Abstract
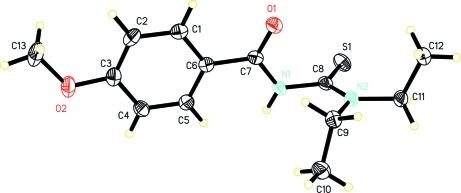
In the title compound, C13H18N2O2S, the 4-methoxybenzoyl fragment is approximately planar [maximum deviation = 0.057 (2) Å] and twisted relative to the thioamide fragment, forming a dihedral angle of 86.62 (6)°. The two Csp 2—Nsp 2 bonds in the thiourea unit differ significantly in length [1.327 (2) and 1.431 (2) Å]. In the crystal, N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds link the molecules into chains parallel to [010].
Related literature
For structural parameters and chemical properties of 1,1 disubstituted 3-benzoylthioureas, see: Al-abbasi et al. (2010 ▶, 2011 ▶); Al-abbasi & Kassim (2011 ▶); Mohamadou et al. (1994 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C13H18N2O2S
M r = 266.35
Orthorhombic,
a = 12.9024 (5) Å
b = 10.0095 (4) Å
c = 20.8585 (11) Å
V = 2693.8 (2) Å3
Z = 8
Cu Kα radiation
μ = 2.11 mm−1
T = 150 K
0.24 × 0.10 × 0.05 mm
Data collection
Oxford Diffraction Gemini diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis RED; Oxford Diffraction, 2006 ▶) T min = 0.810, T max = 0.900
12046 measured reflections
2548 independent reflections
2214 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.030
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.042
wR(F 2) = 0.132
S = 1.12
2548 reflections
163 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.43 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.32 e Å−3
Data collection: CrysAlis CCD (Oxford Diffraction, 2006 ▶); cell refinement: CrysAlis RED (Oxford Diffraction, 2006 ▶); data reduction: CrysAlis RED; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL, PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶) and publCIF (Westrip, 2010 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811049208/gk2435sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811049208/gk2435Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811049208/gk2435Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1A⋯O1i | 0.86 | 2.05 | 2.847 (2) | 154 |
Symmetry code: (i) 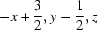 .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia for providing facilities and grants (UKM-ST-06-FRGS0111-2009 and UKM-PTS-016-2010) and the Libyan Government for providing a scholarship for AA.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The title compound (I) has been used as a ligand to form stable complexes with Ni and Co (Mohamadou et al., 1994). Compund I and other similar derivatives act as a bidentate (O,S) chelate forming square planar and tetrahedral complexes with NiII and CoIII, respectively.
In the structure of I, the 4-methoxybenzamide moiety [O2/N1/C1/C2/C3/C4/C5/C6/C7/C8/C13] (A) and the thiourea fragment [S1/N1/N2/C8] (B) are essentially planar with maximum deviations from the mean planes 0.057 (2) Å for C13 and -0.031 (2) Å N1. The dihedral angle between the A and B planes is 86.62 (6)°, which is slightly smaller than the analogous dihedral angle [87.99 (11)°] in 1-benzoyl-3-ethyl-3-phenylthiourea (II) (Al-abbasi & Kassim, 2011).
The C=O [1.237 (2) Å] and C=S [1.658 (3) Å] bond lengths are slightly longer than those in II [1.207 (3) and 1.666 (2) Å, respectively].
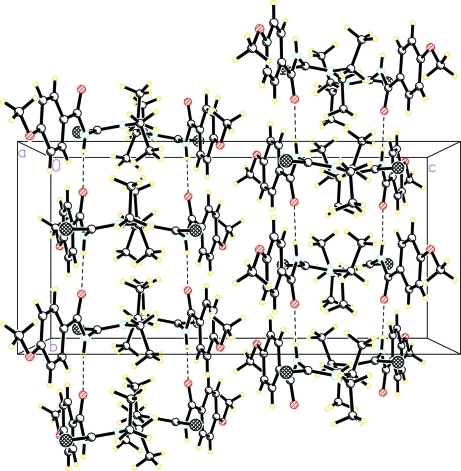
In the crystal, the molecules are stabilized by intermolecular N1—H1A···O1 hydrogen bonds forming a one-dimensional polymeric network along the b axis (Figure 2).
Experimental
A solution of benzoyl chloride (10 mmol) in acetone was added slowly to an equimolar solution of ammonium thiocyanate in acetone. The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature before adding diethylamine (10 mmol) slowly and the mixture was left stirring at room temperature for 2–3 h. The mixture was poured onto a water-ice, filtered and the residue was recrystallized from ethaaol/acetone solution to give colourless crystals, suitable for X-ray crystallography (yield 85%).
