Abstract
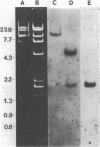
From a recombinant lambda phage, we have determined a 387 bp sequence containing a mouse lysine tRNA gene. The putative lys tRNA (anticodon UUU) differs from rabbit liver lys tRNA at five positions. The flanking regions of the mouse gene are not generally homologous to published human and Drosophila lys tRNA genes. However, the mouse gene contains a 14 bp region comprising 13 A-T base pairs, 30-44 bp from the 5' end of the coding region. Cognate A-T rich regions are present in human and Drosophila genes. The coding region is flanked by two 11 bp direct repeats, similar to those associated with alu family sequences. The sequence was determined by a "walking" protocol that employs, as a novel feature, iodinated single-stranded M13 probes to identify M13 subclones which contain sequences partially overlapping and contiguous to an initially determined sequence. The probes can also be used to screen lambda phage and in Southern and dot blot experiments.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Addison W. R., Astell C. R., Delaney A. D., Gillam I. C., Hayashi S., Miller R. C., Rajput B., Smith M., Taylor D. M., Tener G. M. The structures of genes hybridizing with tRNA4Val from Drosophila melanogaster. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):670–673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. Nucleotide sequences in Xenopus 5S DNA required for transcription termination. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90522-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calos M. P., Miller J. H. Transposable elements. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):579–595. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90305-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFranco D., Burke K. B., Hayashi S., Tener G. M., Miller R. C., Jr, Söll D. Genes for tRNALys5 from Drosophila melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 11;10(19):5799–5808. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.19.5799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFranco D., Sharp S., Söll D. Identification of regulatory sequences contained in the 5'-flanking region of Drosophila lysine tRNA2 genes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12424–12429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner R. C., Howarth A. J., Hahn P., Brown-Luedi M., Shepherd R. J., Messing J. The complete nucleotide sequence of an infectious clone of cauliflower mosaic virus by M13mp7 shotgun sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2871–2888. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi G., Singer M. F. A monkey Alu sequence is flanked by 13-base pair direct repeats by an interrupted alpha-satellite DNA sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1497–1500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han J. H., Harding J. D. Isolation and nucleotide sequence of a mouse histidine tRNA gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 25;10(16):4891–4900. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.16.4891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu N., Messing J. The making of strand-specific M13 probes. Gene. 1982 Mar;17(3):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90143-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Indik Z. K., Tartof K. D. Glutamate tRNA genes are adjacent to 5S RNA genes in Drosophila and reveal a conserved upstream sequence (the ACT-TA box). Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jul 24;10(14):4159–4172. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.14.4159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagadeeswaran P., Forget B. G., Weissman S. M. Short interspersed repetitive DNA elements in eucaryotes: transposable DNA elements generated by reverse transcription of RNA pol III transcripts? Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):141–142. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90296-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prensky W. The radioiodination of RNA and DNA to high specific activities. Methods Cell Biol. 1976;13:121–152. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61800-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raba M., Limburg K., Burghagen M., Katze J. R., Simsek M., Heckman J. E., Rajbhandary U. L., Gross H. J. Nucleotide sequence of three isoaccepting lysine tRNAs from rabbit liver and SV40-transformed mouse fibroblasts. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jun;97(1):305–318. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13115.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy K. L., Cooke H., Buckland R. Nucleotide sequence of a segment of human DNA containing the three tRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7313–7322. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid C. W., Jelinek W. R. The Alu family of dispersed repetitive sequences. Science. 1982 Jun 4;216(4550):1065–1070. doi: 10.1126/science.6281889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekiya T., Nishizawa R., Matsuda K., Taya Y., Nishimura S. A rat tRNA gene cluster containing the genes for tRNAPro and tRNALys. Analysis of nucleotide sequences of the genes and the surrounding regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 25;10(20):6411–6419. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.20.6411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp S., DeFranco D., Silberklang M., Hosbach H. A., Schmidt T., Kubli E., Gergen J. P., Wensink P. C., Söll D. The initiator tRNA genes of Drosophila melanogaster: evidence for a tRNA pseudogene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):5867–5882. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.5867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya K., Noguchi S., Nishimura S., Sekiya T. Characterization of a rat tRNA gene cluster containing the genes for tRNAAsp, tRNAGly and tRNAGlu, and pseudogenes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jul 24;10(14):4441–4448. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.14.4441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprinzl M., Gauss D. H. Compilation of tRNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):r1–55. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- The 1980 pittsburgh conference: a special instrumentation report. Science. 1980 Apr 11;208(4440):161–163. doi: 10.1126/science.208.4440.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Arsdell S. W., Denison R. A., Bernstein L. B., Weiner A. M., Manser T., Gesteland R. F. Direct repeats flank three small nuclear RNA pseudogenes in the human genome. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(1 Pt 1):11–17. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]