Abstract
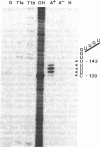
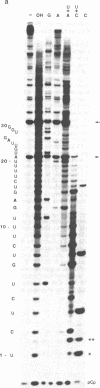
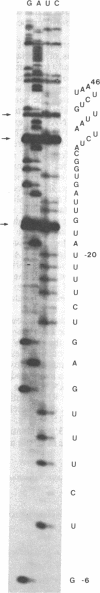
Tobacco infected with the plant rhabdovirus sonchus yellow net virus (SYNV) contains short, 139- to 144-nucleotide (nt) transcripts complementary to the 3′ terminus of the negative-strand genomic RNA. These transcripts are similar to the leader RNAs associated with several animal rhabdovirus infections in that they are encoded by the same region of the genome, but the SYNV transcripts are nearly 3 times longer than the animal rhabdovirus leader RNAs. The SYNV leader RNAs differ markedly in sequence from the leader RNAs associated with strains of vesicular stomatitis virus and rabies virus, although the first 30 nt of all three transcripts are rich in adenylate residues. The nucleotide sequence determined directly from SYNV RNA and from recombinant DNA clones derived from SYNV RNA reveals a possible initiation site for transcription of the N-protein mRNA that is located 147 nt from the 3′ end of genomic RNA. The sequence (UUGU) at this site is complementary to the first 4 nt of the N-protein mRNAs of animal rhabdoviruses. In SYNV, the first AUG codon in the putative N-protein mRNA is located 57 nt downstream (at positions 203-205 in the viral genome) and is followed by an open reading frame for the remainder of the 1020 nt determined in these experiments.
Keywords: negative-strand RNA virus, viral RNA transcripts
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blumberg B. M., Giorgi C., Kolakofsky D. N protein of vesicular stomatitis virus selectively encapsidates leader RNA in vitro. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):559–567. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90475-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buell G. N., Wickens M. P., Payvar F., Schimke R. T. Synthesis of full length cDNAs from four partially purified oviduct mRNAs. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 10;253(7):2471–2482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonno R. J., Banerjee A. K. Complete nucleotide sequence of the leader RNA synthesized in vitro by vesicular stomatitis virus. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):93–101. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90085-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. W., Stanley J., Van Kammen A. Sequence homology adjacent to the 3' terminal poly(A) of cowpea mosaic virus RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Sep 25;7(2):493–500. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.2.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De B. P., Banerjee A. K. Requirements and functions of vesicular stomatitis virus L and NS proteins in the transcription process in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jan 16;126(1):40–49. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90568-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H., Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Mapping adenines, guanines, and pyrimidines in RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2527–2538. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson S. U. Reconstitution studies detect a single polymerase entry site on the vesicular stomatitis virus genome. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):635–642. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90319-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giorgi C., Blumberg B., Kolakofsky D. Sequence determination of the (+) leader RNA regions of the vesicular stomatitis virus Chandipura, Cocal, and Piry serotype genomes. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):125–130. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.125-130.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson A. O., Christie S. R. Purification and some physicochemical properties of sonchus yellow net virus. Virology. 1977 Mar;77(1):344–355. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90431-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson A. O. Partial characterization of the structural proteins of sonchus yellow net virus. Virology. 1978 Jun 1;87(1):172–181. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90169-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keene J. D., Thornton B. J., Emerson S. U. Sequence-specific contacts between the RNA polymerase of vesicular stomatitis virus and the leader RNA gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6191–6195. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurilla M. G., Cabradilla C. D., Holloway B. P., Keene J. D. Nucleotide sequence and host La protein interactions of rabies virus leader RNA. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):773–778. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.773-778.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurilla M. G., Keene J. D. The leader RNA of vesicular stomatitis virus is bound by a cellular protein reactive with anti-La lupus antibodies. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):837–845. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90541-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurilla M. G., Piwnica-Worms H., Keene J. D. Rapid and transient localization of the leader RNA of vesicular stomatitis virus in the nuclei of infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5240–5244. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dolan A., Pringle C. R. Comparisons of nucleotide sequences in the genomes of the New Jersey and Indiana serotypes of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):69–77. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.69-77.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan J. J., Emerson S. U., Wagner R. R. The plus-strand leader RNA of VSV inhibits DNA-dependent transcription of adenovirus and SV40 genes in a soluble whole-cell extract. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):325–333. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90350-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. High-efficiency cloning of full-length cDNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;2(2):161–170. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.2.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peattie D. A. Direct chemical method for sequencing RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1760–1764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K. Complete sequences of the ribosome recognition sites in vesicular stomatitis virus mRNAs: recognition by the 40S and 80S complexes. Cell. 1978 Jun;14(2):345–353. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90120-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roychoudhury R., Jay E., Wu R. Terminal labeling and addition of homopolymer tracts to duplex DNA fragments by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Jan;3(1):101–116. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.1.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley J., Hanau R., Jackson A. O. Sequence comparison of the 3' ends of a subgenomic RNA and the genomic RNAs of barley stripe mosaic virus. Virology. 1984 Dec;139(2):375–383. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90383-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. R., Prevec L., Brown F., Summers D. F., Sokol F., MacLeod R. Classification of rhabdovirus proteins: a proposal. J Virol. 1972 Dec;10(6):1228–1230. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.6.1228-1230.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilusz J., Youngner J. S., Keene J. D. Base mutations in the terminal noncoding regions of the genome of vesicular stomatitis virus isolated from persistent infections of L cells. Virology. 1985 Jan 30;140(2):249–256. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90363-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]