Abstract
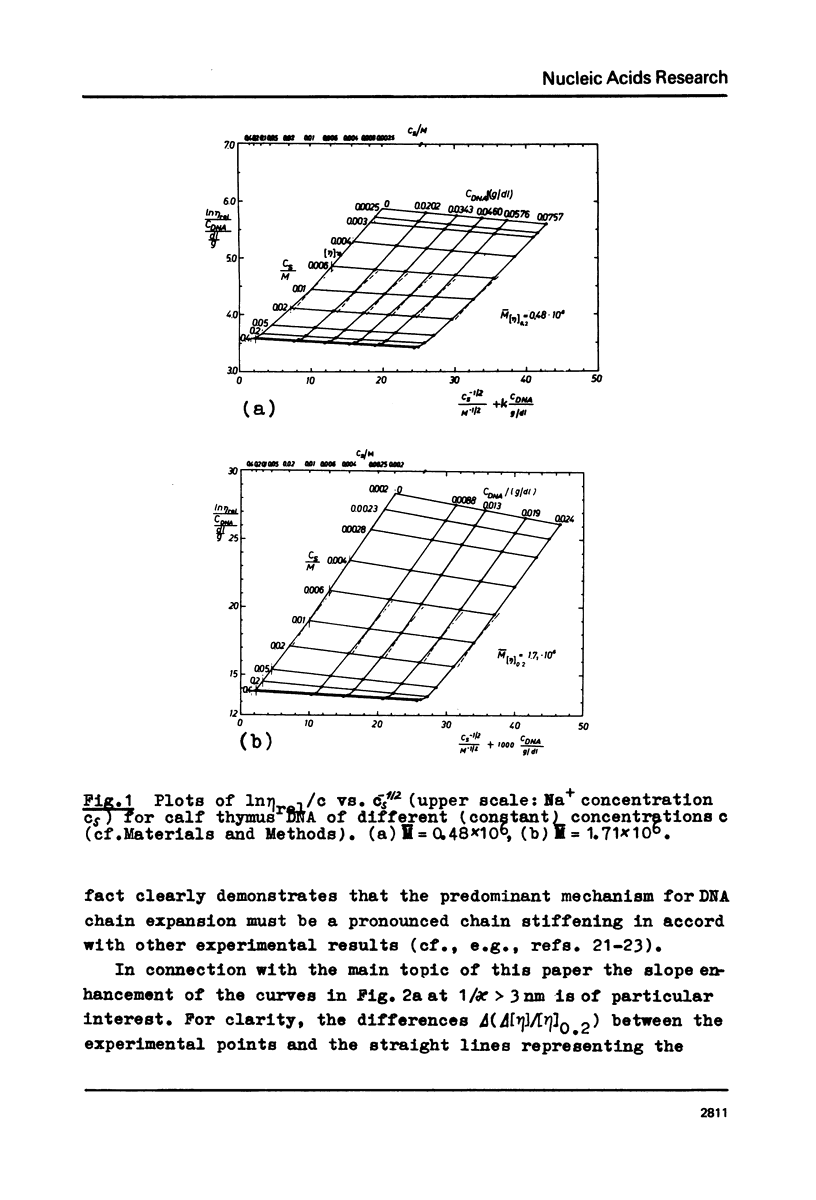
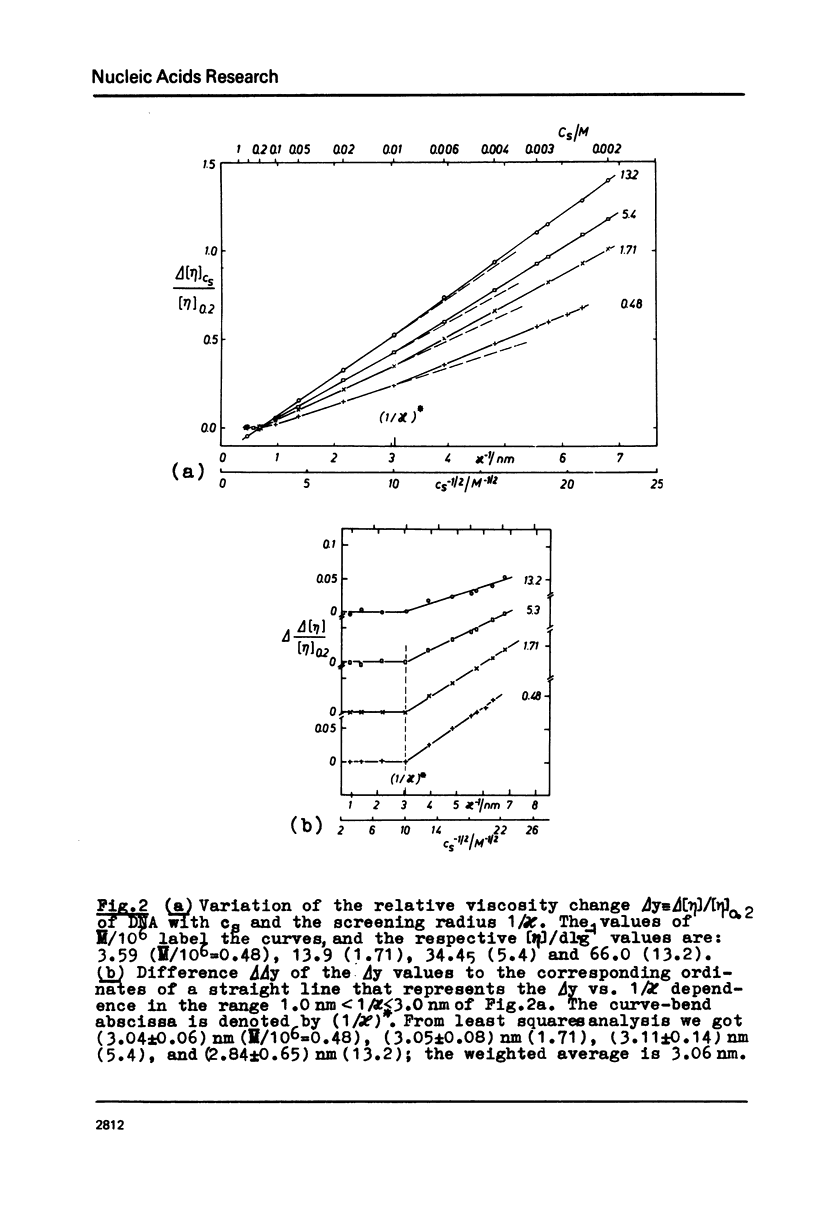
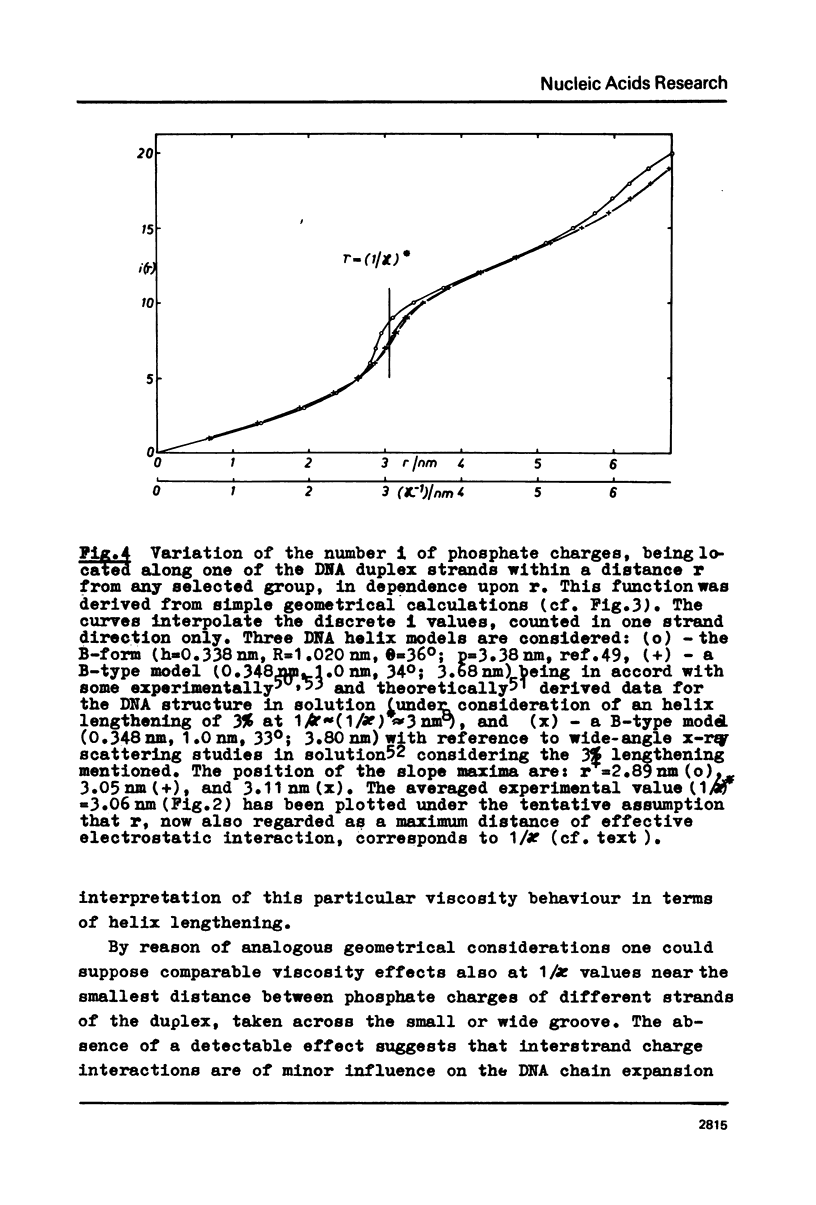
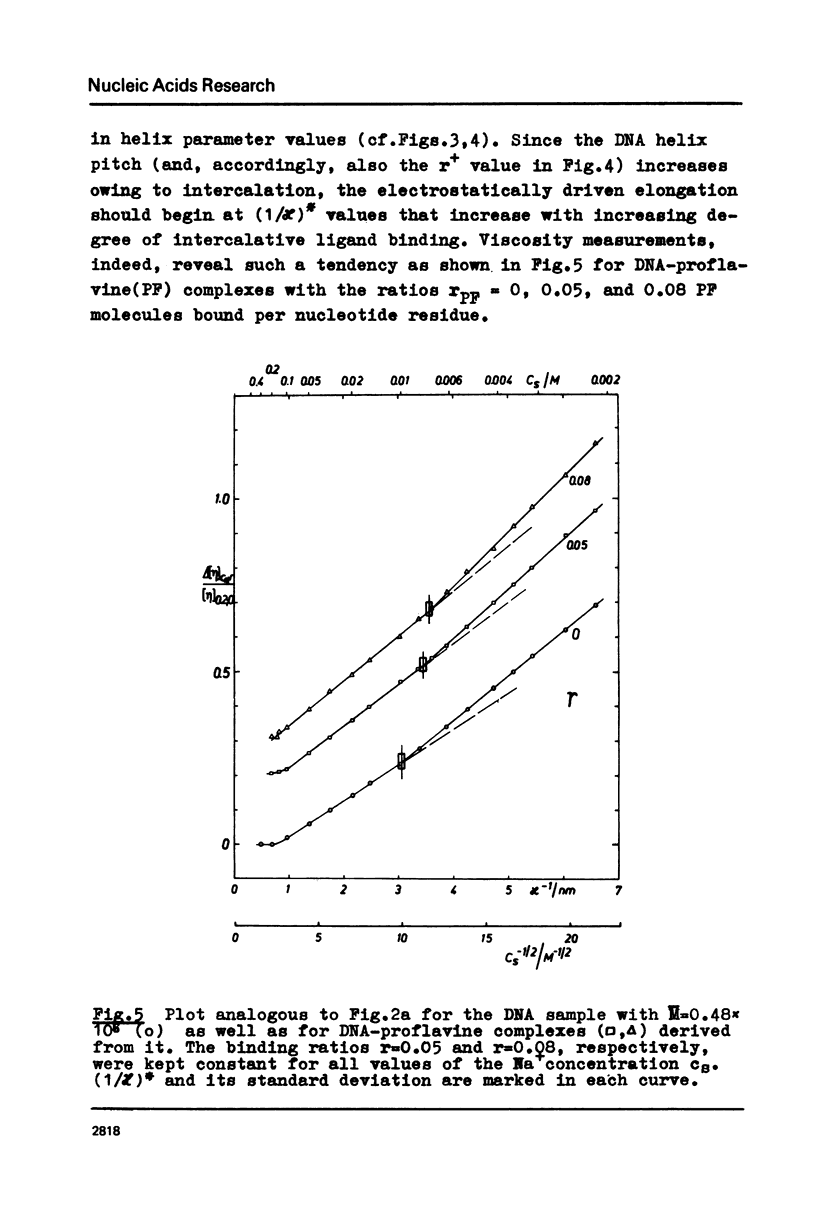
The polyion chain expansion of DNA was studied by viscometry within the Na+ concentration range c5 = 0.002 M to 0.4 M. The DNA molecular weights M were between 0.5 x 10(6) and 13 x 10(6). The relative change of intrinsic viscosity [eta] is linearly correlated to c5(-1/2) with a slope that increases with increasing M. This behaviour reflects the predominance of helix stiffening in chain expansion. At c5(112) > 0.01(-1/2 M-1/2 (Debye-Hückel screening radius 1/chi > (1/chi)*=3nm) the relative change of [eta] rises with a steeper slope. This effect increases with decreasing M suggesting that helix lengthening contributes to the chain expansion. Our model enables us to interpret other ionic-strength dependent effects known from literature. The start of the significant duplex elongation at (1/chi)* can be correlated to the polyion-charge arrangement. In accordance with our interpretation (1/chi)* is found to be greater for DNA-intercalator complexes.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnott S., Hukins D. W. Optimised parameters for A-DNA and B-DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jun 28;47(6):1504–1509. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90243-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury E. M., Chapman G. E., Danby S. E., Hartman P. G., Riches P. L. Studies on the role and mode of operation of the very-lysine-rich histone H1 (F1) in eukaryote chromatin. The properties of the N-terminal and C-terminal halves of histone H1. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Sep 15;57(2):521–528. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02327.