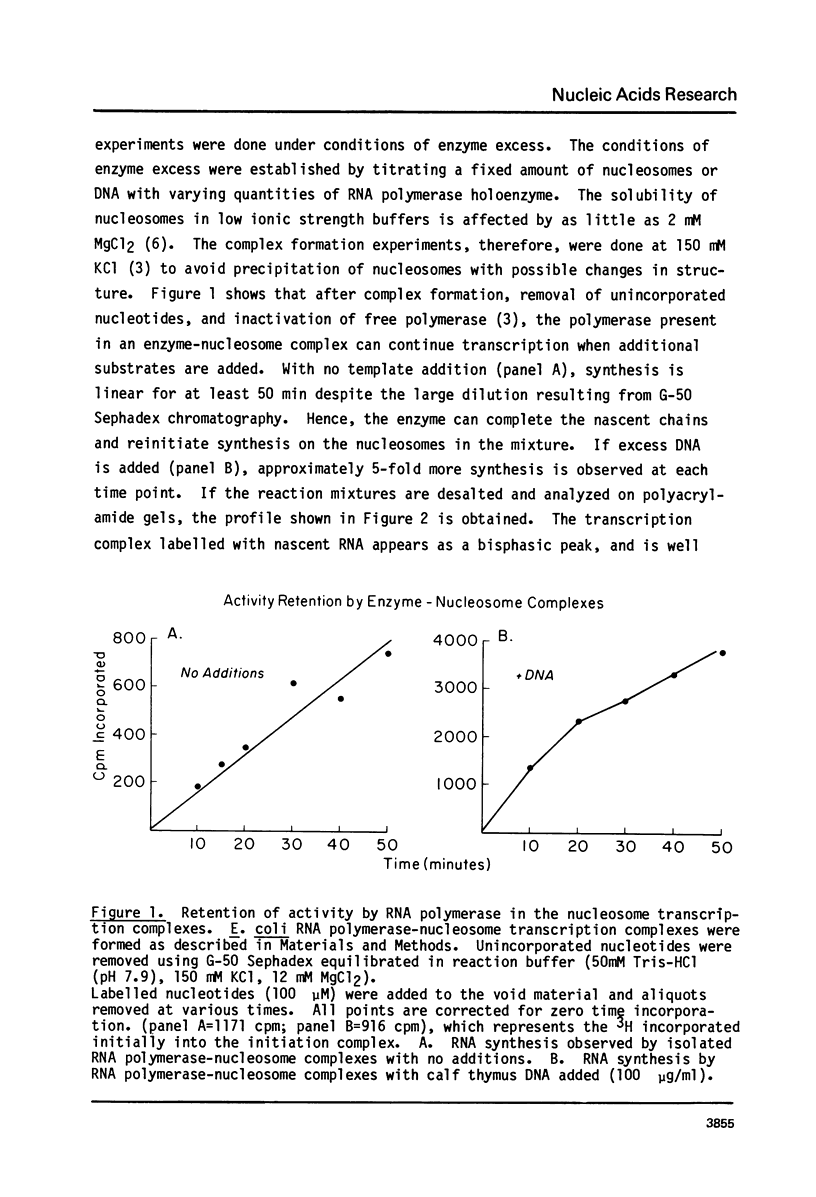
Abstract
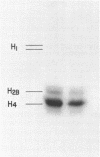
Nucleosomes prepared from human placental nuclei and Escherichia coli DNA-dependent RNA polymerase (nucleoside triphosphate: RNA nucleotidyl transferase EC.2.7.7.6) form stable initiation complexes. This property is utilized as a probe of nucleosome structure. RNA polymerase initiation has been studied on purified nucleosomes, nucleosome cores, and nucleosomal DNA. The affinity of E. coli RNA polymerase for both nucleosome cores and monomers was 5-6 fold less than found for nucleosomal DNA. No difference in apparent initiation Km was found between cores and mononucleosomes. This suggests that initiation does not preferentially occur on the DNA tails of nucleosomes. Once initiated and allowed to form nascent RNA, these complexes are very stable to ionic strength changes. Under conditions in which free enzyme is inactivated with rifampicin, the enzyme in the complex retains activity as demonstrated by its ability to transcribe and reinitiate on both nucleosomes and free DNA. These complexes can be well resolved from free nucleosomes on preparative polyacrylamide gels and both can be eluted from gels for analysis of proteins and DNA sequence complexity. Studies using (125I) labelled nucleosomes show that histones are retained in the initiation complex, and are not dissociated by the enzyme during initiation.
