Abstract
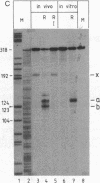
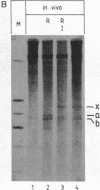
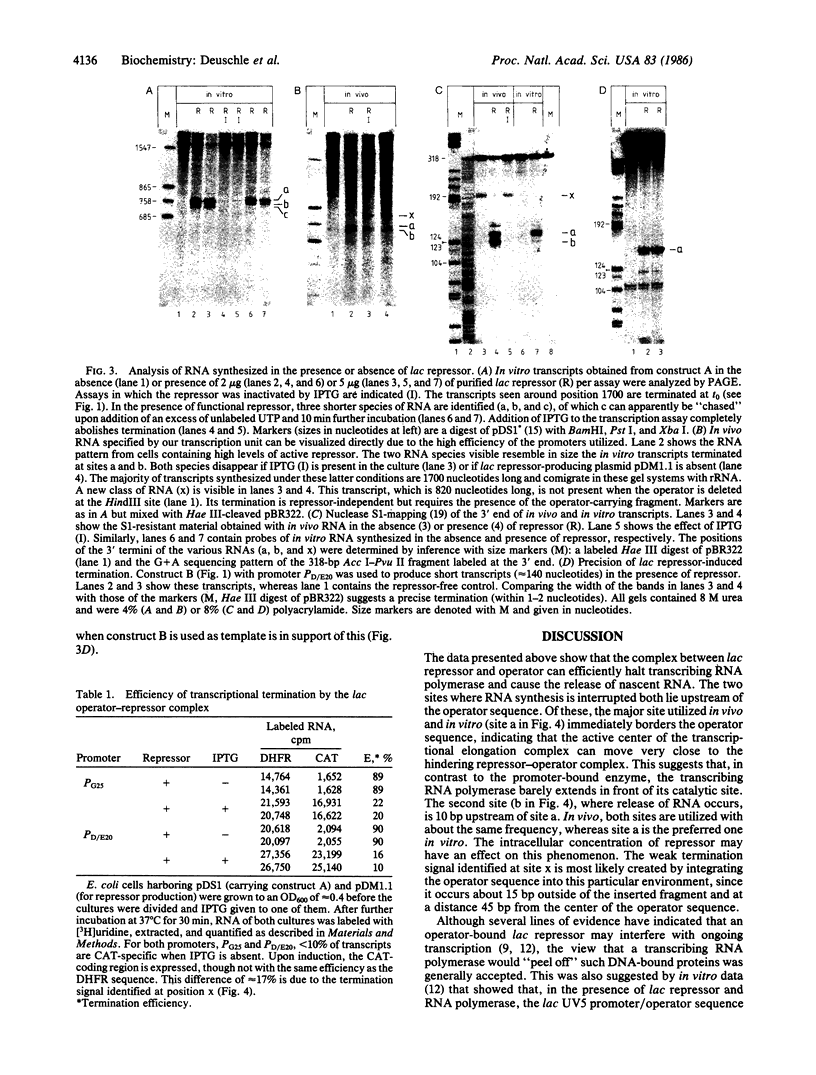
Operator sequences are essential elements in many negatively controlled operons. By binding repressors, they prevent the formation of active complexes between RNA polymerase and promoters. Here we show that the Escherichia coli lac operator-repressor complex also efficiently interrupts ongoing transcription. This observation suggests a mechanism of action for operators located distal to promoter sequences.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adhya S., Miller W. Modulation of the two promoters of the galactose operon of Escherichia coli. Nature. 1979 Jun 7;279(5713):492–494. doi: 10.1038/279492a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentz R., Bujard H. Promoters recognized by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase selected by function: highly efficient promoters from bacteriophage T5. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):70–77. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.70-77.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentz R., Langner A., Chang A. C., Cohen S. N., Bujard H. Cloning and analysis of strong promoters is made possible by the downstream placement of a RNA termination signal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4936–4940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert W., Maxam A. The nucleotide sequence of the lac operator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3581–3584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunsalus R. P., Yanofsky C. Nucleotide sequence and expression of Escherichia coli trpR, the structural gene for the trp aporepressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7117–7121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrin G. L., Jr, Bennett G. N. Role of DNA regions flanking the tryptophan promoter of Escherichia coli. II. Insertion of lac operator fragments. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):349–356. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90010-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz H., Platt T. Regulation of transcription from tandem and convergent promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Sep 25;10(18):5447–5465. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.18.5447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irani M. H., Orosz L., Adhya S. A control element within a structural gene: the gal operon of Escherichia coli. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):783–788. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90064-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majors J. Initiation of in vitro mRNA synthesis from the wild-type lac promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4394–4398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majumdar A., Adhya S. Demonstration of two operator elements in gal: in vitro repressor binding studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6100–6104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell D. H., Reznikoff W. S., Beckwith J. R. Genetic fusions defining trp and lac operon regulatory elements. J Mol Biol. 1975 Apr 15;93(3):331–350. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90281-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reznikoff W. S., Miller J. H., Scaife J. G., Beckwith J. R. A mechanism for repressor action. J Mol Biol. 1969 Jul 14;43(1):201–213. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90089-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanblatt S. H., Revzin A. Two catabolite activator protein molecules bind to the galactose promoter region of Escherichia coli in the presence of RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1594–1598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stueber D., Bujard H. Transcription from efficient promoters can interfere with plasmid replication and diminish expression of plasmid specified genes. EMBO J. 1982;1(11):1399–1404. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01329.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Crombrugghe B., Busby S., Buc H. Cyclic AMP receptor protein: role in transcription activation. Science. 1984 May 25;224(4651):831–838. doi: 10.1126/science.6372090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]