Abstract
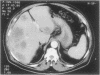
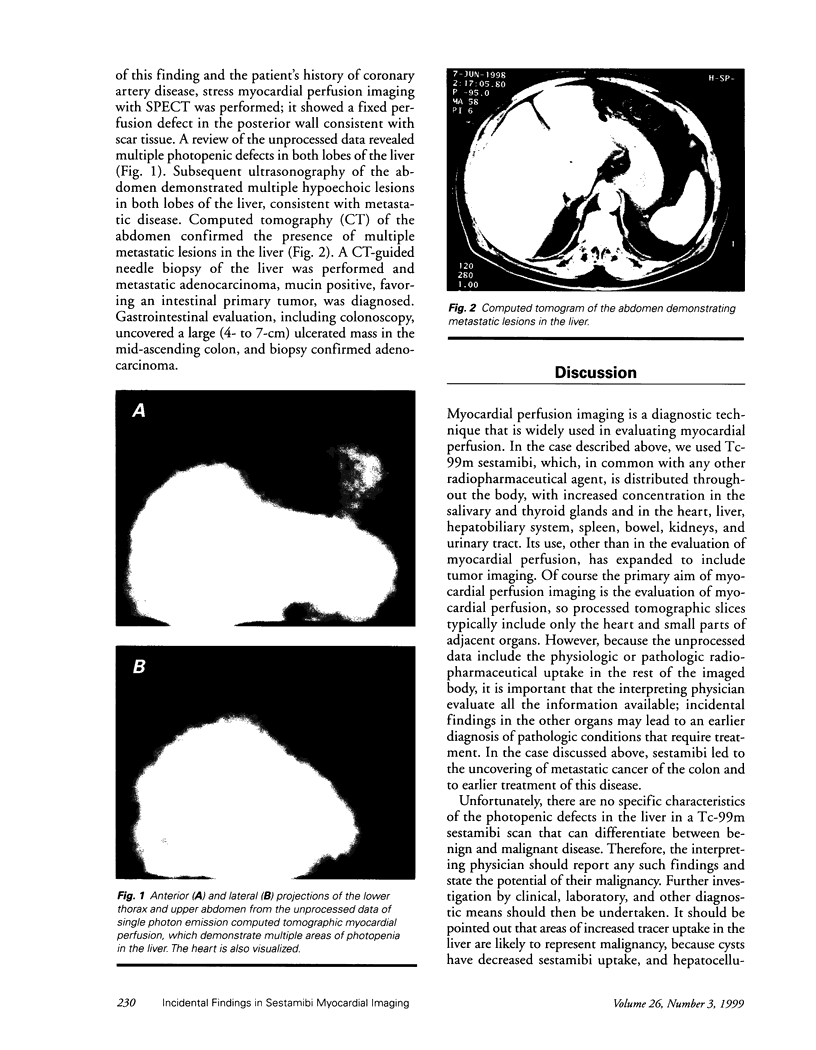
Technetium 99m sestamibi is widely used in the evaluation of myocardial perfusion imaging. Although the aim of such imaging is cardiac evaluation, numerous other organs are included in the imaging field. Failure to identify incidental abnormal findings in these organs delays diagnosis and treatment. In common with other radiopharmaceutical agents, technetium 99m sestamibi is distributed throughout the body and accumulates in multiple tissues. When interpreting studies that involve this radiotracer, the physician must be aware of its physiologic distribution, in order to recognize abnormal uptake. We present an illustrative case in which areas of decreased tracer activity were noted incidentally during the evaluation of unprocessed single photon emission computed tomography data. These findings were due to metastasis of colon cancer to the liver.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alonso O., Lago G., Mut F., Hermida J. C., Nunez M., De Palma G., Touya E. Thyroid imaging with Tc-99m MIBI in patients with solitary cold single nodules on pertechnetate imaging. Clin Nucl Med. 1996 May;21(5):363–367. doi: 10.1097/00003072-199605000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baillet G., Albuquerque L., Chen Q., Poisson M., Delattre J. Y. Evaluation of single-photon emission tomography imaging of supratentorial brain gliomas with technetium-99m sestamibi. Eur J Nucl Med. 1994 Oct;21(10):1061–1066. doi: 10.1007/BF00181060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman D. S., Hachamovitch R., Kiat H., Cohen I., Cabico J. A., Wang F. P., Friedman J. D., Germano G., Van Train K., Diamond G. A. Incremental value of prognostic testing in patients with known or suspected ischemic heart disease: a basis for optimal utilization of exercise technetium-99m sestamibi myocardial perfusion single-photon emission computed tomography. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1995 Sep;26(3):639–647. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(95)00218-S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bom H. S., Kim Y. C., Song H. C., Min J. J., Kim J. Y., Park K. O. Technetium-99m-MIBI uptake in small cell lung cancer. J Nucl Med. 1998 Jan;39(1):91–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. A., Altland E., Rowen M. Prognostic value of normal technetium-99m-sestamibi cardiac imaging. J Nucl Med. 1994 Apr;35(4):554–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatziioannou S. N., Moore W. H., Ford P. V., Fisher R. E., Lee V. V., Alfaro-Franco C., Dhekne R. D. Prognostic value of myocardial perfusion imaging in patients with high exercise tolerance. Circulation. 1999 Feb 23;99(7):867–872. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.99.7.867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima K., Kono M., Ishii K., Sakai E., Hirota S., Yuri H. Technetium-99m methoxyisobutylisonitrile single-photon emission tomography in hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Nucl Med. 1997 Nov;24(11):1426–1428. doi: 10.1007/s002590050171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindié E., Mellière D., Perlemuter L., Jeanguillaume C., Galle P. Primary hyperparathyroidism: higher success rate of first surgery after preoperative Tc-99m sestamibi-I-123 subtraction scanning. Radiology. 1997 Jul;204(1):221–228. doi: 10.1148/radiology.204.1.9205251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz G. A., Duan H. Y., Blais M., Mattar A. G., Gravelle D. R. An atlas of renography with Tc-99m sestamibi: comparison with Tc-99m DTPA. Clin Nucl Med. 1995 Sep;20(9):821–829. doi: 10.1097/00003072-199509000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iskandrian A. S., Heo J., Kong B., Lyons E., Marsch S. Use of technetium-99m isonitrile (RP-30A) in assessing left ventricular perfusion and function at rest and during exercise in coronary artery disease, and comparison with coronary arteriography and exercise thallium-201 SPECT imaging. Am J Cardiol. 