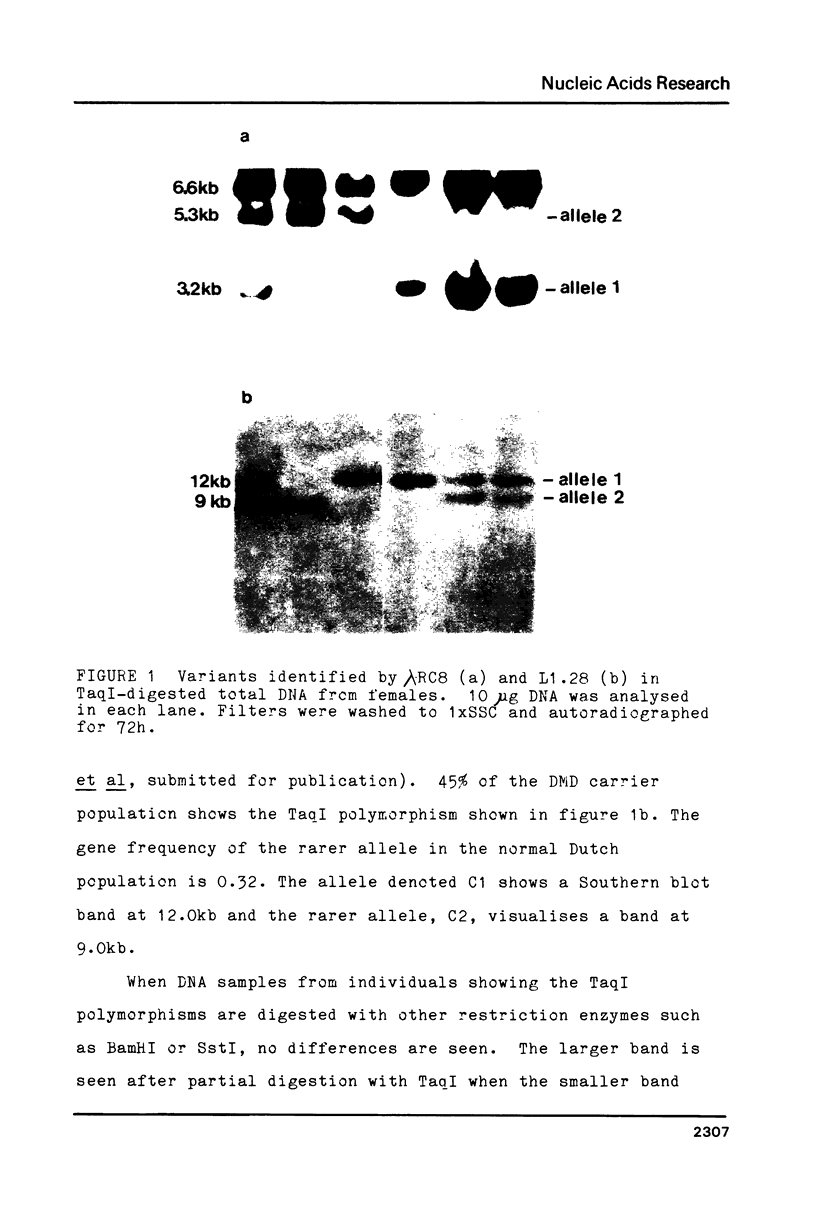
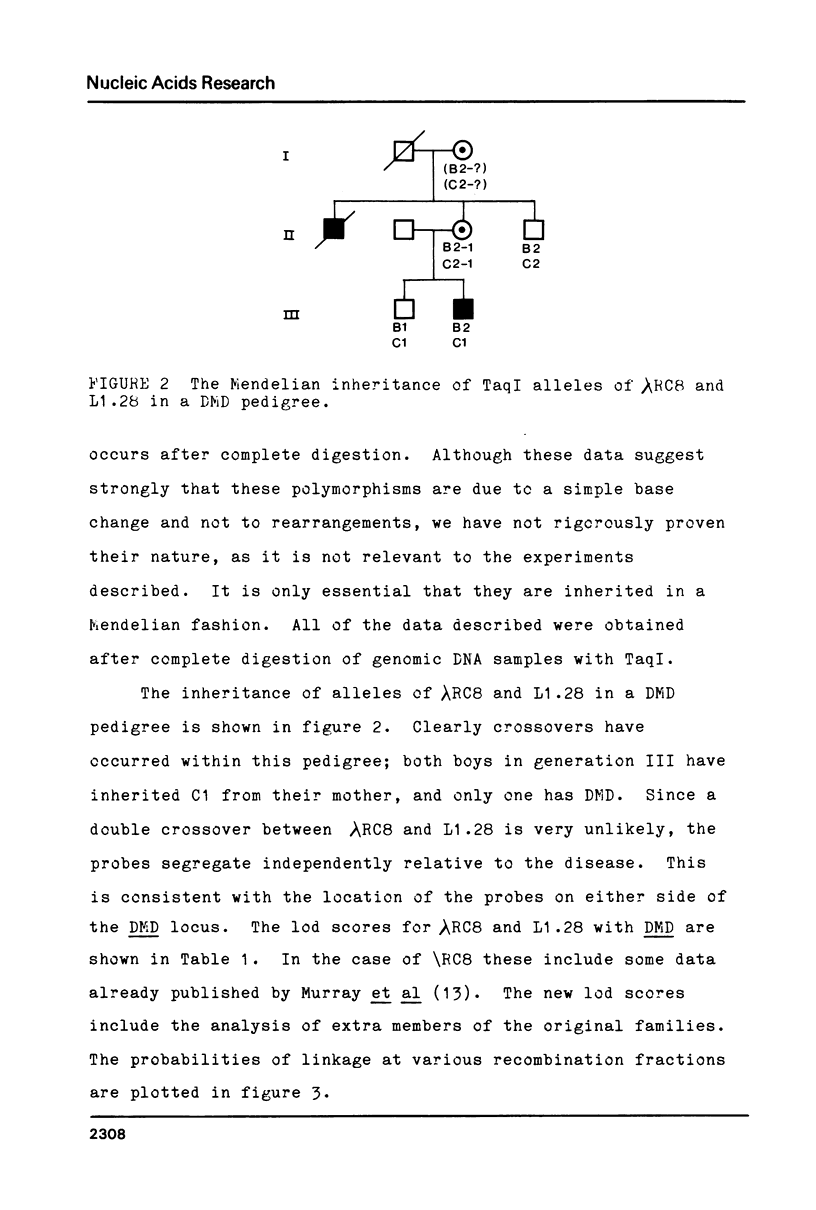
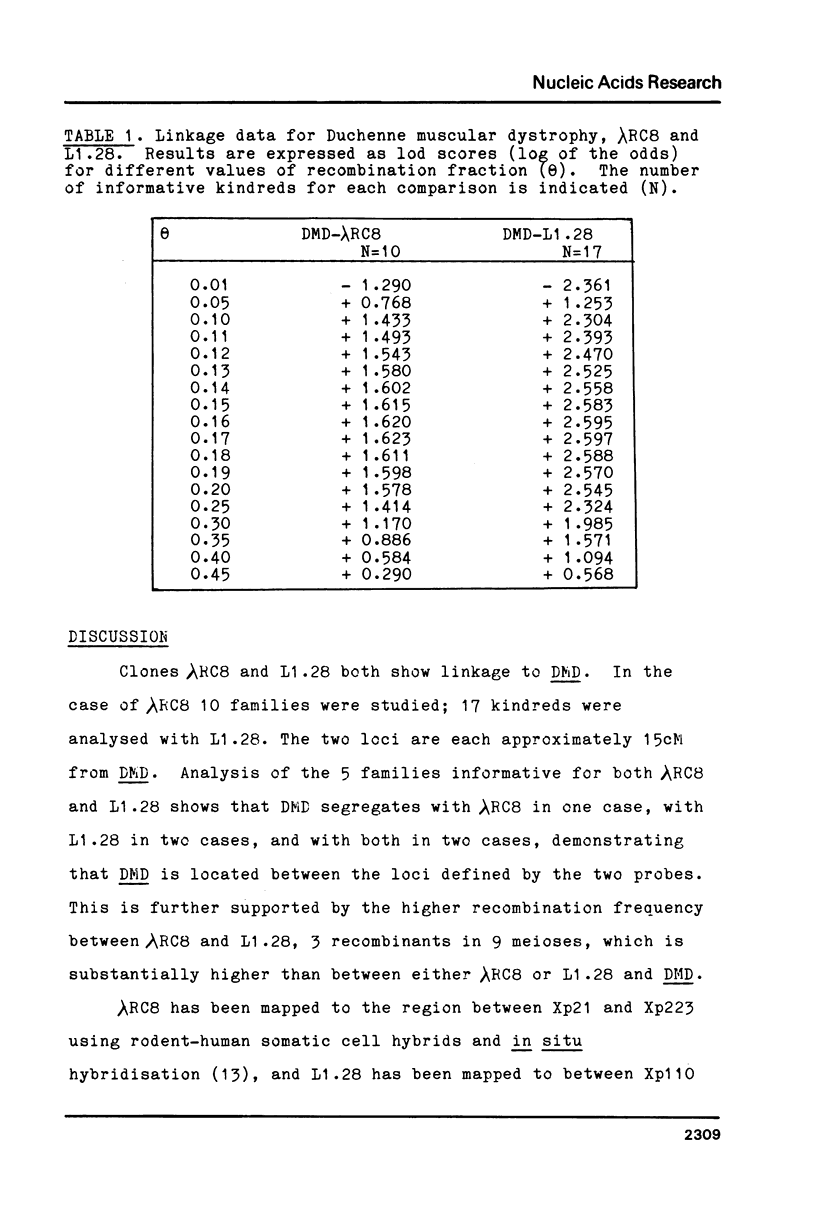
Abstract
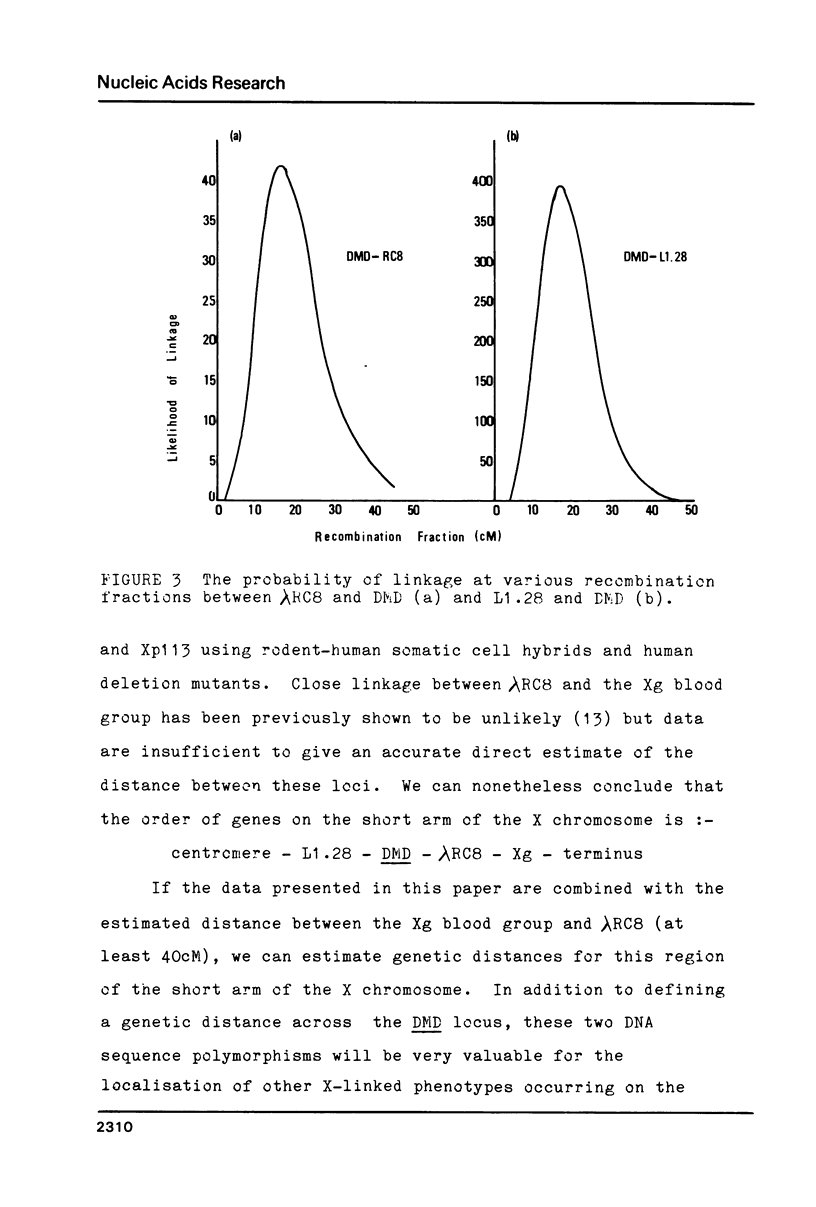
The inheritance of two restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs) on the short arm of the human X chromosome has been studied relative to Duchenne muscular dystrophy. This provides a partial genetic map of the short arm of the human X chromosome between Xp110 and Xp223. The data were derived from the segregation between a RFLP located at Xp21-Xp223, the DMD locus, and a RFLP located at Xp110-Xp113. The genetic distance from Xp110 to Xp223 was found to be approximately 40 centimorgans (cM). This provides experimental confirmation that 1cM corresponds to approximately 1,000 kilobase pairs of DNA for this region of the human X chromosome. Our data confirm that the DMD mutation lies between Xp223 and Xp110. The availability of flanking probes surrounding the DMD locus will assist in the ordering of further DNA sequences relative to the mutation.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Botstein D., White R. L., Skolnick M., Davis R. W. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet. 1980 May;32(3):314–331. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. J., Robson E. B., Buckton K. E., Jacobs P. A., Polani P. E. Segregation of genetic markers in families with chromosome polymorphisms and structural rearrangements involving chromosome 1. Ann Hum Genet. 