Abstract
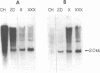
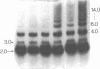
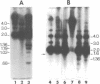
We report the identification and characterization of a family of repeated restriction fragments whose molecular organization is apparently specific to the human X chromosome. This fragment, identified as an ethidium bromide-staining 2.0 kilobase (kb) band in BamHI-digested DNA from a Chinese hamster-human somatic cell hybrid containing a human X chromosome, has been cloned into pBR325 and characterized. The 2.0 kb repeated family has been assigned to the Xp11 leads to Xq12 region on the X by Southern blot analysis of somatic cell hybrids and is predominantly arranged in tandem clusters of up to seven 2.0 kb monomers. Homologous DNA sequences, not organized as 2.0 kb BamHI fragments, are found elsewhere on the X chromosome and on at least some autosomes, but are not found on the Y chromosome. From a dosing experiment using various amounts of the cloned repeat, we estimate that there are 5,000-7,500 copies of the 2.0 kb BamHI repeat per haploid genome. Since the vast majority, if not all, of these are confined to the X chromosome, this repeated DNA family must account for 5-10% of all X chromosome DNA and must constitute the major sequence component of the pericentromeric region of the X.
Full text
PDF
















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balazs I., Szabo P., Siniscalco M. Hybridization properties of human X-chromosomal RNA transcripts from murine--human hybrids. Somatic Cell Genet. 1978 Nov;4(6):617–631. doi: 10.1007/BF01543154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beauchamp R. S., Mitchell A. R., Buckland R. A., Bostock C. J. Specific arrangements of human satellite III DNA sequences in human chromosomes. Chromosoma. 1979 Feb 21;71(2):153–166. doi: 10.1007/BF00292820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennand J., Chinault A. C., Konecki D. S., Melton D. W., Caskey C. T. Cloned cDNA sequences of the hypoxanthine/guanine phosphoribosyltransferase gene from a mouse neuroblastoma cell line found to have amplified genomic sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1950–1954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childs G., Maxson R., Cohn R. H., Kedes L. Orphons: dispersed genetic elements derived from tandem repetitive genes of eucaryotes. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):651–663. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90428-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo K. H., Gould K. G., Rees D. J., Brownlee G. G. Molecular cloning of the gene for human anti-haemophilic factor IX. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):178–180. doi: 10.1038/299178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke H. J., Hindley J. Cloning of human satellite III DNA: different components are on different chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jul 25;6(10):3177–3197. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.10.3177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke H. J., McKay R. D. Evolution of a human Y chromosome-specific repeated sequence. Cell. 1978 Mar;13(3):453–460. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90319-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke H. Repeated sequence specific to human males. Nature. 1976 Jul 15;262(5565):182–186. doi: 10.1038/262182a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies K. E., Young B. D., Elles R. G., Hill M. E., Williamson R. Cloning of a representative genomic library of the human X chromosome after sorting by flow cytometry. Nature. 1981 Oct 1;293(5831):374–376. doi: 10.1038/293374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Disteche C. M., Kunkel L. M., Lojewski A., Orkin S. H., Eisenhard M., Sahar E., Travis B., Latt S. A. Isolation of mouse x-chromosome specific DNA from an x-enriched lambda phage library derived from flow sorted chromosomes. Cytometry. 1982 Mar;2(5):282–286. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990020503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorman B. P., Shimizu N., Ruddle F. H. Genetic analysis of the human cell surface: antigenic marker for the human X chromosome in human-mouse hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2363–2367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goss S. J., Harris H. Gene transfer by means of cell fusion I. Statistical mapping of the human X-chromosome by analysis of radiation-induced gene segregation. J Cell Sci. 1977 Jun;25:17–37. doi: 10.1242/jcs.25.1.17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi R., Stang H. D., Browne J. K., Martin M. O., Huot M., Lipeles J., Salser W. Human ribosomal RNA gene spacer sequences are found interspersed elsewhere in the genome. Gene. 1981 Nov;15(2-3):177–186. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90127-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolly D. J., Esty A. C., Bernard H. U., Friedmann T. Isolation of a genomic clone partially encoding human hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):5038–5041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.5038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Smith K. D., Boyer S. H. Human Y-chromosome-specific reiterated DNA. Science. 1976 Mar 19;191(4232):1189–1190. doi: 10.1126/science.1257744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Smith K. D. Evolution of human Y-chromosome DNA. Chromosoma. 1982;86(2):209–228. doi: 10.1007/BF00288677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Tantravahi U., Eisenhard M., Latt S. A. Regional localization on the human X of DNA segments cloned from flow sorted chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 11;10(5):1557–1578. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.5.1557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurachi K., Davie E. W. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA coding for human factor IX. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6461–6464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon M. F. X-chromosome inactivation and developmental patterns in mammals. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 1972 Jan;47(1):1–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185x.1972.tb00969.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L. Chromosomal localization of complex and simple repeated human DNAs. Chromosoma. 1978 Mar 22;66(1):23–32. doi: 10.1007/BF00285813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus M., Tantravahi R., Dev V. G., Miller D. A., Miller O. J. Human-mouse cell hybrid with human multiple Y chromosomes. Nature. 1976 Jul 1;262(5563):63–65. doi: 10.1038/262063a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelson A. M., Markham A. F., Orkin S. H. Isolation and DNA sequence of a full-length cDNA clone for human X chromosome-encoded phosphoglycerate kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):472–476. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OHNO S., BECAK W., BECAK M. L. X-AUTOSOME RATIO AND THE BEHAVIOR PATTERN OF INDIVIDUAL X-CHROMOSOMES IN PLACENTAL MAMMALS. Chromosoma. 1964 Apr 1;15:14–30. doi: 10.1007/BF00326912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peden K., Mounts P., Hayward G. S. Homology between mammalian cell DNA sequences and human herpesvirus genomes detected by a hybridization procedure with high-complexity probe. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):71–80. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90406-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persico M. G., Toniolo D., Nobile C., D'Urso M., Luzzatto L. cDNA sequences of human glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase cloned in pBR322. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):778–780. doi: 10.1038/294778a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmeckpeper B. J., Smith K. D., Dorman B. P., Ruddle F. H., Talbot C. C., Jr Partial purification and characterization of DNA from the human X chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6525–6528. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmeckpeper B. J., Willard H. F., Smith K. D. Isolation and characterization of cloned human DNA fragments carrying reiterated sequences common to both autosomes and the X chromosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 24;9(8):1853–1872. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.8.1853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Therman E., Sarto G. E., Patau K. Center for Barr body condensation on the proximal part of the human Xq: a hypothesis. Chromosoma. 1974 Jan 29;44(4):361–366. doi: 10.1007/BF00284895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf S. F., Mareni C. E., Migeon B. R. Isolation and characterization of cloned DNA sequences that hybridize to the human X chromosome. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):95–102. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90117-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang T. P., Hansen S. K., Oishi K. K., Ryder O. A., Hamkalo B. A. Characterization of a cloned repetitive DNA sequence concentrated on the human X chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6593–6597. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]