Abstract
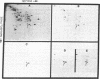
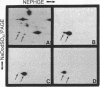
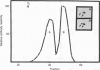
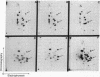
A method was devised that allows the identification of proteins related to the Mr 36,000 tyrosine kinase substrate calpactin based on their ability to interact with actin and phospholipid in a calcium-dependent manner. Two distinct proteins, detected in human A431 cells and fibroblasts, were resolved by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. One of these proteins (calpactin I) appears identical to the Mr 34,000-39,000 substrate of the pp60src tyrosine kinase and the second (calpactin II) reacts with antibodies to the Mr 35,000 substrate of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Both proteins interact with phospholipid and actin, are rather basic, and share structural and antigenic determinants. A major difference between the two proteins is noted in their state of association with the Mr 10,000 light chain; i.e., calpactin I is associated with the light chain while calpactin II is not.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashendel C. L. The phorbol ester receptor: a phospholipid-regulated protein kinase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Sep 9;822(2):219–242. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(85)90009-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y. S., Chen L. B. Detection of phosphotyrosine-containing 34,000-dalton protein in the framework of cells transformed with Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2388–2392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Hunter T. Discrete primary locations of a tyrosine-protein kinase and of three proteins that contain phosphotyrosine in virally transformed chick fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;94(2):287–296. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.2.287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creutz C. E. Secretory vesicle - cytosol interactions in exocytosis: isolation by Ca2+-dependent affinity chromatography of proteins that bind to the chromaffin granule membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Dec 31;103(4):1395–1400. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90278-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. H., Pickett R. A., 2nd, Hampton J., Lerner R. A. Radioiodination of proteins in single polyacrylamide gel slices. Tryptic peptide analysis of all the major members of complex multicomponent systems using microgram quantities of total protein. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6510–6515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Erikson R. L. Identification of a cellular protein substrate phosphorylated by the avian sarcoma virus-transforming gene product. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):829–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90446-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Shealy D. J., Erikson R. L. Evidence that viral transforming gene products and epidermal growth factor stimulate phosphorylation of the same cellular protein with similar specificity. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11381–11384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Tomasiewicz H. G., Erikson R. L. Biochemical characterization of a 34-kilodalton normal cellular substrate of pp60v-src and an associated 6-kilodalton protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;4(1):77–85. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fava R. A., Cohen S. Isolation of a calcium-dependent 35-kilodalton substrate for the epidermal growth factor receptor/kinase from A-431 cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2636–2645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerke V., Weber K. Identity of p36K phosphorylated upon Rous sarcoma virus transformation with a protein purified from brush borders; calcium-dependent binding to non-erythroid spectrin and F-actin. EMBO J. 1984 Jan;3(1):227–233. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01789.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerke V., Weber K. The regulatory chain in the p36-kd substrate complex of viral tyrosine-specific protein kinases is related in sequence to the S-100 protein of glial cells. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2917–2920. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04023.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh-Dastidar P., Fox C. F. Epidermal growth factor and epidermal growth factor receptor-dependent phosphorylation of a Mr = 34,000 protein substrate for pp60src. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):2041–2044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giugni T. D., James L. C., Haigler H. T. Epidermal growth factor stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of specific proteins in permeabilized human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15081–15090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Glenney P. Comparison of Ca++-regulated events in the intestinal brush border. J Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;100(3):754–763. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.3.754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Glenney P. Comparison of spectrin isolated from erythroid and non-erythroid sources. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Nov 2;144(3):529–539. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08498.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr Phosphorylation of p36 in vitro with pp60src. Regulation by Ca2+ and phospholipid. FEBS Lett. 1985 Nov 11;192(1):79–82. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80047-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Tack B. F. Amino-terminal sequence of p36 and associated p10: identification of the site of tyrosine phosphorylation and homology with S-100. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7884–7888. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. Phospholipid-dependent Ca2+ binding by the 36-kDa tyrosine kinase substrate (calpactin) and its 33-kDa core. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 5;261(16):7247–7252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Cooper J. A., Hunter T. The 46,000-dalton tyrosine protein kinase substrate is widespread, whereas the 36,000-dalton substrate is only expressed at high levels in certain rodent tissues. J Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;98(2):487–497. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.2.487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Brackenbury R., Edelman G. M. Changes in the distribution of the 34-kdalton tyrosine kinase substrate during differentiation and maturation of chicken tissues. J Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;98(2):473–486. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.2.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Edelman G. M. The 34 kd pp60src substrate is located at the inner face of the plasma membrane. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):767–779. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hexham J. M., Totty N. F., Waterfield M. D., Crumpton M. J. Homology between the subunits of S100 and a 10kDa polypeptide associated with p36 of pig lymphocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jan 14;134(1):248–254. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90554-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Epidermal growth factor induces rapid tyrosine phosphorylation of proteins in A431 human tumor cells. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90100-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehto V. P., Virtanen I., Paasivuo R., Ralston R., Alitalo K. The p36 substrate of tyrosine-specific protein kinases co-localizes with non-erythrocyte alpha-spectrin antigen, p230, in surface lamina of cultured fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1983;2(10):1701–1705. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01645.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigg E. A., Cooper J. A., Hunter T. Immunofluorescent localization of a 39,000-dalton substrate of tyrosine protein kinases to the cytoplasmic surface of the plasma membrane. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;96(6):1601–1609. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.6.1601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radke K., Carter V. C., Moss P., Dehazya P., Schliwa M., Martin G. S. Membrane association of a 36,000-dalton substrate for tyrosine phosphorylation in chicken embryo fibroblasts transformed by avian sarcoma viruses. J Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;97(5 Pt 1):1601–1611. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.5.1601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radke K., Gilmore T., Martin G. S. Transformation by Rous sarcoma virus: a cellular substrate for transformation-specific protein phosphorylation contains phosphotyrosine. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):821–828. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90445-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radke K., Martin G. S. Transformation by Rous sarcoma virus: effects of src gene expression on the synthesis and phosphorylation of cellular polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5212–5216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer S. T., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor stimulates the phosphorylation of the calcium-dependent 35,000-dalton substrate in intact A-431 cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 15;260(14):8233–8236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A., Watt S. The regulation of rabbit skeletal muscle contraction. I. Biochemical studies of the interaction of the tropomyosin-troponin complex with actin and the proteolytic fragments of myosin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4866–4871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Walker J. H., Obrocki J. Calelectrin self-aggregates and promotes membrane aggregation in the presence of calcium. EMBO J. 1982;1(10):1167–1170. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb00008.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]