Abstract
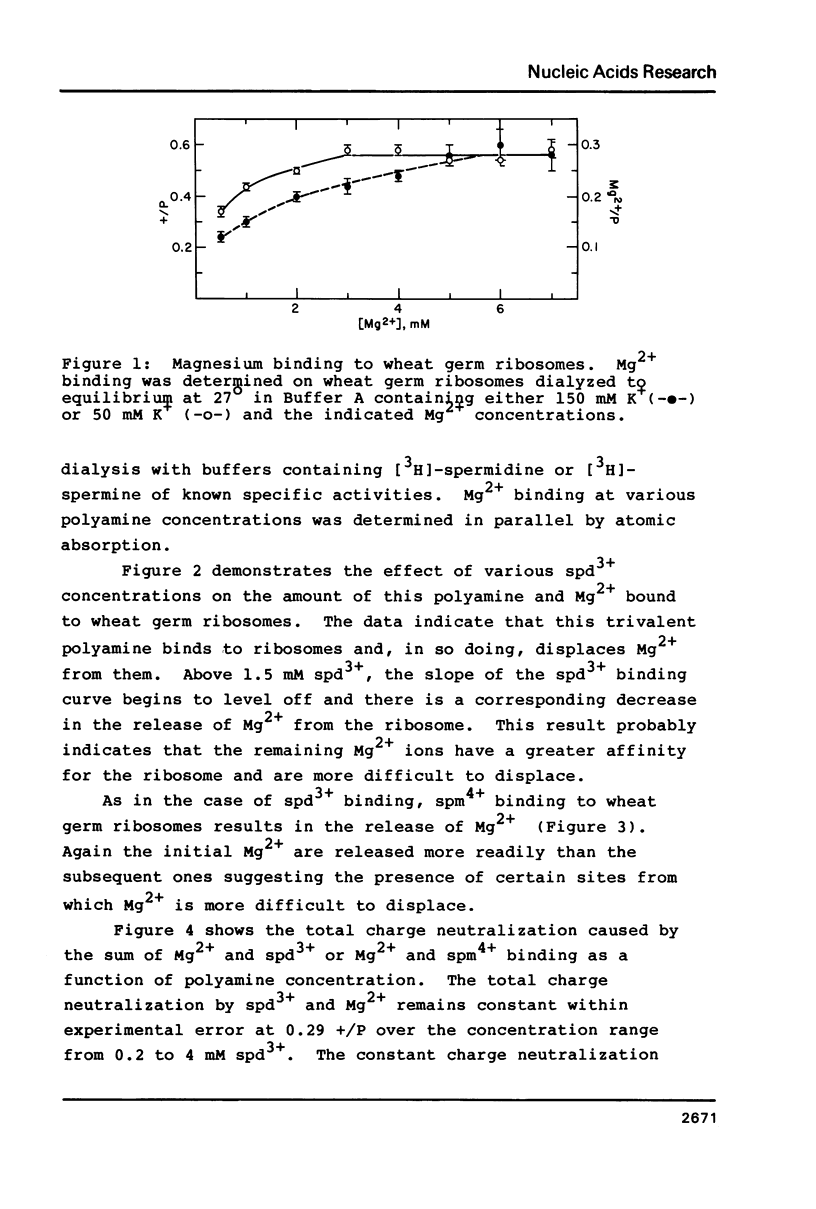
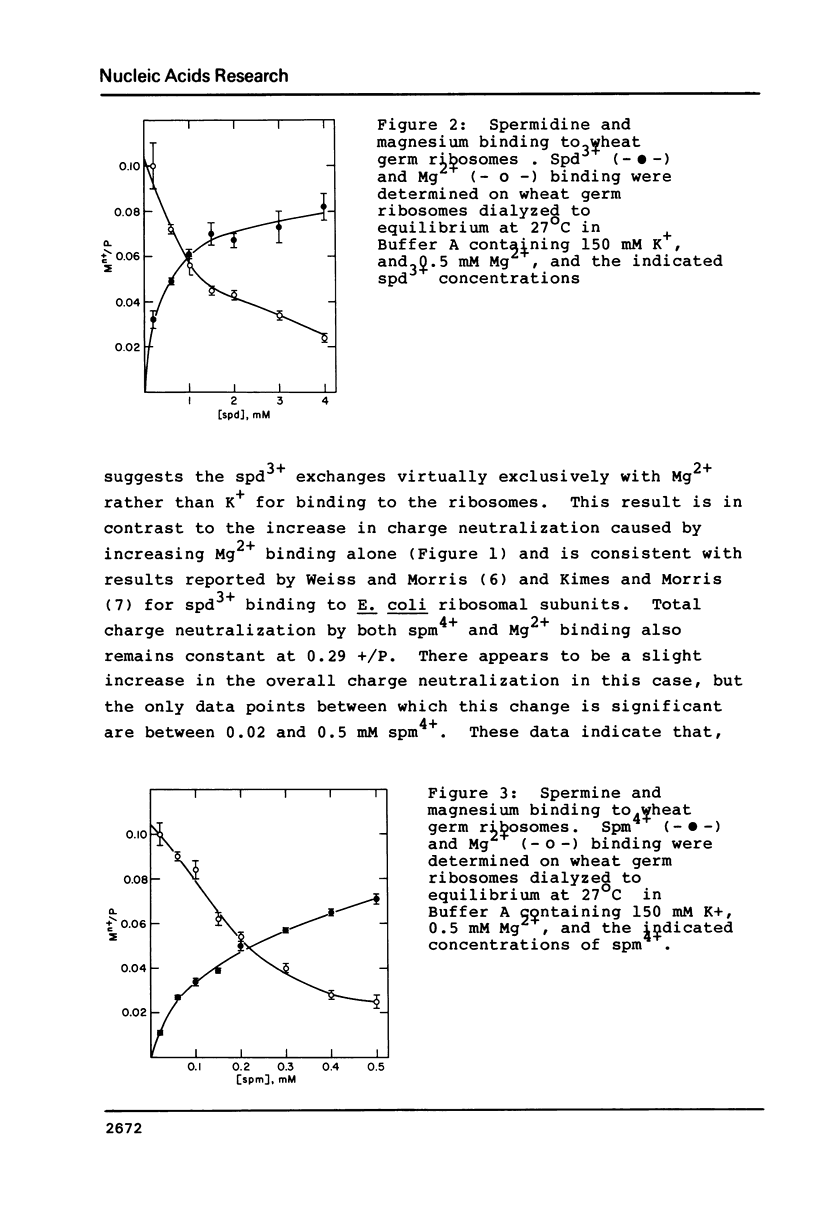
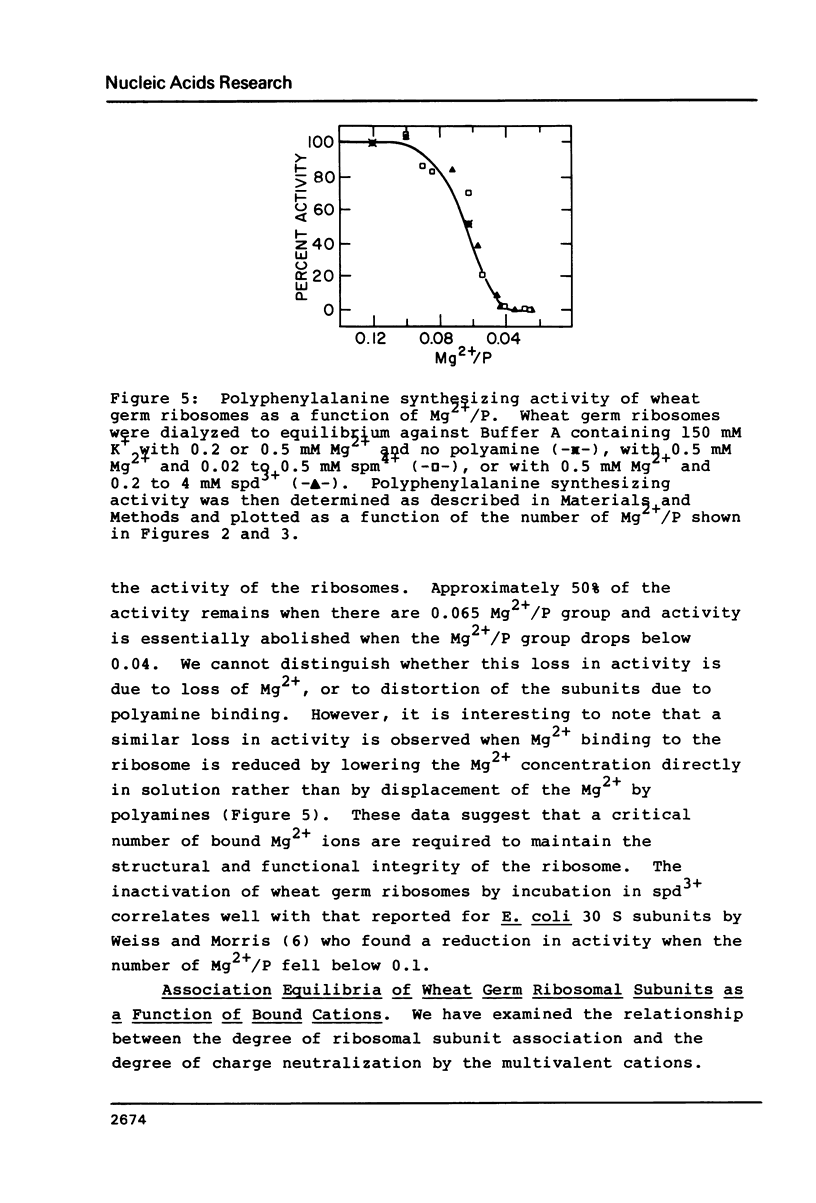
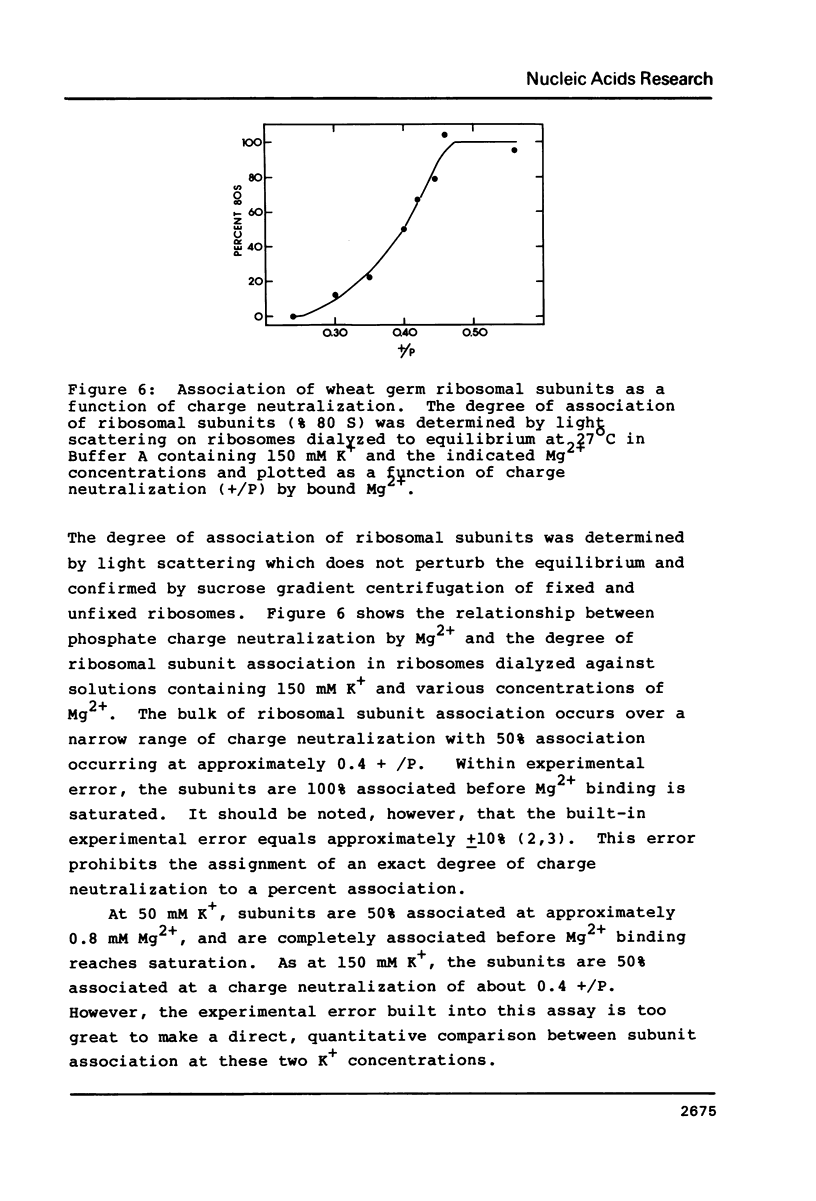
The binding of Mg2+, spermine, and spermidine to wheat germ ribosomes was quantitated following equilibrium dialysis. The Mg2+ binding data demonstrate that Mg2+ and K+ compete for binding to the ribosomes. Mg2+ binding saturates at approximately 0.56 positive charges per phosphate (+/P). The Mg2+, spermine and spermidine binding data indicate that either polyamine replaces Mg2+ upon binding to the ribosomes. Mg2+ and polyamine binding combined saturates at approximately 0.29 +/P under the conditions reported. When a critical number of Mg2+ ions are replaced by either polyamine, the activity of the ribosomes falls dramatically. Ribosomal subunit association increases with the degree of phosphate charge neutralization due to the binding of Mg2+. Total charge neutralization during subunit association by Mg2+ and polyamine binding combined, is much less than that achieved by Mg2+ alone.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cammarano P., Romeo A., Gentile M., Felsani A., Gualerzi C. Size heterogeneity of the large ribosomal subunits and conservation of the small subunits in eucaryote evolution. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 9;281(4):597–624. