Abstract
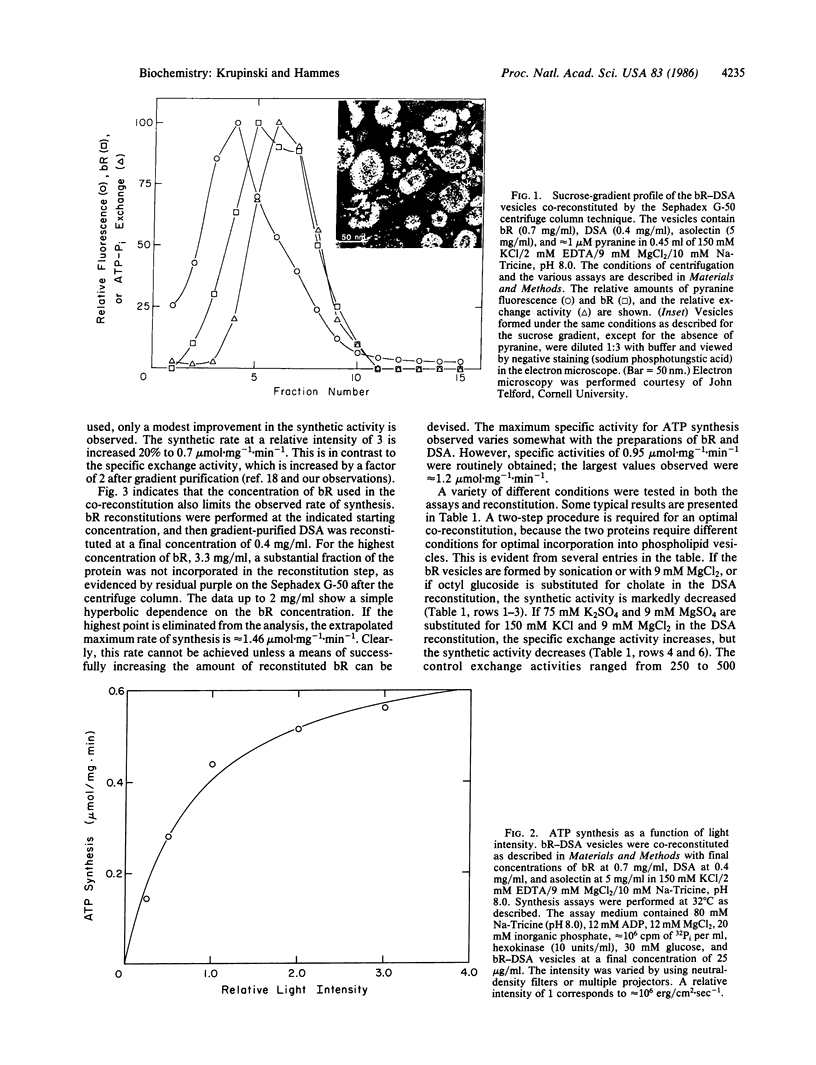
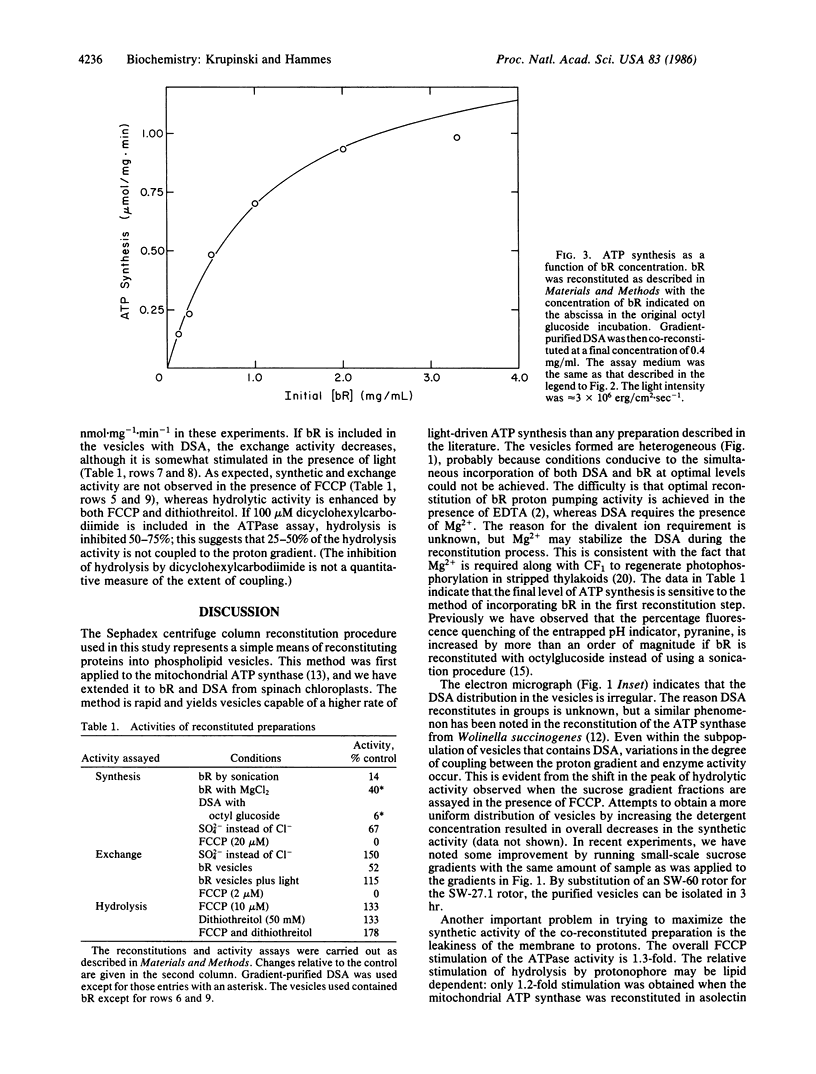
A method was developed for the co-reconstitution of bacteriorhodopsin and chloroplast coupling factor in asolectin vesicles. First, bacteriorhodopsin was reconstituted from a mixture of octyl glucoside, asolectin, and protein in the presence of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid by passage through a Sephadex G-50 centrifuge column. Then, the purified coupling factor was reconstituted from a mixture of sodium cholate, bacteriorhodopsin vesicles, and coupling factor in the presence of Mg2+ by passage through the centrifuge column. Sucrose density-gradient centrifugation indicated a band of vesicles with slightly different positions in the gradient for maximum vesicle concentration, bacteriorhodopsin vesicle concentration, ATP synthesis, and ATP hydrolysis. The rate of light-driven ATP synthesis reaches a limiting value as the concentration of bacteriorhodopsin and the light intensity are increased. A steady-state rate of ATP synthesis of 1 mumol per mg of coupling factor X min-1 has been achieved. Apparently this rate is limited by the heterogeneity within the vesicle population and by the ability of bacteriorhodopsin to form a sufficiently large pH gradient.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alfonzo M., Kandrach M. A., Racker E. Isolation, characterization, and reconstitution of a solubilized fraction containing the hydrophobic sector of the mitochondrial proton pump. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1981 Dec;13(5-6):375–391. doi: 10.1007/BF00743211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensadoun A., Weinstein D. Assay of proteins in the presence of interfering materials. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):241–250. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokranz M., Mörschel E., Kröger A. Phosphorylation and phosphate-ATP exchange catalyzed by the ATP synthase isolated from Wolinella succinogenes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Dec 16;810(3):332–339. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(85)90218-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewey T. G., Hammes G. G. Steady state kinetics of ATP synthesis and hydrolysis catalyzed by reconstituted chloroplast coupling factor. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):8941–8946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauska G., Samoray D., Orlich G., Nelson N. Reconstitution of photosynthetic energy conservation. II. Photophosphorylation in liposomes containing photosystem-I reaction center and chloroplast coupling-factor complex. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Oct;111(2):535–543. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04969.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K. S., Bayley H., Khorana H. G. Delipidation of bacteriorhodopsin and reconstitution with exogenous phospholipid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):323–327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupinski J., Hammes G. G. Phase-lifetime spectrophotometry of deoxycholate-purified bacteriorhodopsin reconstituted into asolectin vesicles. Biochemistry. 