Refinement
The hydrogen atom positions were calculated geometrically and refined in a riding model approximation with C–H bond lengths in the range 0.93–0.97 Å and N-H= 0.86 Å with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C, N) for N-H, aromatic C-H and CH2 groups, and Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(C) for methyl group.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of 1,1-diethyl-3-(4-methoxybenzoyl)thiourea with displacement ellipsods drawn at the 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.
The crystal packing of 1,1-diethyl-3-(4-methoxybenzoyl)thiourea with intermolecular hydrogen bonds shown as dashed lines.
Crystal data
| C13H18N2O2S | Dx = 1.314 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 266.35 | Melting point = 407.15–408.15 K |
| Orthorhombic, Pbca | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54178 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ac 2ab | Cell parameters from 5648 reflections |
| a = 12.9024 (5) Å | θ = 4.2–71.1° |
| b = 10.0095 (4) Å | µ = 2.11 mm−1 |
| c = 20.8585 (11) Å | T = 150 K |
| V = 2693.8 (2) Å3 | Plate, colourless |
| Z = 8 | 0.24 × 0.10 × 0.05 mm |
| F(000) = 1136 |
Data collection
| Oxford Diffraction Gemini diffractometer | 2548 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2214 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.030 |
| ω/2θ scans | θmax = 71.1°, θmin = 4.2° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis RED; Oxford Diffraction, 2006) | h = −13→15 |
| Tmin = 0.810, Tmax = 0.900 | k = −12→12 |
| 12046 measured reflections | l = −23→25 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.042 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.132 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.12 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0835P)2 + 0.6035P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2548 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 163 parameters | Δρmax = 0.43 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.32 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Experimental. The crystal was placed in the cold stream of an Oxford Cryosystems open-flow nitrogen cryostat (Cosier & Glazer, 1986) with a nominal stability of 0.1 K.Cosier, J. & Glazer, A.M., 1986. J. Appl. Cryst. 105 107. |
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.96773 (4) | 0.08865 (5) | 0.60731 (2) | 0.0302 (2) | |
| O1 | 0.72174 (10) | 0.27396 (13) | 0.63046 (7) | 0.0282 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.29590 (10) | 0.00839 (15) | 0.54492 (7) | 0.0327 (4) | |
| N1 | 0.76759 (11) | 0.05775 (15) | 0.63691 (7) | 0.0210 (3) | |
| H1A | 0.7495 | −0.0246 | 0.6332 | 0.025* | |
| N2 | 0.87609 (11) | 0.11414 (15) | 0.72156 (7) | 0.0215 (3) | |
| C1 | 0.52575 (14) | 0.21406 (19) | 0.58056 (9) | 0.0242 (4) | |
| H1B | 0.5472 | 0.3028 | 0.5811 | 0.029* | |
| C2 | 0.42448 (15) | 0.1834 (2) | 0.56253 (9) | 0.0271 (4) | |
| H2A | 0.3785 | 0.2510 | 0.5513 | 0.033* | |
| C3 | 0.39293 (14) | 0.0509 (2) | 0.56149 (8) | 0.0246 (4) | |
| C4 | 0.46228 (14) | −0.05050 (19) | 0.57806 (9) | 0.0236 (4) | |
| H4A | 0.4410 | −0.1393 | 0.5771 | 0.028* | |
| C5 | 0.56228 (14) | −0.01898 (19) | 0.59584 (8) | 0.0220 (4) | |
| H5A | 0.6082 | −0.0870 | 0.6067 | 0.026* | |
| C6 | 0.59545 (14) | 0.11370 (18) | 0.59775 (8) | 0.0201 (4) | |
| C7 | 0.69945 (13) | 0.15522 (17) | 0.62164 (8) | 0.0202 (4) | |
| C8 | 0.86948 (13) | 0.08980 (16) | 0.65915 (9) | 0.0213 (4) | |
| C9 | 0.78567 (13) | 0.11498 (19) | 0.76513 (9) | 0.0236 (4) | |
| H9A | 0.7265 | 0.1524 | 0.7427 | 0.028* | |
| H9B | 0.8007 | 0.1721 | 0.8015 | 0.028* | |
| C10 | 0.75793 (15) | −0.0231 (2) | 0.78918 (10) | 0.0298 (4) | |
