Abstract
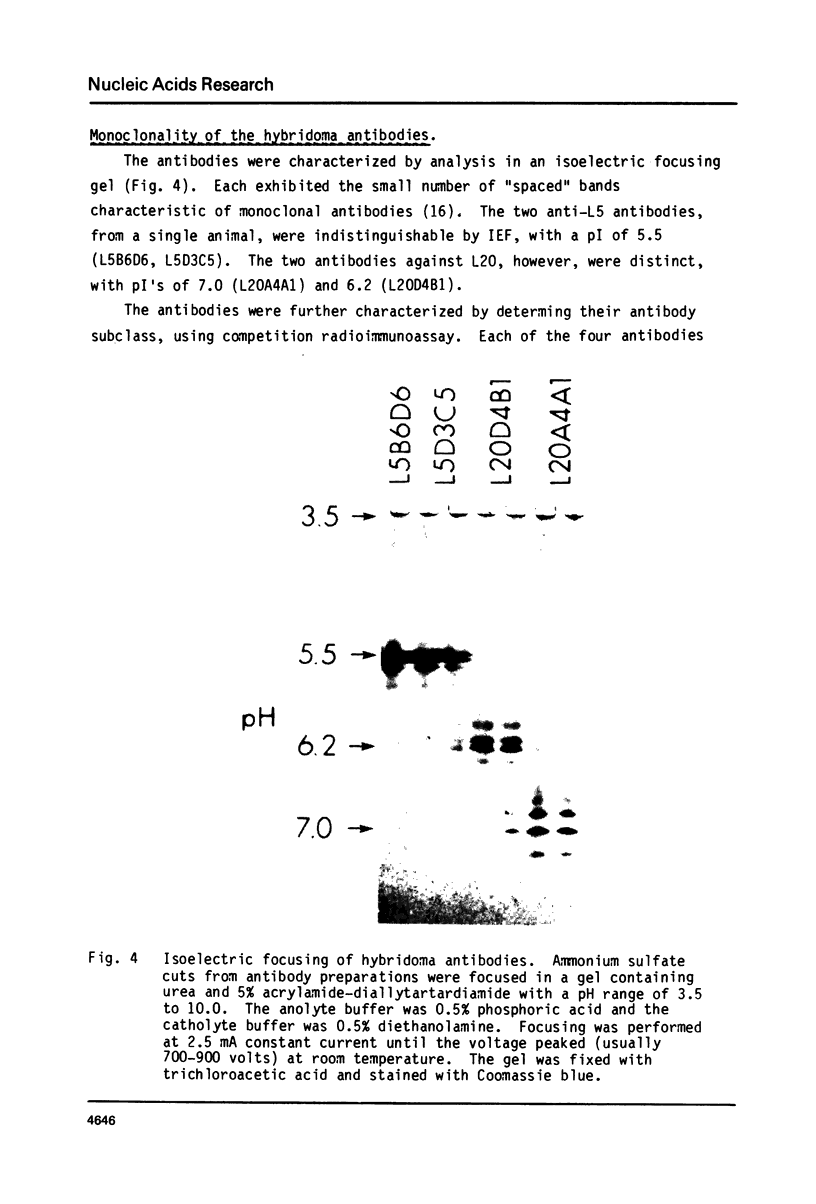
Hybridoma cell lines that produce monoclonal antibodies directed against 50S Ribosomal proteins have been isolated. Spleen cells (from BALB/c mice immunized with 50S ribosomal subunits extracted from Escherichia coli) were fused to mouse myeloma cell line SP2/O-Ag 14. The initial screening for antibody producing hybridomas was carried out by a double antibody sandwich method; hybridomas were subsequently cloned in soft agar. Antibodies were characterized by their specific binding to individual 50S ribsomal proteins separated on phosphocellulose columns and in two-dimensional polyacrylamide gels. The assignments were confirmed with purified single ribosomal proteins. Of four clones analyzed thus far, two are identical with specificity for r-protein L5. The other clones produce two different antibodies directed against r-protein L20. Each monoclonal antibody formed ribosome dimers visualizable in the electron microscope. Dimers could be reacted with a different second antibody to form chains containing 8 or more ribosomes, which may be useful for structural studies.
