Abstract
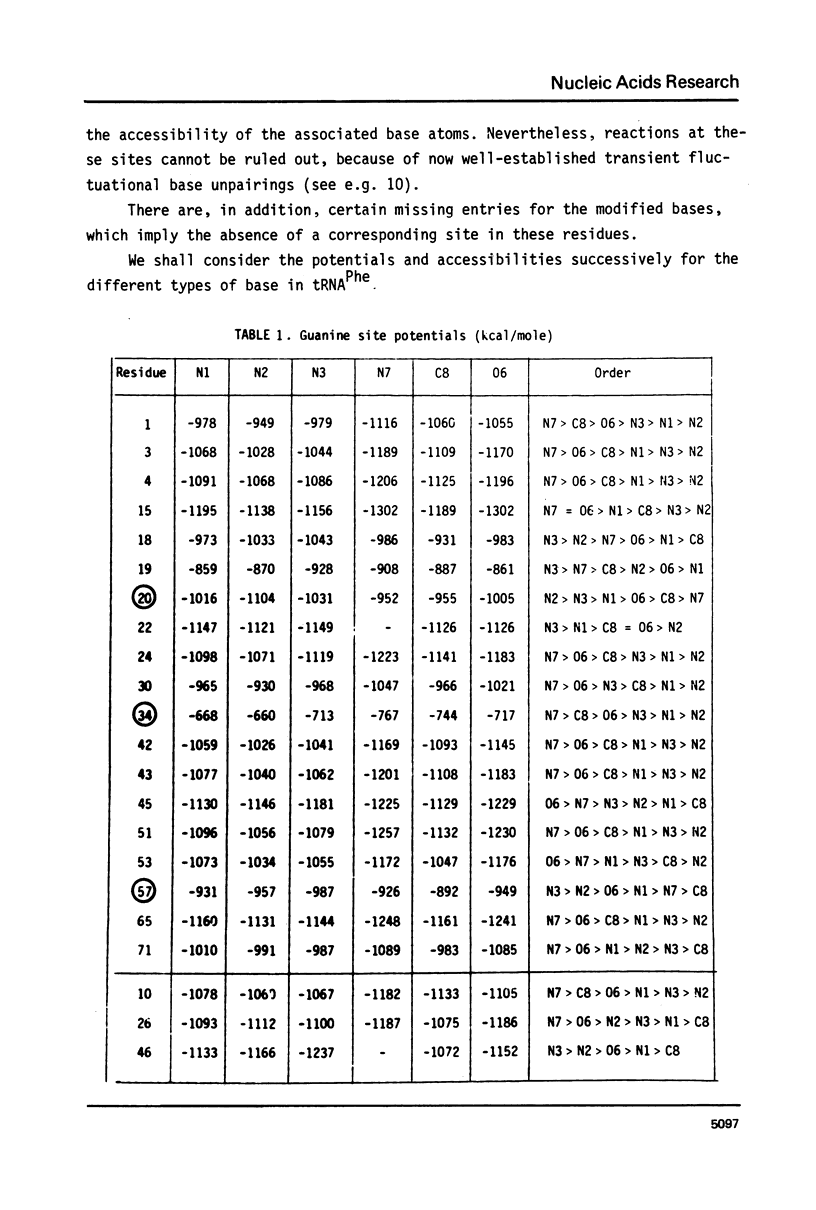
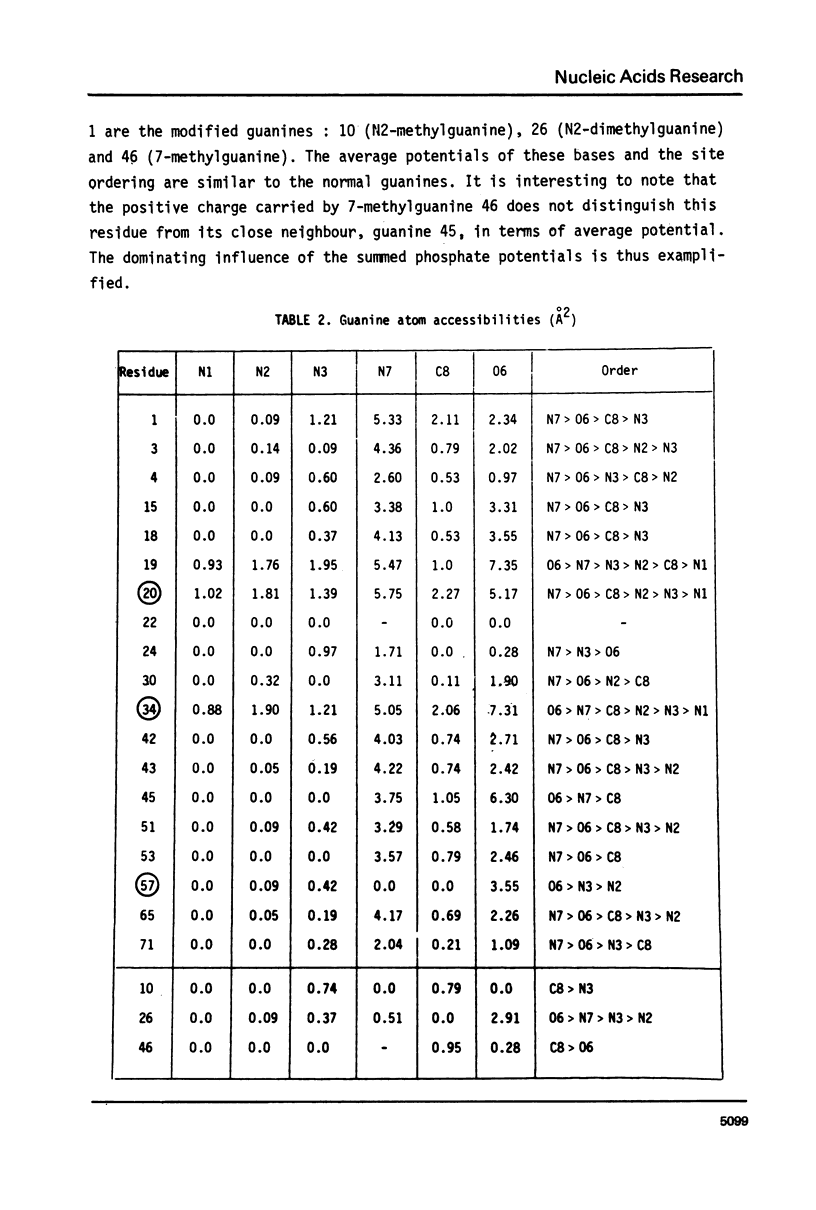
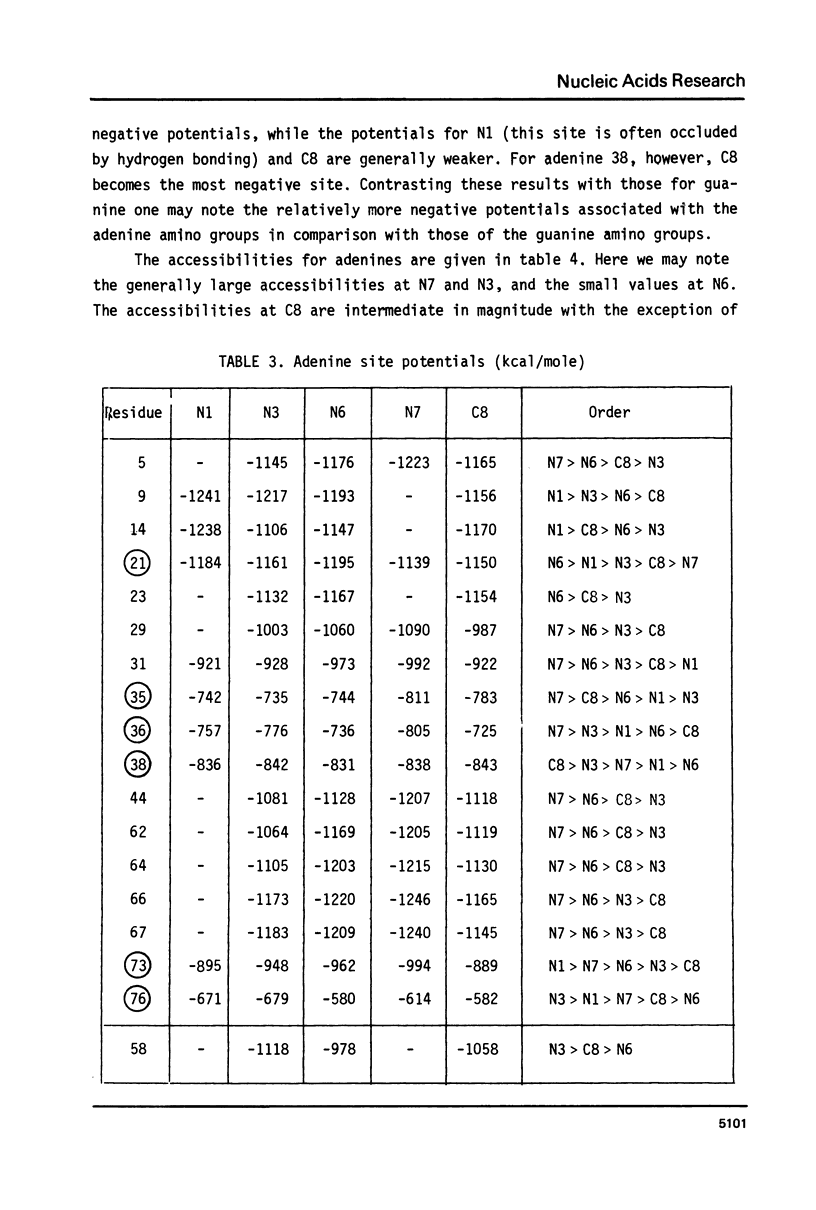
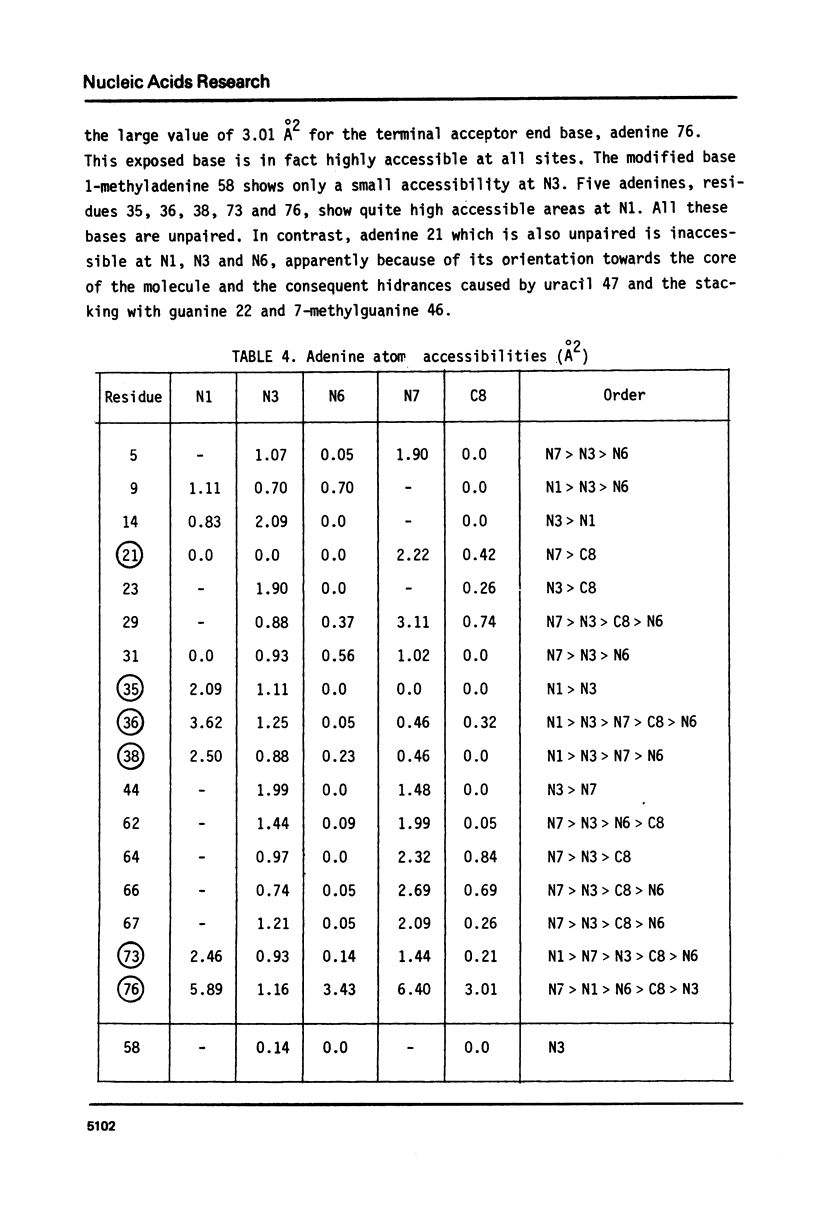
The sites of the 76 nucleic acid bases of tRNAPhe potentially reactive towards electrophiles are studied by calculations on the associated molecular electrostatic potentials and the static steric accessibilities. Each of these sites is treated in its environment within the macromolecule. The influence of various schemes of screening by countercations of the backbone phosphates on the electrostatic potentials is investigated. The possible significance of the potentials and accessibilities in connection with observed chemical reactivities is discussed.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alden C. J., Kim S. H. Solvent-accessible surfaces of nucleic acids. J Mol Biol. 1979 Aug 15;132(3):411–434. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90268-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura S., Grunberger D., Carvajal G., Weinstein I. B. Modifications of ribonucleic acid by chemical carcinogens. Modification of Escherichia coli formylmethionine transfer ribonucleic acid with N-acetoxy-2-acetylaminofluorene. Biochemistry. 1972 Sep 12;11(19):3629–3635. doi: 10.1021/bi00769a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavery R., Pullman A., Pullman B. The electrostatic molecular potential of yeast tRNAPhe. (I). The potential due to the phosphate backbone. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Mar 11;8(5):1061–1079. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.5.1061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litt M., Greenspan C. M. Kethoxal inactivation of three transfer ribonucleic acids chargeable by yeast phenylalanyl transfer ribonucleic acid synthetase. Biochemistry. 1972 Apr 11;11(8):1437–1442. doi: 10.1021/bi00758a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litt M. Structural studies on transfer ribonucleic acid. I. Labeling of exposed guanine sites in yeast phenylalanine transfer ribonucleic acid with kethoxal. Biochemistry. 1969 Aug;8(8):3249–3253. doi: 10.1021/bi00836a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulkrabek P., Grunberger D., Weinstein I. B. Effects of the ionic environment on modification of yeast tyrosine transfer ribonucleic acid with N-acetoxy-2-acetylaminofluorene. Biochemistry. 1974 May 21;13(11):2414–2419. doi: 10.1021/bi00708a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pullman B., Perahia D., Cauchy D. The molecular electrostatic potential of the B-DNA helix. VI. The regions of the base pairs in poly (dG.dC) and poly (dA.dT). Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 24;6(12):3821–3829. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.12.3821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes D. Accessible and inaccessible bases in yeast phenylalanine transfer RNA as studied by chemical modification. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 25;94(3):449–460. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90214-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprinzl M., Grueter F., Spelzhaus A., Gauss D. H. Compilation of tRNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):r1–r22. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman J. L., Holbrook S. R., Warrant R. W., Church G. M., Kim S. H. Crystal structure of yeast phenylalanine transfer RNA. I. Crystallographic refinement. J Mol Biol. 1978 Aug 25;123(4):607–630. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90209-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiyagarajan P., Ponnuswamy P. K. Solvent accessibility study on tRNAPhe. Biopolymers. 1979 Sep;18(9):2233–2247. doi: 10.1002/bip.1979.360180911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