| H10A | 0.6989 | −0.0174 | 0.8171 | 0.045* | |
| H10B | 0.8156 | −0.0599 | 0.8123 | 0.045* | |
| H10C | 0.7417 | −0.0798 | 0.7534 | 0.045* | |
| C11 | 0.97664 (13) | 0.14064 (18) | 0.75210 (9) | 0.0246 (4) | |
| H11A | 1.0310 | 0.0973 | 0.7277 | 0.029* | |
| H11B | 0.9768 | 0.1028 | 0.7949 | 0.029* | |
| C12 | 0.99913 (15) | 0.28917 (19) | 0.75623 (10) | 0.0296 (5) | |
| H12A | 1.0650 | 0.3028 | 0.7766 | 0.044* | |
| H12B | 0.9459 | 0.3322 | 0.7808 | 0.044* | |
| H12C | 1.0008 | 0.3265 | 0.7138 | 0.044* | |
| C13 | 0.22137 (16) | 0.1077 (3) | 0.52797 (11) | 0.0401 (5) | |
| H13A | 0.1567 | 0.0654 | 0.5177 | 0.060* | |
| H13B | 0.2457 | 0.1569 | 0.4914 | 0.060* | |
| H13C | 0.2116 | 0.1676 | 0.5634 | 0.060* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.0251 (3) | 0.0307 (3) | 0.0347 (3) | −0.00535 (18) | 0.00843 (18) | −0.00309 (18) |
| O1 | 0.0258 (7) | 0.0211 (7) | 0.0378 (8) | −0.0015 (5) | −0.0037 (6) | 0.0012 (5) |
| O2 | 0.0193 (7) | 0.0438 (9) | 0.0351 (8) | −0.0006 (6) | −0.0042 (5) | 0.0002 (6) |
| N1 | 0.0196 (7) | 0.0170 (8) | 0.0265 (8) | −0.0021 (5) | −0.0025 (6) | −0.0007 (6) |
| N2 | 0.0188 (7) | 0.0181 (7) | 0.0275 (8) | −0.0002 (5) | −0.0016 (6) | 0.0003 (6) |
| C1 | 0.0273 (10) | 0.0215 (10) | 0.0238 (10) | 0.0017 (7) | 0.0004 (7) | 0.0011 (7) |
| C2 | 0.0255 (9) | 0.0315 (11) | 0.0244 (9) | 0.0085 (8) | −0.0015 (7) | 0.0035 (7) |
| C3 | 0.0207 (9) | 0.0348 (11) | 0.0184 (9) | 0.0003 (7) | 0.0004 (6) | −0.0014 (7) |
| C4 | 0.0242 (9) | 0.0227 (9) | 0.0239 (10) | −0.0025 (7) | 0.0016 (7) | −0.0026 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0209 (9) | 0.0240 (9) | 0.0212 (9) | 0.0018 (7) | 0.0021 (6) | 0.0005 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0210 (9) | 0.0206 (9) | 0.0187 (8) | 0.0009 (7) | 0.0016 (6) | −0.0006 (6) |
| C7 | 0.0226 (9) | 0.0184 (9) | 0.0197 (8) | −0.0012 (7) | 0.0022 (6) | 0.0008 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0194 (9) | 0.0149 (9) | 0.0295 (10) | 0.0000 (6) | −0.0012 (7) | 0.0010 (6) |
| C9 | 0.0220 (9) | 0.0222 (9) | 0.0265 (10) | 0.0007 (7) | 0.0001 (7) | −0.0027 (7) |
| C10 | 0.0261 (10) | 0.0314 (11) | 0.0318 (10) | −0.0026 (8) | 0.0028 (8) | 0.0030 (8) |
| C11 | 0.0204 (9) | 0.0211 (10) | 0.0323 (10) | 0.0008 (7) | −0.0066 (7) | 0.0002 (7) |
| C12 | 0.0252 (9) | 0.0268 (11) | 0.0367 (11) | −0.0050 (7) | −0.0082 (8) | 0.0024 (8) |
| C13 | 0.0229 (10) | 0.0591 (15) | 0.0384 (12) | 0.0080 (9) | −0.0058 (8) | 0.0033 (10) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| S1—C8 | 1.6663 (18) | C5—C6 | 1.396 (3) |
| O1—C7 | 1.237 (2) | C5—H5A | 0.9300 |
| O2—C3 | 1.367 (2) | C6—C7 | 1.490 (2) |
| O2—C13 | 1.428 (3) | C9—C10 | 1.514 (3) |
| N1—C7 | 1.351 (2) | C9—H9A | 0.9700 |
| N1—C8 | 1.431 (2) | C9—H9B | 0.9700 |
| N1—H1A | 0.8600 | C10—H10A | 0.9600 |
| N2—C8 | 1.327 (2) | C10—H10B | 0.9600 |
| N2—C11 | 1.470 (2) | C10—H10C | 0.9600 |
| N2—C9 | 1.479 (2) | C11—C12 | 1.517 (3) |
| C1—C2 | 1.394 (3) | C11—H11A | 0.9700 |
| C1—C6 | 1.395 (3) | C11—H11B | 0.9700 |
| C1—H1B | 0.9300 | C12—H12A | 0.9600 |
| C2—C3 | 1.387 (3) | C12—H12B | 0.9600 |
| C2—H2A | 0.9300 | C12—H12C | 0.9600 |
| C3—C4 | 1.397 (3) | C13—H13A | 0.9600 |
| C4—C5 | 1.379 (3) | C13—H13B | 0.9600 |
| C4—H4A | 0.9300 | C13—H13C | 0.9600 |
| C3—O2—C13 | 117.56 (17) | N2—C9—C10 | 112.64 (15) |
| C7—N1—C8 | 120.83 (15) | N2—C9—H9A | 109.1 |
| C7—N1—H1A | 119.6 | C10—C9—H9A | 109.1 |
| C8—N1—H1A | 119.6 | N2—C9—H9B | 109.1 |
| C8—N2—C11 | 121.01 (15) | C10—C9—H9B | 109.1 |
| C8—N2—C9 | 123.58 (14) | H9A—C9—H9B | 107.8 |