Full text
PDF



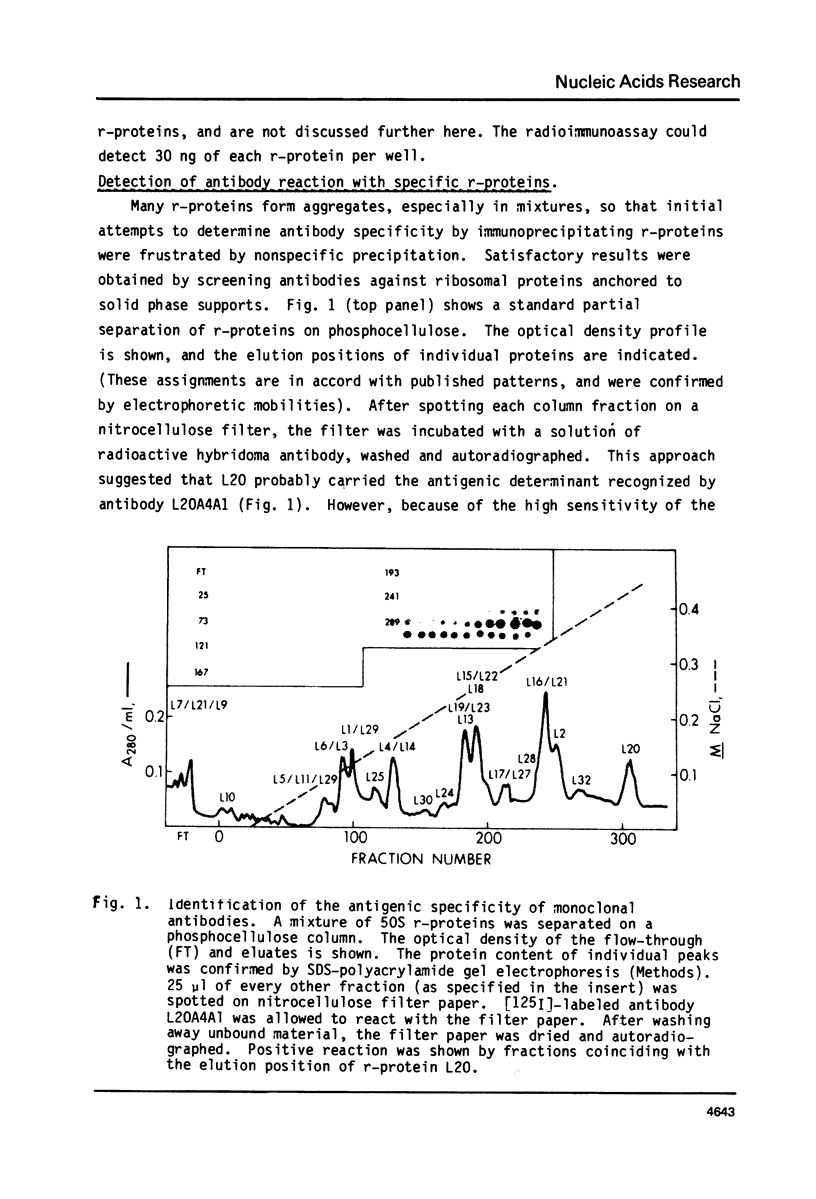





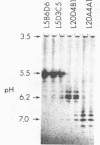
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bowen B., Steinberg J., Laemmli U. K., Weintraub H. The detection of DNA-binding proteins by protein blotting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):1–20. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfre G., Howe S. C., Milstein C., Butcher G. W., Howard J. C. Antibodies to major histocompatibility antigens produced by hybrid cell lines. Nature. 1977 Apr 7;266(5602):550–552. doi: 10.1038/266550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaltschmidt E., Kahan L., Nomura M. In vitro synthesis of ribosomal proteins directed by Escherichia coli DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):446–450. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakopoulos A., Subramanian A. R. Positions of individual ribosomal proteins after two-dimensional electrophoresis by a sensitive procedure. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jan 20;474(2):308–311. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(77)90204-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTLEFIELD J. W. SELECTION OF HYBRIDS FROM MATINGS OF FIBROBLASTS IN VITRO AND THEIR PRESUMED RECOMBINANTS. Science. 1964 Aug 14;145(3633):709–710. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3633.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lelong J. C., Gros D., Gros F., Bollen A., Maschler R., Stöffler G. Function of individual 30S subunit proteins of Escherichia coli. Effect of specific immunoglobulin fragments (Fab) on activities of ribosomal decoding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):248–252. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolotti R. A., Briles D. E., Schroer J. A., Davie J. M. Isoelectric focusing of immunoglobulins: improved methodology. J Immunol Methods. 1980;33(2):101–115. doi: 10.1016/s0022-1759(80)80001-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roehrig J. T., Corser J. A., Schlesinger M. J. Isolation and characterization of hybrid cell lines producing monoclonal antibodies directed against the structural proteins of Sindbis virus. Virology. 1980 Feb;101(1):41–49. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90481-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack J., Der-Balian G. P., Nahm M., Davie J. M. Subclass restriction of murine antibodies. II. The IgG plaque-forming cell response to thymus-independent type 1 and type 2 antigens in normal mice and mice expressing an X-linked immunodeficiency. J Exp Med. 1980 Apr 1;151(4):853–862. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.4.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strycharz W. A., Nomura M., Lake J. A. Ribosomal proteins L7/L12 localized at a single region of the large subunit by immune electron microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 5;126(2):123–140. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90355-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stöffler G., Wittmann H. G. Sequence differences of Escherichia coli 30S ribosomal proteins as determined by immunochemical methods. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2283–2287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun T. T., Traut R. R., Kahan L. Protein-protein proximity in the association of ribosomal subunits of Escherichia coli: crosslinking of 30 S protein S16 to 50 S proteins by glutaraldehyde or formaldehyde. J Mol Biol. 1974 Aug 15;87(3):509–522. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90101-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tischendorf G. W., Zeichhardt H., Stöffler G. Determination of the location of proteins L14, L17, L18, L19, L22, L23 on the surface of the 5oS ribosomal subunit of Escherichia coli by immune electron microscopy. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;134(3):187–208. doi: 10.1007/BF00267715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittmann H. G., Stöfflet G., Hindennach I., Kurland C. G., Birge E. A., Randall-Hazelbauer L., Nomura M., Kaltschmidt E., Mizushima S., Traut R. R. Correlation of 30S ribosomal proteins of Escherichia coli isolated in different laboratories. Mol Gen Genet. 1971;111(4):327–333. doi: 10.1007/BF00569784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]