Full text
PDF



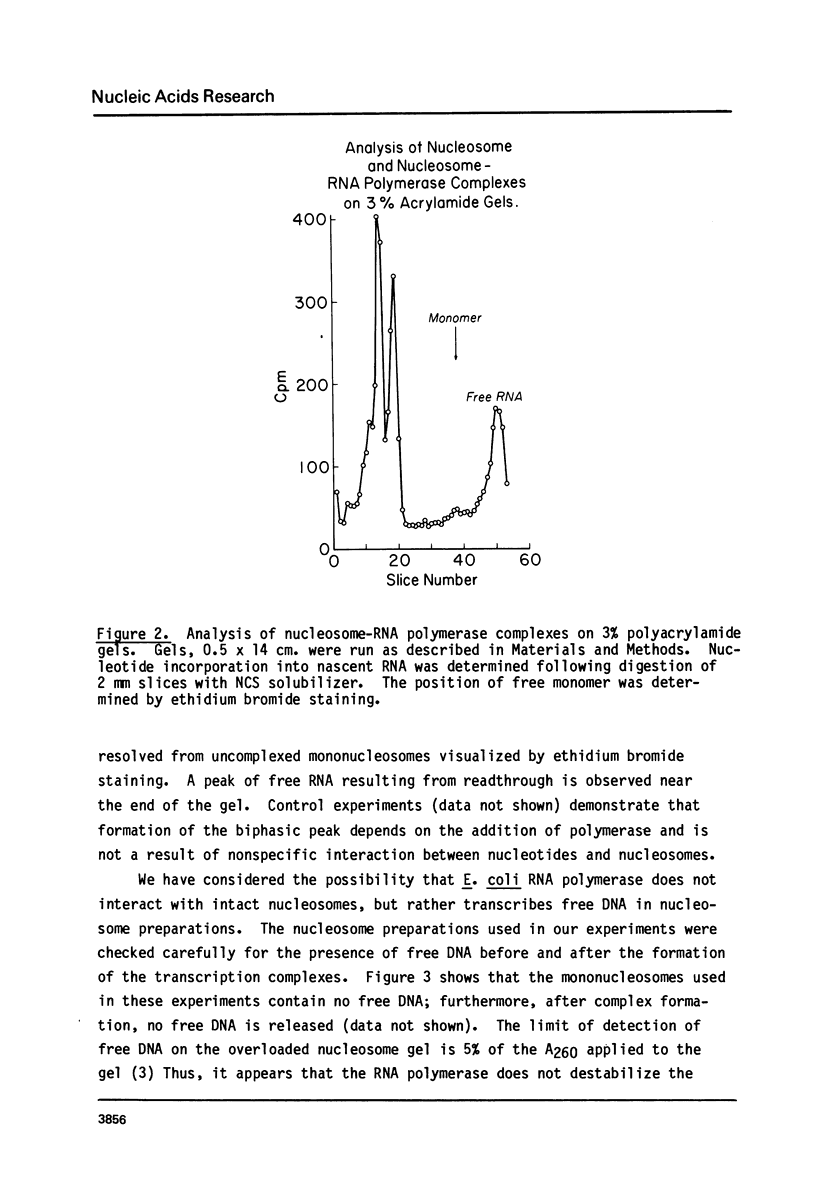
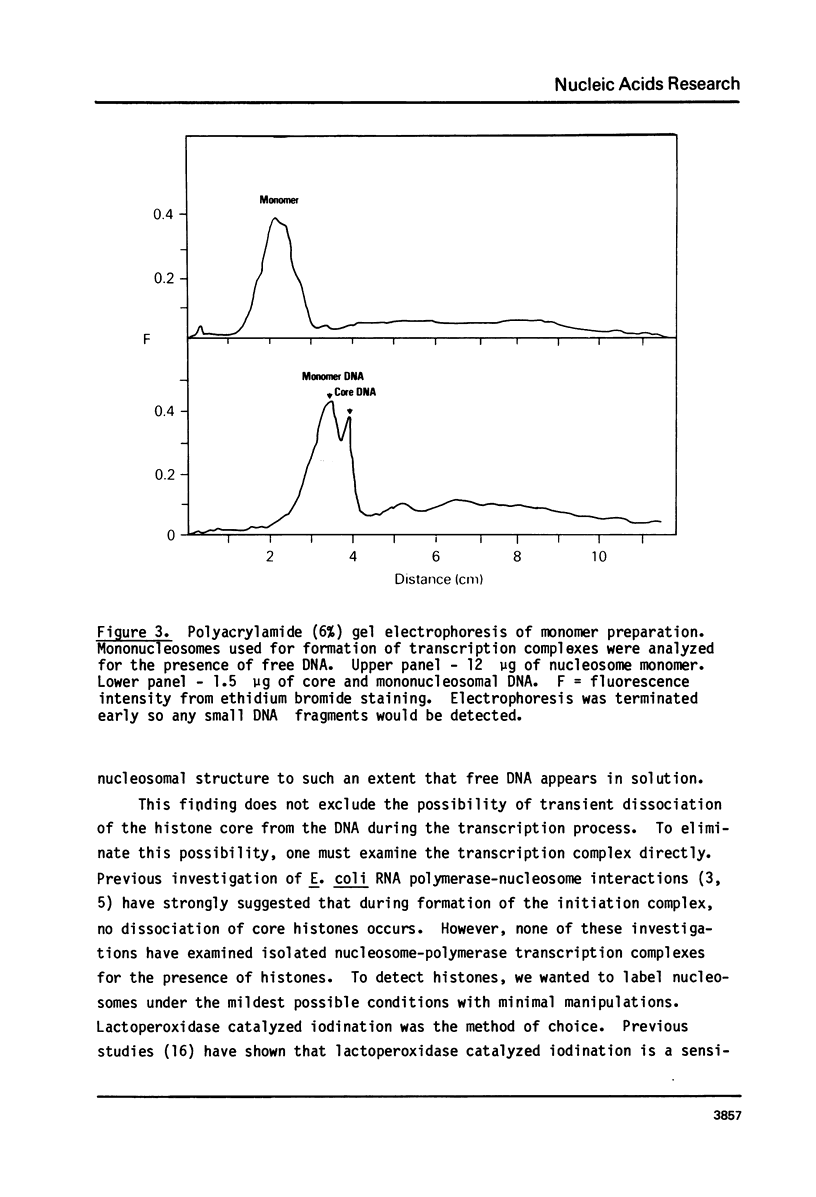

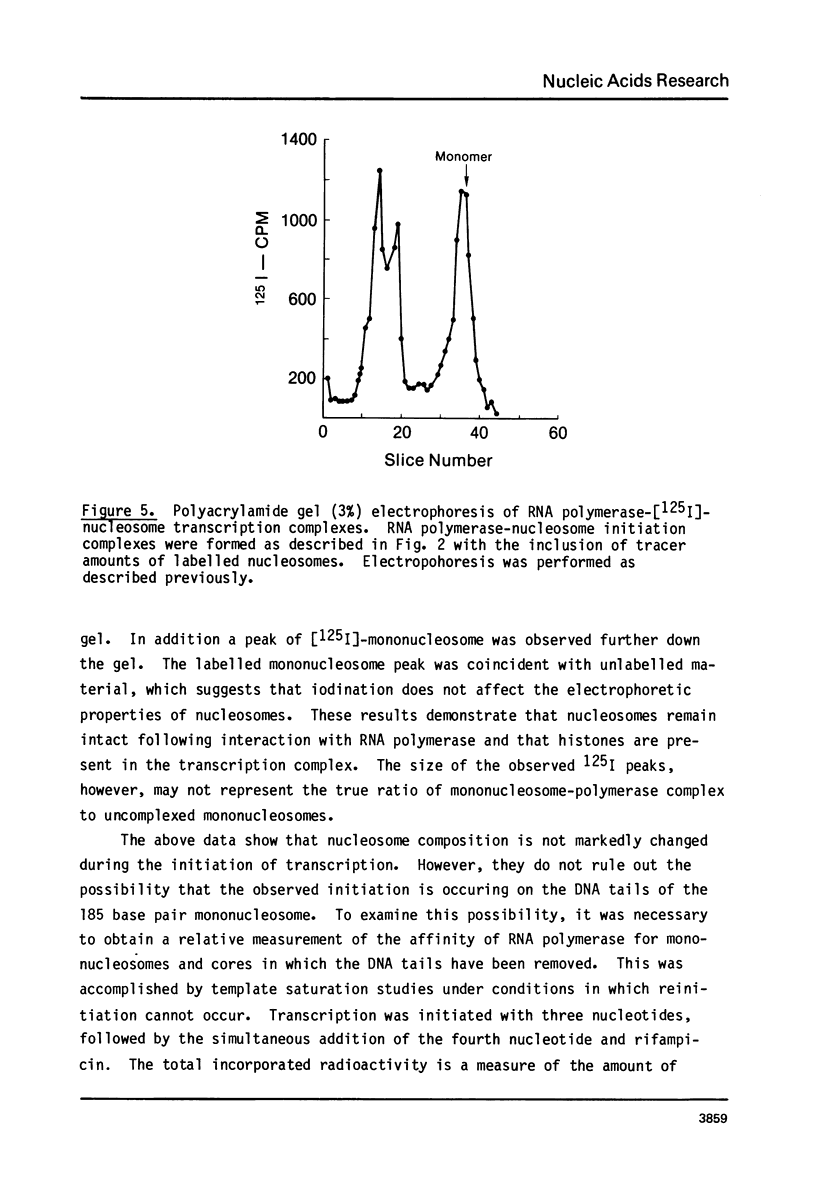





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balmain A., Birnie G. D. Nick translation of mammalian DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jan 26;561(1):155–166. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(79)90499-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bautz E. K., Dunn J. J. DNA-dependent RNA polymerase from phage T4 infected E. coli: an enzyme missing a factor required for transcription of T4 DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Jan 27;34(2):230–237. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90636-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustin M. Binding of E. coli RNA polymerase to chromatin subunits. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Mar;5(3):925–932. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.3.925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cedar H., Felsenfeld G. Transcription of chromatin in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1973 Jun 25;77(2):237–254. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90334-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlin M., Ring J. Characterization of T7-specific ribonucleic acid polymerase. 1. General properties of the enzymatic reaction and the template specificity of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1973 Mar 25;248(6):2235–2244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davie J. R., Candido E. P. Acetylated histone H4 is preferentially associated with template-active chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3574–3577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foe V. E., Wilkinson L. E., Laird C. D. Comparative organization of active transcription units in Oncopeltus fasciatus. Cell. 1976 Sep;9(1):131–146. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garel A., Axel R. Selective digestion of transcriptionally active ovalbumin genes from oviduct nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3966–3970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmour R. S., Paul J. Tissue-specific transcription of the globin gene in isolated chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3440–3442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G. R., Huang P. C. Radioiodination of chicken erythrocyte histones H4 and H5 in chromatin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):8057–8066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. A., Walseth