| C11—N2—C9 | 115.40 (14) | C9—C10—H10A | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 121.00 (17) | C9—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—H1B | 119.5 | H10A—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—H1B | 119.5 | C9—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 119.34 (17) | H10A—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—H2A | 120.3 | H10B—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—H2A | 120.3 | N2—C11—C12 | 111.73 (14) |
| O2—C3—C2 | 124.80 (17) | N2—C11—H11A | 109.3 |
| O2—C3—C4 | 115.01 (17) | C12—C11—H11A | 109.3 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 120.19 (17) | N2—C11—H11B | 109.3 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 119.97 (18) | C12—C11—H11B | 109.3 |
| C5—C4—H4A | 120.0 | H11A—C11—H11B | 107.9 |
| C3—C4—H4A | 120.0 | C11—C12—H12A | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.81 (17) | C11—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—H5A | 119.6 | H12A—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—H5A | 119.6 | C11—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 118.69 (17) | H12A—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—C7 | 117.74 (16) | H12B—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 123.43 (16) | O2—C13—H13A | 109.5 |
| O1—C7—N1 | 120.50 (16) | O2—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| O1—C7—C6 | 121.81 (16) | H13A—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| N1—C7—C6 | 117.60 (15) | O2—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| N2—C8—N1 | 114.73 (15) | H13A—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| N2—C8—S1 | 126.08 (14) | H13B—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| N1—C8—S1 | 119.16 (13) | ||
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −0.2 (3) | C1—C6—C7—O1 | 5.0 (3) |
| C13—O2—C3—C2 | −0.6 (3) | C5—C6—C7—O1 | −170.57 (16) |
| C13—O2—C3—C4 | 179.54 (17) | C1—C6—C7—N1 | −178.57 (16) |
| C1—C2—C3—O2 | 179.78 (17) | C5—C6—C7—N1 | 5.9 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.3 (3) | C11—N2—C8—N1 | 176.34 (14) |
| O2—C3—C4—C5 | −179.75 (16) | C9—N2—C8—N1 | −2.8 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.3 (3) | C11—N2—C8—S1 | −1.5 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.2 (3) | C9—N2—C8—S1 | 179.41 (13) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.8 (3) | C7—N1—C8—N2 | 84.6 (2) |
| C2—C1—C6—C7 | −175.01 (16) | C7—N1—C8—S1 | −97.46 (17) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −0.8 (3) | C8—N2—C9—C10 | 84.7 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 174.78 (16) | C11—N2—C9—C10 | −94.45 (18) |
| C8—N1—C7—O1 | −4.6 (3) | C8—N2—C11—C12 | 94.1 (2) |
| C8—N1—C7—C6 | 178.96 (15) | C9—N2—C11—C12 | −86.69 (19) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1A···O1i | 0.86 | 2.05 | 2.847 (2) | 154 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+3/2, y−1/2, z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: GK2435).
References
- Al-abbasi, A. A. & Kassim, M. B. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, o611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Al-abbasi, A. A., Yamin, B. M. & Kassim, M. B. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, o1891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Al-abbasi, A. A., Yarmo, M. A. & Kassim, M. B. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o2896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Mohamadou, A., Dechamps-Olivier, I. & Barbier, J. (1994). Polyhedron, 13, 1363–1370.
- Oxford Diffraction (2006). CrysAlis CCD and CrysAlis RED Oxford Diffraction, Abingdon, England.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811049208/gk2435sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811049208/gk2435Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811049208/gk2435Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report