1989 Aug 1;64(5):270–275. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(89)90518-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khalkhali I., Cutrone J., Mena I., Diggles L., Venegas R., Vargas H., Jackson B., Klein S. Technetium-99m-sestamibi scintimammography of breast lesions: clinical and pathological follow-up. J Nucl Med. 1995 Oct;36(10):1784–1789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamont A. E., Joyce J. M., Grossman S. J. Acute cholecystitis detected on a Tc-99m sestamibi myocardial imaging. Clin Nucl Med. 1996 Nov;21(11):879–879. doi: 10.1097/00003072-199611000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddahi J., Kiat H., Van Train K. F., Prigent F., Friedman J., Garcia E. V., Alazraki N., DePuey E. G., Nichols K., Berman D. S. Myocardial perfusion imaging with technetium-99m sestamibi SPECT in the evaluation of coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol. 1990 Oct 16;66(13):55E–62E. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(90)90613-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui R., Komori T., Narabayashi I., Namba R., Nakata Y., Tabuchi K., Adachi I., Tatu Y., Shimizu T., Sueyoshi K. Tc-99m sestamibi uptake by malignant lymphoma and slow washout. Clin Nucl Med. 1995 Apr;20(4):352–356. doi: 10.1097/00003072-199504000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishiyama Y., Kawasaki Y., Yamamoto Y., Fukunaga K., Satoh K., Takashima H., Ohkawa M., Tanabe M. Technetium-99m-MIBI and thallium-201 scintigraphy of primary lung cancer. J Nucl Med. 1997 Sep;38(9):1358–1361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishiyama Y., Yamamoto Y., Kawasaki Y., Satoh K., Takashima H., Ohkawa M., Tanabe M. Accumulation of Tc-99m MIBI in breast lymphoma: comparison with Ga-67 citrate. Ann Nucl Med. 1996 Nov;10(4):429–432. doi: 10.1007/BF03164805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onsel C., Sönmezoglu K., Camsari G., Atay S., Cetin S., Erdil Y. T., Uslu I., Uzun A., Kanmaz B., Sayman H. B. Technetium-99m-MIBI scintigraphy in pulmonary tuberculosis. J Nucl Med. 1996 Feb;37(2):233–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piwnica-Worms D. P., Kronauge J. F., LeFurgey A., Backus M., Hockett D., Ingram P., Lieberman M., Holman B. L., Jones A. G., Davison A. Mitochondrial localization and characterization of 99Tc-SESTAMIBI in heart cells by electron probe X-ray microanalysis and 99Tc-NMR spectroscopy. Magn Reson Imaging. 1994;12(4):641–652. doi: 10.1016/0730-725x(94)92459-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundram F. X., Mack P. Evaluation of thyroid nodules for malignancy using 99Tcm-sestamibi. Nucl Med Commun. 1995 Aug;16(8):687–693. doi: 10.1097/00006231-199508000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderlund V., Jonsson C., Bauer H. C., Brosjö O., Jacobsson H. Comparison of technetium-99m-MIBI and technetium-99m-tetrofosmin uptake by musculoskeletal sarcomas. J Nucl Med. 1997 May;38(5):682–686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taillefer R., Robidoux A., Turpin S., Lambert R., Cantin J., Léveillé J. Metastatic axillary lymph node technetium-99m-MIBI imaging in primary breast cancer. J Nucl Med. 1998 Mar;39(3):459–464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman A. D. The role of (99m)Tc methoxyisobutylisonitrile in imaging breast cancer. Semin Nucl Med. 1997 Jan;27(1):40–54. doi: 10.1016/s0001-2998(97)80035-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]