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90159-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor K. P., Hearst J. E. The structure of metaphase chromosomes. I. Electrometric titration, magnesium ion binding and circular dichroism. J Mol Biol. 1970 Apr 14;49(1):213–229. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90387-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi Y. S., Carr C. W. Ion-binding studies of ribonucleic acid and Escherichia coli ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1967 Apr 28;25(2):331–345. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90145-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDELMAN I. S., TS'O P. O., VINOGRAD J. The binding of magnesium to microsomal nucleoprotein and ribonucleic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Oct 7;43:393–403. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90464-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson D., Spitnik-Elson P., Avital S., Abramowitz R. Binding of magnesium ions and ethidium bromide: comparison of ribosomes and free ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Sep 25;7(2):465–480. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.2.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. Magnesium binding by Escherichia coli ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1966 Feb;15(2):663–673. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80134-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimes B. W., Morris D. R. Cations and ribosome structure. II. Effects on the 50S subunit of substituting polyamines for magnesium ion. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 30;12(3):442–449. doi: 10.1021/bi00727a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOBEL A. E., HANOK A. A rapid method for the determination of ultramicro quantities of calcium and magnesium. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1951 Aug;77(4):737–740. doi: 10.3181/00379727-77-18911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperrazza J. M., Moore M. N., Spremulli L. L. Influence of various cations on the equilibria between wheat germ ribosomes and their subunits. Biochemistry. 1981 Aug 18;20(17):5073–5079. doi: 10.1021/bi00520a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperrazza J. M., Russell D. W., Spremulli L. L. Reversible dissociation of wheat germ ribosomal subunits: cation-dependent equilibria and thermodynamic parameters. Biochemistry. 1980 Mar 18;19(6):1053–1058. doi: 10.1021/bi00547a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spremulli L. L., Walthall B. J., Lax S. R., Ravel J. M. Partial purification of the factors required for the initiation of protein synthesis in wheat germ. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 10;254(1):143–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spremulli L. L., Walthall B. J., Lax S. R., Ravel J. M. Purification and properties of a Met-tRNAf binding factor from wheat germ. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Jan 30;178(2):565–575. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90227-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walters J. A., Van Os G. A. The dissociation and association behaviour of yeast ribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Feb 18;199(2):453–463. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90088-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walters J. A., van Os G. A. Magnesium binding to yeast ribosomes. Biopolymers. 1971;10(1):11–20. doi: 10.1002/bip.360100103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. L., Morris D. R. Cations and ribosome structure. I. Effects on the 30S subunit of substituting polyamines for magnesium ion. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 30;12(3):435–441. doi: 10.1021/bi00727a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wishnia A., Boussert A. S. The non-specific role of Mg2+ in ribosomal subunit association: kinetics and equilibrium in the presence of other divalent metal ions. J Mol Biol. 1977 Nov 5;116(3):577–591. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90085-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