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bram S. The secondary structure of DNA in solution and in nucleohistone. J Mol Biol. 1971 May 28;58(1):277–288. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90246-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crothers D. M., Zimm B. H. Viscosity and sedimentation of the DNA from bacteriophages T2 and T7 and the relation to molecular weight. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jul;12(3):525–536. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80310-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch J. T., Lutter L. C., Rhodes D., Brown R. S., Rushton B., Levitt M., Klug A. Structure of nucleosome core particles of chromatin. Nature. 1977 Sep 1;269(5623):29–36. doi: 10.1038/269029a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank-Kamenetskii F. Simplification of the empirical relationship between melting temperature of DNA, its GC content and concentration of sodium ions in solution. Biopolymers. 1971;10(12):2623–2624. doi: 10.1002/bip.360101223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frontali C., Dore E., Ferrauto A., Gratton E., Bettini A., Pozzan M. R., Valdevit E. An absolute method for the determination of the persistence length of native DNA from electron micrographs. Biopolymers. 1979 Jun;18(6):1353–1373. doi: 10.1002/bip.1979.360180604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon C. N. On the molecular length of the replicative form DNA of bacteriophage phiX174. J Mol Biol. 1973 Aug 25;78(4):601–615. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90282-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoh O., Wada A., Yabuki S. Salt-concentration dependence of melting profiles of lambda phage DNAs: evidence for long-range interactions and pronounced end effects. Biopolymers. 