T. F. The enzymatic preparation of [alpha-32P]ATP, [alpha-32P]GTP, [32P]cAMP, and [32P]cGMP, and their use in the assay of adenylate and guanylate cyclases and cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;10:135–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krohn K. A., Welch M. J. Studies of radioiodinated fibrinogen. II. Lactoperoxidase iodination of fibrinogen and model compounds. Int J Appl Radiat Isot. 1974 Jul;25(7):315–323. doi: 10.1016/0020-708x(74)90041-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kårsnäs P., Roos P. Two methods for electrophoretic elution of proteins from polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1977 Jan;77(1):168–175. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90302-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy E., Axel R. Analysis of DNA of isolated chromatin subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3978–3982. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy B., Dixon G. H. Partial purification of transcriptionally active nucleosomes from trout testis cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Nov;5(11):4155–4163. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.11.4155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M., Jacobs M. F., Houghton M. The nature of the interaction of nucleosomes with a eukaryotic RNA polymerase II. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Sep 25;7(2):377–399. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.2.377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahasrabuddhe C. G., Saunders G. F. Salt-induced structural changes in nucleosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Apr;4(4):853–866. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.4.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw P. A., Sahasrabuddhe C. G., Hodo H. G., 3rd, Saunders G. F. Transcription of nucleosomes from human chromatin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Aug;5(8):2999–3012. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.8.2999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. T. Protein kinase in HeLA nucleosomes: a reevaluation of the interactions of histomes with the ends of core particle DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Apr;5(4):1109–1119. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.4.1109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. T., Whitlock J. P. Mapping DNAase l-susceptible sites in nucleosomes labeled at the 5' ends. Cell. 1976 Oct;9(2):347–353. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90124-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai M. J., Towle T. C., Harris S. E., O'Malley B. W. Effect of estrogen on gene expression in the chick oviduct. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 10;251(7):1960–1968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai M. J., Tsai S. Y., Chang C. W., O'Malley B. W. Effect of estrogen on gene expression in the chick oviduct. In vitro transcription of the ovalbumin gene. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Dec 21;521(2):689–707. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(78)90309-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidali G., Boffa L. C., Bradbury E. M., Allfrey V. G. Butyrate suppression of histone deacetylation leads to accumulation of multiacetylated forms of histones H3 and H4 and increased DNase I sensitivity of the associated DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2239–2243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil P. A., Blatti S. P. Partial purification and properties of calf thymus deoxyribonucleic acid dependent RNA polymerase III. Biochemistry. 1975 Apr 22;14(8):1636–1642. doi: 10.1021/bi00679a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Groudine M. Chromosomal subunits in active genes have an altered conformation. Science. 1976 Sep 3;193(4256):848–856. doi: 10.1126/science.948749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisbrod S., Groudine M., Weintraub H. Interaction of HMG 14 and 17 with actively transcribed genes. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):289–301. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90410-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisbrod S., Weintraub H. Isolation of a subclass of nuclear proteins responsible for conferring a DNase I-sensitive structure on globin chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):630–634. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson P., Felsenfeld G. Transcription of histone-covered T7 DNA by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Biochemistry. 1978 Dec 26;17(26):5695–5705. doi: 10.1021/bi00619a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zasloff M., Felsenfeld G. Use of mercury-substituted ribonucleoside triphosphates can lead to artefacts in the analysis of in vitro chromatin transcrits. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Apr 11;75(3):598–603. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91514-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]