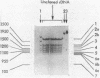
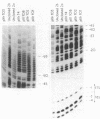
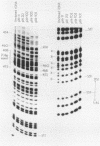
Abstract
Ribosomal DNA (rDNA) from Xenopus laevis contains several heterogeneities in all three transcribed spacers, as revealed by analysis of cloned and uncloned amplified rDNA from oocytes and cloned chromosomal rDNA from erythrocytes. Heterogeneities include single base changes and length variants of one to several nucleotides. Sites of variation are widely but non-uniformly distributed, some occurring only a short distance outside the boundaries of the rRNA coding regions. No two transcription units that we have yet examined are identical throughout their transcribed spacer regions.
Full text
PDF

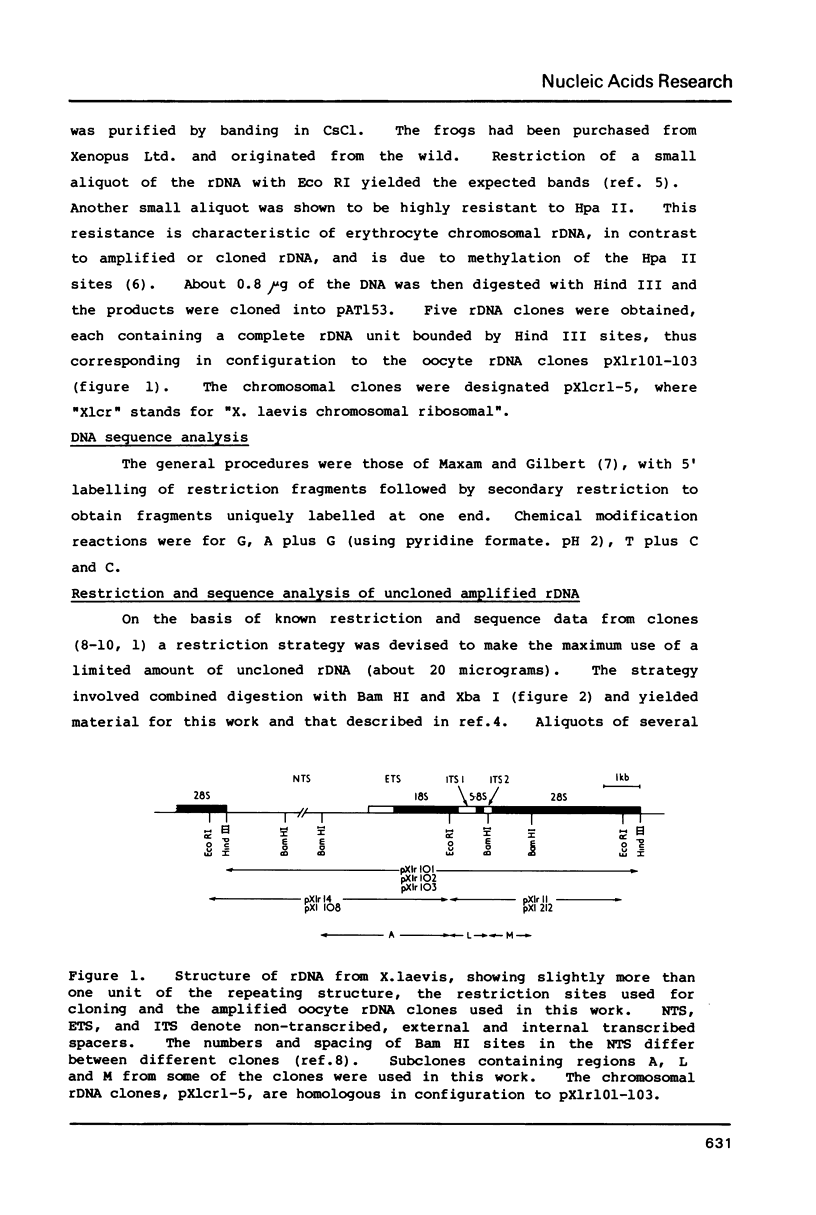
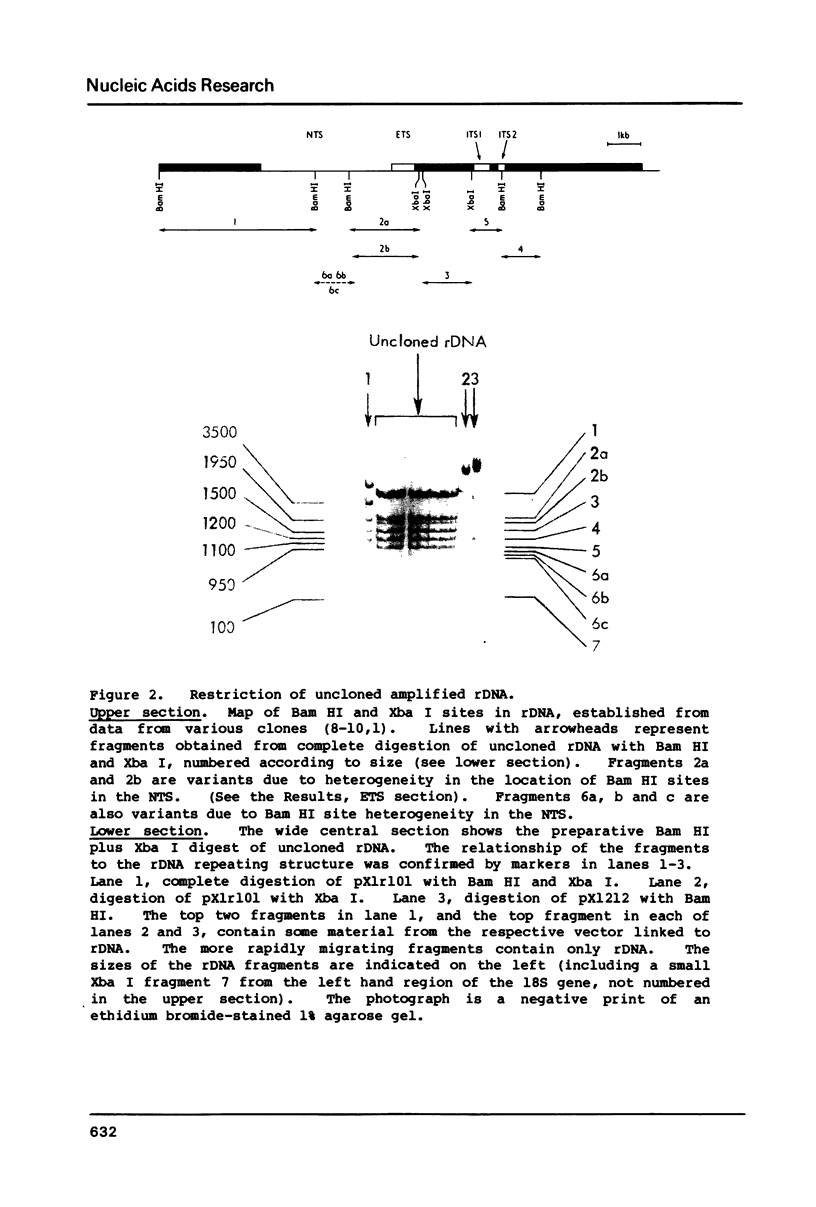




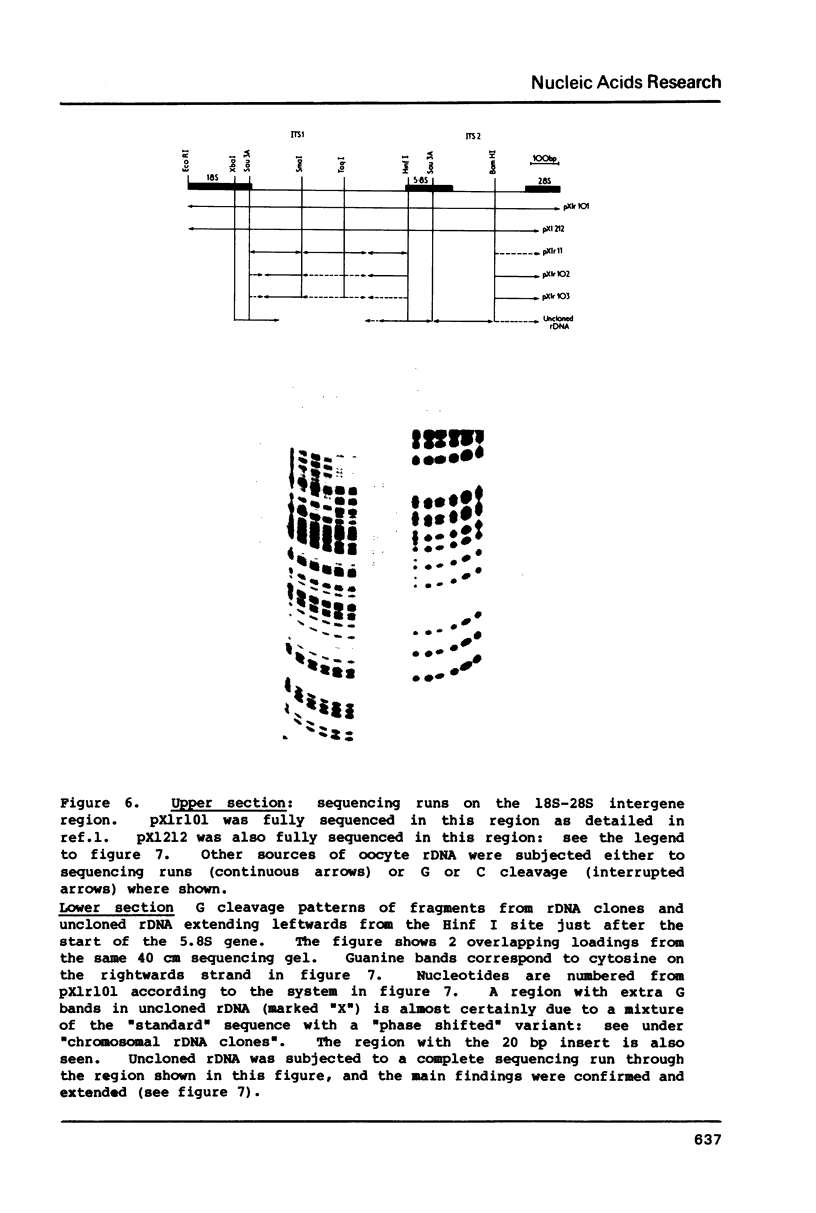




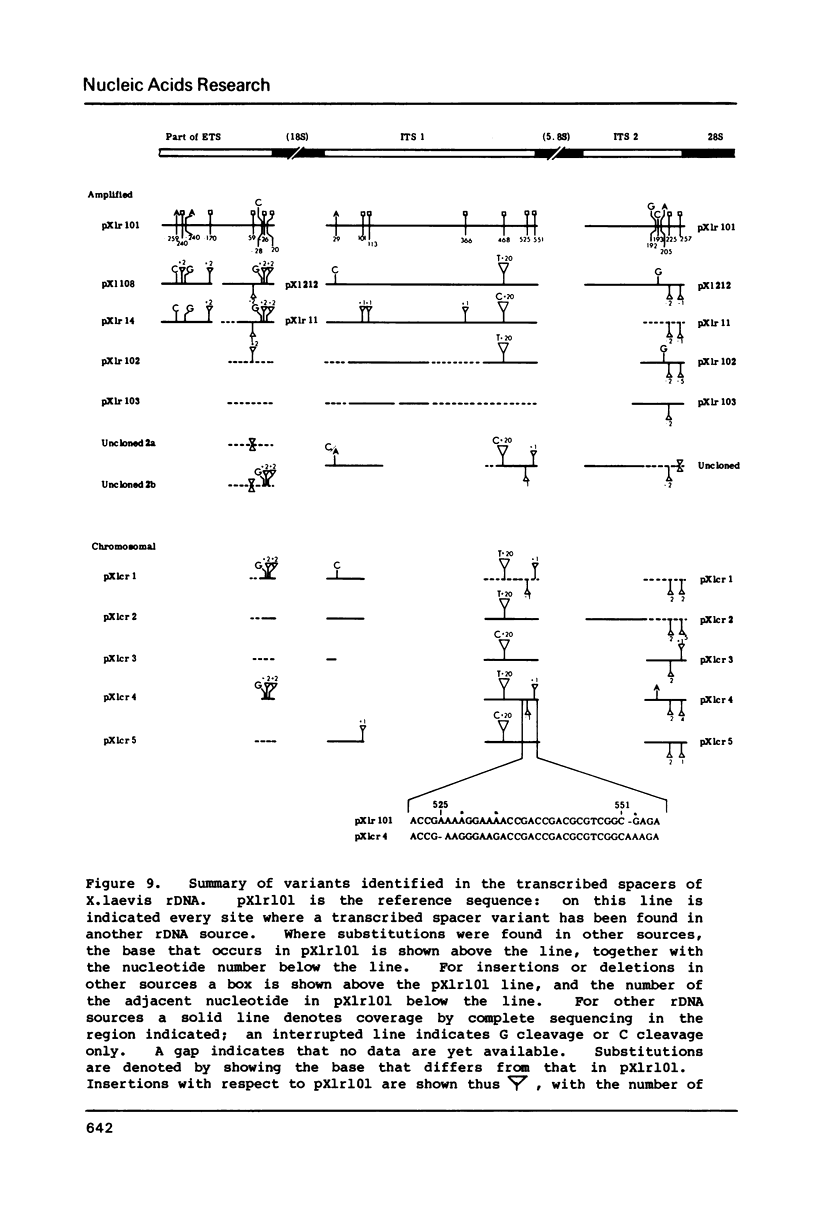




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bird A. P., Southern E. M. Use of restriction enzymes to study eukaryotic DNA methylation: I. The methylation pattern in ribosomal DNA from Xenopus laevis. J Mol Biol. 1978 Jan 5;118(1):27–47. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90242-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boseley P. G., Tuyns A., Birnstiel M. L. Mapping of the Xenopus laevis 5.8S rDNA by restriction and DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Apr;5(4):1121–1137. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.4.