Abstract
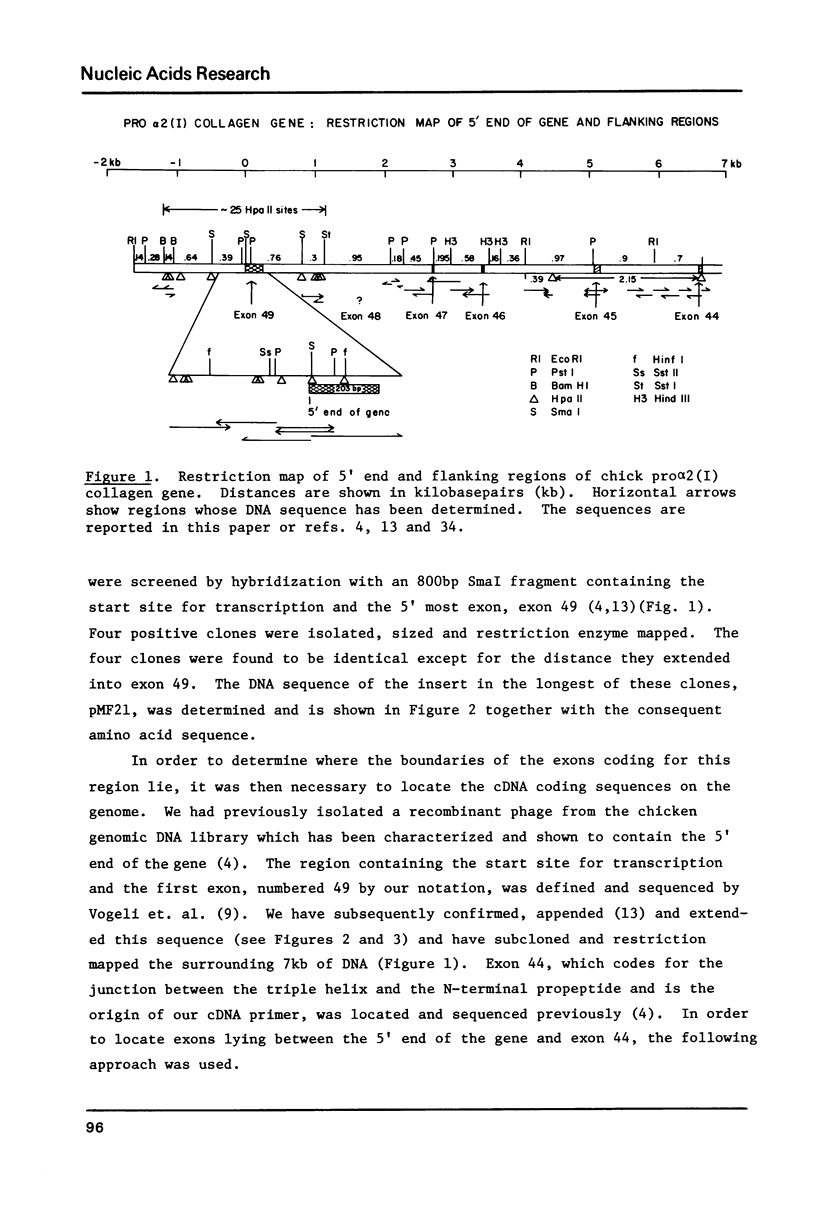
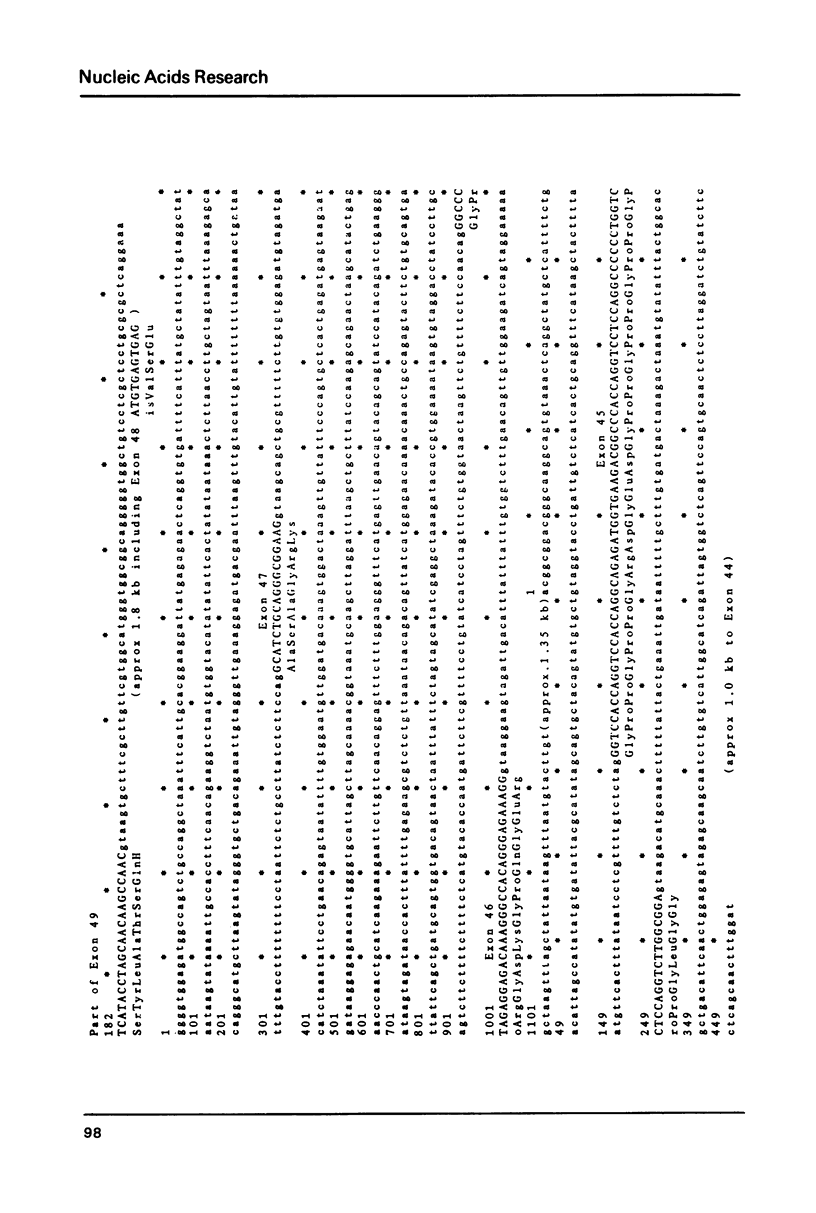
We report the DNA sequence of a cDNA clone complementary to the 5' end of the chick pro alpha 2(I) mRNA. The sequence enables us to deduce the amino acid sequence of this region, which has been refractory to conventional protein sequencing techniques. Its importance lies in the role of the prepropeptide in secretion, triple helix formation of the mature protein and initiation of fibrillogenesis. We have also located four of the five exons which code for this region on the genome. One exon is only 11bp in size and appears to code exclusively for the signal propeptidase cleavage site. This is an extreme example of an exon defining a functional unit.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey J. M., Davidson N. Methylmercury as a reversible denaturing agent for agarose gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker U., Helle O., Timpl R. Characterization of the amino-terminal segment in procollagen palpha2 chain from dermatosparactic sheep. FEBS Lett. 1977 Feb 1;73(2):197–200. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80979-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boedtker H., Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H. Isolation and translation of calvaria procollagen messenger ribonucleic acids. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 2;15(22):4765–4770. doi: 10.1021/bi00667a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyre D. R. Collagen: molecular diversity in the body's protein scaffold. Science. 1980 Mar 21;207(4437):1315–1322. doi: 10.1126/science.7355290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favaloro J., Treisman R., Kamen R. Transcription maps of polyoma virus-specific RNA: analysis by two-dimensional nuclease S1 gel mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):718–749. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischmajer R., Timpl R., Tuderman L., Raisher L., Wiestner M., Perlish J. S., Graves P. N. Ultrastructural identification of extension aminopropeptides of type I and III collagens in human skin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7360–7364. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller F., Boedtker H. Sequence determination and analysis of the 3' region of chicken pro-alpha 1(I) and pro-alpha 2(I) collagen messenger ribonucleic acids including the carboxy-terminal propeptide sequences. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 17;20(4):996–1006. doi: 10.1021/bi00507a054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves P. N., Olsen B. R., Fietzek P. P., Prockop D. J., Monson J. M. Comparison of the NH2-Terminal sequences of chick Type I preprocollagen chains synthesized in an nRNA-dependent reticulocyte lysate. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Aug;118(2):363–369. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06411.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D., Meselson M. Plasmid screening at high colony density. Gene. 1980 Jun;10(1):63–67. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörlein D., Fietzek P. P., Wachter E., Lapière C. M., Kühn K. Amino acid sequence of the aminoterminal segment of dermatosparactic calf-skin procollagen type I. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Aug 15;99(1):31–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13227.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreil G. Transfer of proteins across membranes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:317–348. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.001533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Grez M., Hauser H., Lindenmaier W., Schütz G. 5'-Terminal sequences of eucaryotic mRNA can be cloned with high efficiency. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 25;9(10):2251–2266. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.10.2251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Frischauf A. M., Hanahan D., Wozney J., Fuller F., Boedtker H. Construction and characterization of pro alpha 1 collagen complementary deoxyribonucleic acid clones. Biochemistry. 1979 Jul 10;18(14):3146–3152. doi: 10.2196/47873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Frischauf A. M., Hanahan D., Wozney J., Fuller F., Crkvenjakov R., Boedtker H., Doty P. Construction and characterization of a 2.5-kilobase procollagen clone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5417–5421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlino G. T., Vogeli G., Yamamoto T., de Crombrugghe B., Pastan I. Accurate in vitro transcriptional initiation of the chick alpha 2 (Type I) collagen gene. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11251–11258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monson J. M., McCarthy B. J. Identification of a Balb/c mouse pro alpha 1(I) procollagen gene: evidence for insertions or deletions in gene coding sequences. DNA. 1981;1(1):59–69. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1981.1.