1974 Jan;37(3):261–274. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1974.tb01834.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies K. E. The application of DNA recombinant technology to the analysis of the human genome and genetic disease. Hum Genet. 1981;58(4):351–357. doi: 10.1007/BF00282814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies K. E., Young B. D., Elles R. G., Hill M. E., Williamson R. Cloning of a representative genomic library of the human X chromosome after sorting by flow cytometry. Nature. 1981 Oct 1;293(5831):374–376. doi: 10.1038/293374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray J. W., Carrano A. V., Steinmetz L. L., Van Dilla M. A., Moore D. H., 2nd, Mayall B. H., Mendelsohn M. L. Chromosome measurement and sorting by flow systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1231–1234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill M. E., Davies K. E., Harper P., Williamson R. The Mendelian inheritance of a human X chromosome-specific DNA sequence polymorphism and its use in linkage studies of genetic disease. Hum Genet. 1982;60(3):222–226. doi: 10.1007/BF00303007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J. DNA sequence variants in the G gamma-, A gamma-, delta- and beta-globin genes of man. Cell. 1979 Sep;18(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90348-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Smith K. D., Boyer S. H., Borgaonkar D. S., Wachtel S. S., Miller O. J., Breg W. R., Jones H. W., Jr, Rary J. M. Analysis of human Y-chromosome-specific reiterated DNA in chromosome variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1245–1249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurie D. A., Palmer R. W., Hultén M. A. Chiasma derived genetic lengths and recombination fractions: chromosomes 2 and 9. Ann Hum Genet. 1982 Jul;46(Pt 3):233–244. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1982.tb00715.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindenbaum R. H., Clarke G., Patel C., Moncrieff M., Hughes J. T. Muscular dystrophy in an X; 1 translocation female suggests that Duchenne locus is on X chromosome short arm. J Med Genet. 1979 Oct;16(5):389–392. doi: 10.1136/jmg.16.5.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKusick V. A., Ruddle F. H. The status of the gene map of the human chromosomes. Science. 1977 Apr 22;196(4288):390–405. doi: 10.1126/science.850784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKusick V. A. The human genome through the eyes of a clinical geneticist. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1982;32(1-4):7–23. doi: 10.1159/000131682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn M. L., Mayall B. H., Bogart E., Moore D. H., 2nd, Perry B. H. DNA content and DNA-based centromeric index of the 24 human chromosomes. Science. 1973 Mar 16;179(4078):1126–1129. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4078.1126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. M., Davies K. E., Harper P. S., Meredith L., Mueller C. R., Williamson R. Linkage relationship of a cloned DNA sequence on the short arm of the X chromosome to Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Nature. 1982 Nov 4;300(5887):69–71. doi: 10.1038/300069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renwick J. H. Progress in mapping human autosomes. Br Med Bull. 1969 Jan;25(1):65–73. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon E., Bodmer W. F. Evolution of sickle variant gene. Lancet. 1979 Apr 28;1(8122):923–923. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91398-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyman A. R., White R. A highly polymorphic locus in human DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6754–6758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zatz M., Vianna-Morgante A. M., Campos P., Diament A. J. Translocation (X;6) in a female with Duchenne muscular dystrophy: implications for the localisation of the DMD locus. J Med Genet. 1981 Dec;18(6):442–447. doi: 10.1136/jmg.18.6.442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]