1985 Nov 19;24(24):6963–6972. doi: 10.1021/bi00345a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozier R. H., Niederberger W., Bogomolni R. A., Hwang S., Stoeckenius W. Kinetics and stoichiometry of light-induced proton release and uptake from purple membrane fragments, Halobacterium halobium cell envelopes, and phospholipid vesicles containing oriented purple membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 13;440(3):545–556. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(76)90041-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oren R., Weiss S., Garty H., Caplan S. R., Gromet-Elhanan Z. ATP synthesis catalyzed by the ATPase complex from Rhodospirillum rubrum reconstituted into phospholipid vesicles together with bacteriorhodopsin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Dec;205(2):503–509. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90133-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penefsky H. S. A centrifuged-column procedure for the measurement of ligand binding by beef heart F1. Methods Enzymol. 1979;56:527–530. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)56050-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick U., Racker E. Purification and reconstitution of the N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide-sensitive ATPase complex from spinach chloroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2793–2799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racker E., Stoeckenius W. Reconstitution of purple membrane vesicles catalyzing light-driven proton uptake and adenosine triphosphate formation. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):662–663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryrie I. J., Critchley C., Tillberg J. E. Structure and energy-linked activities in reconstituted bacteriorhodopsin--yeast ATPase proteoliposomes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Nov;198(1):182–194. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90409-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sone N., Takeuchi Y., Yoshida M., Ohno K. Formations of electrochemical proton gradient and adenosine triphosphate in proteoliposomes containing purified adenosine triphosphatase and bacteriorhodopsin. J Biochem. 1977 Dec;82(6):1751–1758. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckenius W., Bogomolni R. A. Bacteriorhodopsin and related pigments of halobacteria. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:587–616. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.003103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takabe T., Hammes G. G. pH dependence of adenosine 5'-triphosphate synthesis and hydrolysis catalyzed by reconstituted chloroplast coupling factor. Biochemistry. 1981 Nov 24;20(24):6859–6864. doi: 10.1021/bi00527a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winget G. D., Kanner N., Racker E. Formation of ATP by the adenosine triphosphatase complex from spinach chloroplasts reconstituted together with bacteriorhodopsin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jun 9;460(3):490–499. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(77)90087-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]