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkubo H., Vogeli G., Mudryj M., Avvedimento V. E., Sullivan M., Pastan I., de Crombrugghe B. Isolation and characterization of overlapping genomic clones covering the chicken alpha 2 (type I) collagen gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7059–7063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Davidson J. M., Gagnon J., Rowe D. W., Bornstein P. NH2-terminal sequence of the chick proalpha1(I) chain synthesized in the reticulocyte lysate system. Evidence for a transient hydrophobic leader sequence. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 10;254(5):1433–1436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. W., Moen R. C., Davidson J. M., Byers P. H., Bornstein P., Palmiter R. D. Correlation of procollagen mRNA levels in normal and transformed chick embryo fibroblasts with different rates of procollagen synthesis. Biochemistry. 1978 May 2;17(9):1581–1590. doi: 10.1021/bi00602a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogeli G., Ohkubo H., Avvedimento V. E., Sullivan M., Yamada Y., Mudryj M., Pastan I., de Crombrugghe B. A repetitive structure in the chick alpha 2-collagen gene. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 2):777–783. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogeli G., Ohkubo H., Sobel M. E., Yamada Y., Pastan I., de Crombrugghe B. Structure of the promoter for chicken alpha 2 type I collagen gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5334–5338. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wozney J., Hanahan D., Morimoto R., Boedtker H., Doty P. Fine structural analysis of the chicken pro alpha 2 collagen gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):712–716. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wozney J., Hanahan D., Tate V., Boedtker H., Doty P. Structure of the pro alpha 2 (I) collagen gene. Nature. 1981 Nov 12;294(5837):129–135. doi: 10.1038/294129a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada Y., Avvedimento V. E., Mudryj M., Ohkubo H., Vogeli G., Irani M., Pastan I., de Crombrugghe B. The collagen gene: evidence for its evolutinary assembly by amplification of a DNA segment containing an exon of 54 bp. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):887–892. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90565-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Hagenbüchle O., Schibler U. A single mouse alpha-amylase gene specifies two different tissue-specific mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):451–458. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90140-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]