action of benzodiazepines. Life Sci. 1975 Jul 15;17(2):167–185. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90501-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cott J., Carlsson A., Engel J., Lindqvist M. Suppression of ethanol-induced locomotor stimulation by GABA-like drugs. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1976 Dec;295(3):203–209. doi: 10.1007/BF00505087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidoff R. A. Alcohol and presynaptic inhibition in an isolated spinal cord preparation. Arch Neurol. 1973 Jan;28(1):60–63. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1973.00490190078011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis W. C., Ticku M. K. Ethanol enhances [3H]diazepam binding at the benzodiazepine-gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor-ionophore complex. Mol Pharmacol. 1981 Sep;20(2):287–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. B. Alcohol withdrawal reactions in mice: effects of drugs that modify neurotransmission. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1973 Jul;186(1):1–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. B., Chin J. H. Interaction of ethanol with biological membranes. Fed Proc. 1981 May 15;40(7):2073–2076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg D. A., Cooper E. C., Gordon A., Diamond I. Ethanol and the gamma-aminobutyric acid-benzodiazepine receptor complex. J Neurochem. 1984 Apr;42(4):1062–1068. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb12711.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti A., Corda M. G., Wise B. C., Vaccarino F., Costa E. GABAergic synapses. Supramolecular organization and biochemical regulation. Neuropharmacology. 1983 Dec;22(12B):1471–1479. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(83)90115-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R. A., Allan A. M. Functional coupling of gamma-aminobutyric acid receptors to chloride channels in brain membranes. Science. 1985 May 31;228(4703):1108–1110. doi: 10.1126/science.2581319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingsworth E. B., McNeal E. T., Burton J. L., Williams R. J., Daly J. W., Creveling C. R. Biochemical characterization of a filtered synaptoneurosome preparation from guinea pig cerebral cortex: cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-generating systems, receptors, and enzymes. J Neurosci. 1985 Aug;5(8):2240–2253. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-08-02240.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt W. A., Majchrowicz E. Studies of neurotransmitter interactions after acute and chronic ethanol administration. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1983;18 (Suppl 1):371–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koob G. F., Strecker R. E., Bloom F. E. Effects of naloxone on the anticonflict properties of alcohol and chlordiazepoxide. Subst Alcohol Actions Misuse. 1980;1(5-6):447–457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljequist S., Engel J. A. The effects of GABA and benzodiazepine receptor antagonists on the anti-conflict actions of diazepam or ethanol. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1984 Oct;21(4):521–525. doi: 10.1016/s0091-3057(84)80033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljequist S., Engel J. A. The effects of GABA and benzodiazepine receptor antagonists on the anti-conflict actions of diazepam or ethanol. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1984 Oct;21(4):521–525. doi: 10.1016/s0091-3057(84)80033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majchrowicz E. Induction of physical dependence upon ethanol and the associated behavioral changes in rats. Psychopharmacologia. 1975 Sep 17;43(3):245–254. doi: 10.1007/BF00429258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelis E. K., Chang H. H., Roy S., McFaul J. A., Zimbrick J. D. Ethanol effects on synaptic glutamate receptor function and on membrane lipid organization. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1983;18 (Suppl 1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(83)90138-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestoros J. N. Ethanol specifically potentiates GABA-mediated neurotransmission in feline cerebral cortex. Science. 1980 Aug 8;209(4457):708–710. doi: 10.1126/science.7394531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. W. Drug interactions at the GABA receptor-ionophore complex. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1982;22:245–277. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.22.040182.001333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. W. GABA-benzodiazepine-barbiturate receptor interactions. J Neurochem. 1981 Jul;37(1):1–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb05284.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramanjaneyulu R., Ticku M. K. Binding characteristics and interactions of depressant drugs with [35S]t-butylbicyclophosphorothionate, a ligand that binds to the picrotoxinin site. J Neurochem. 1984 Jan;42(1):221–229. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb09721.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohde B. H., Harris R. A. Effects of barbiturates and ethanol on muscimol-induced release of [3H]-D-aspartate from rodent cerebellum. Neuropharmacology. 1983 Jun;22(6):721–727. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(83)90096-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandoval M. E. Sodium-dependent efflux of [3H]GABA from synaptosomes probably related to mitochondrial calcium mobilization. J Neurochem. 1980 Oct;35(4):915–921. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb07090.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. D., Jackson J. A., Weigert D., Skolnick P., Paul S. M. Characterization of barbiturate-stimulated chloride efflux from rat brain synaptoneurosomes. J Neurosci. 1985 Nov;5(11):2963–2970. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-11-02963.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. D., Skolnick P., Hollingsworth E. B., Paul S. M. Barbiturate and picrotoxin-sensitive chloride efflux in rat cerebral cortical synaptoneurosomes. FEBS Lett. 1984 Sep 17;175(1):193–196. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80597-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds M. A. Distinction between the effects of barbiturates, benzodiazepines and phenytoin on responses to gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor activation and antagonism by bicuculline and picrotoxin. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Jul;73(3):739–747. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb16810.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires R. F., Casida J. E., Richardson M., Saederup E. [35S]t-butylbicyclophosphorothionate binds with high affinity to brain-specific sites coupled to gamma-aminobutyric acid-A and ion recognition sites. Mol Pharmacol. 1983 Mar;23(2):326–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strong R., Wood W. G. Membrane properties and aging: in vivo and in vitro effects of ethanol on synaptosomal gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) release. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Jun;229(3):726–730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sytinsky I. A., Guzikov B. M., Gomanko M. V., Eremin V. P., Konovalova N. N. The gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) system in brain during acute and chronic ethanol intoxication. J Neurochem. 1975 Jul;25(1):43–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1975.tb07691.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thampy K. G., Barnes E. M., Jr gamma-Aminobutyric acid-gated chloride channels in cultured cerebral neurons. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1753–1757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ticku M. K., Burch T. P., Davis W. C. The interactions of ethanol with the benzodiazepine-GABA receptor-ionophore complex. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1983;18 (Suppl 1):15–18. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(83)90140-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wixon H. N., Hunt W. A. Effect of acute and chronic ethanol treatment on gamma-aminobutyric acid levels and on aminooxyacetic acid-induced GABA accumulation. Subst Alcohol Actions Misuse. 1980;1(5-6):481–491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong E. H., Leeb-Lundberg L. M., Teichberg V. I., Olsen R. W. gamma-Aminobutyric acid activation of 36Cl- flux in rat hippocampal slices and its potentiation by barbiturates. Brain Res. 1984 Jun 15;303(2):267–275. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)91213-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