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boseley P., Moss T., Mächler M., Portmann R., Birnstiel M. Sequence organization of the spacer DNA in a ribosomal gene unit of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):19–31. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90291-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botchan P., Reeder R. H., Dawid I. B. Restriction analysis of the nontranscribed spacers of Xenopus laevis ribosomal DNA. Cell. 1977 Jul;11(3):599–607. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90077-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawid I. B., Brown D. D., Reeder R. H. Composition and structure of chromosomal and amplified ribosomal DNA's of Xenopus laevis. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jul 28;51(2):341–360. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90147-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsheit A. B., Davidson N., Brown D. D. An electron microscope heteroduplex study of the ribosomal DNAs of Xenopus laevis and Xenopus mulleri. J Mol Biol. 1974 Dec 5;90(2):301–314. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90375-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourse R. L., Gerbi S. A. Fine structure of ribosomal RNA. III. Location of evolutionarily conserved regions within ribosomal DNA. J Mol Biol. 1980 Jun 25;140(2):321–339. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90109-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall L. M., Maden B. E. Nucleotide sequence through the 18S-28S intergene region of a vertebrate ribosomal transcription unit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):5993–6005. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.5993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maden B. E., Forbes J. M., Stewart M. A., Eason R. 18S coding sequences in amplified ribosomal DNA from Xenopus laevis oocytes are highly homogeneous, unmethylated, and lack major open reading frames. EMBO J. 1982;1(5):597–601. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01214.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maden B. E., Moss M., Salim M. Nucleotide sequence of an external transcribed spacer in Xenopus laevis rDNA: sequences flanking the 5' and 3' ends of 18S rRNA are non-complementary. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Apr 10;10(7):2387–2398. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.7.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T., Boseley P. G., Birnstiel M. L. More ribosomal spacer sequences from Xenopus laevis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Feb 11;8(3):467–485. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.3.467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salim M., Maden B. E. Nucleotide sequence of Xenopus laevis 18S ribosomal RNA inferred from gene sequence. Nature. 1981 May 21;291(5812):205–208. doi: 10.1038/291205a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subrahmanyam C. S., Cassidy B., Busch H., Rothblum L. I. Nucleotide sequence of the region between the 18S rRNA sequence and the 28S rRNA sequence of rat ribosomal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jun 25;10(12):3667–3680. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.12.3667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldman G. M., Brand R. C., Klootwijk J., Planta R. Some characteristics of processing sites in ribosomal precursor RNA of yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jul 11;8(13):2907–2920. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.13.2907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldman G. M., Klootwijk J., van Heerikhuizen H., Planta R. J. The nucleotide sequence of the intergenic region between the 5.8S and 26S rRNA genes of the yeast ribosomal RNA operon. Possible implications for the interaction between 5.8S and 26S rRNA and the processing of the primary transcript. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 10;9(19):4847–4862. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.19.4847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellauer P. K., Reeder R. H., Dawid I. B., Brown D. D. Arrangement of length heterogeneity in repeating units of amplified and chromosomal ribosomal DNA from Xenopus laevis. J Mol Biol. 1976 Aug 25;105(4):487–505. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90230-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwieb C., Glotz C., Brimacombe R. Secondary structure comparisons between small subunit ribosomal RNA molecules from six different species. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 11;9(15):3621–3640. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.15.3621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]