1979 Apr;18(4):805–824. doi: 10.1002/bip.1979.360180406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan M., Dattagupta N., Crothers D. M. Transient electric dichroism of rod-like DNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):195–199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain S. C., Tsai C. C., Sobell H. M. Visualization of drug-nucleic acid interactions at atomic resolution. II. Structure of an ethidium/dinucleoside monophosphate crystalline complex, ethidium:5-iodocytidylyl (3'-5') guanosine. J Mol Biol. 1977 Aug 15;114(3):317–331. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90253-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller W. Determination of the number of superhelical turns in simian virus 40 DNA by gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4876–4880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang D., Bujard H., Wolff B., Russell D. Electron microscopy of size and shape of viral DNA in solutions of different ionic strengths. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jan 28;23(2):163–181. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(67)80024-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt M. How many base-pairs per turn does DNA have in solution and in chromatin? Some theoretical calculations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):640–644. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd P. H., Prutton R. N., Peacocke A. R. Sedimentation studies on the interaction of proflavine with deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1968 Apr;107(3):353–359. doi: 10.1042/bj1070353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo K., Mitsui Y., Iitaka Y., Tsuboi M. Interaction of poly-L-lysine with nucleic acid. 3. An infrared and x-ray examination. J Mol Biol. 1968 Nov 28;38(1):129–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90133-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidle S., Achari A., Taylor G. L., Berman H. M., Carrell H. L., Glusker J. P., Stallings W. C. Structure of a dinucleoside phosphate--drug complex as model for nucleic acid--drug interaction. Nature. 1977 Sep 22;269(5626):304–307. doi: 10.1038/269304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puigdoménech P., Martínez P., Palau J., Bradbury E. M., Crane-Robinson C. Studies on the role and mode of operation of the very-lysine-rich histones in eukaryote chromatin. Nuclear-magnetic-resonance studies on nucleoprotein and histone phi 1-DNA complexes from marine invertebrate sperm. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jun 1;65(2):357–363. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10349.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulleyblank D. E., Morgan A. R. The sense of naturally occurring superhelices and the unwinding angle of intercalated ethidium. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jan 5;91(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90368-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinert K. E. Adenosine-thymidine cluster-specific elongation and stiffening of DNA induced by the oligopeptide antibiotic netropsin. J Mol Biol. 1972 Dec 30;72(3):593–607. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90178-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinert K. E., Stutter E., Schweiss H. Aspects of specific protein-DNA interaction; multi-mode binding of the oligopeptide antibiotic netropsin to (A.T)-rich DNA segments. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1375–1392. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schildkraut C. Dependence of the melting temperature of DNA on salt concentration. Biopolymers. 1965;3(2):195–208. doi: 10.1002/bip.360030207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiao D. D., Sturtevant J. M. Heats of thermally induced helix-coil transitions of DNA in aqueous solution. Biopolymers. 1973;12(8):1829–1836. doi: 10.1002/bip.1973.360120810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. C., Jain S. C., Sobell H. M. Visualization of drug-nucleic acid interactions at atomic resolution. I. Structure of an ethidium/dinucleoside monophosphate crystalline complex, ethidium:5-iodouridylyl (3'-5') adenosine. J Mol Biol. 1977 Aug 15;114(3):301–315. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90252-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Hippel P. H., Wong K. Y. Dynamic aspects of native DNA structure: kinetics of the formaldehyde reaction with calf thymus DNA. J Mol Biol. 1971 Nov 14;61(3):587–613. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90066-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring M. Variation of the supercoils in closed circular DNA by binding of antibiotics and drugs: evidence for molecular models involving intercalation. J Mol Biol. 1970 Dec 14;54(2):247–279. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90429-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Marky N., Manning G. S. On the application of polyelectrolyte limiting laws to the helix-coil transition of DNA. IV. Depedence of helix stability on the concentration of divalent metal ions. Biopolymers. 1976 Mar;15(3):457–468. doi: 10.1002/bip.1976.360150303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


