Abstract
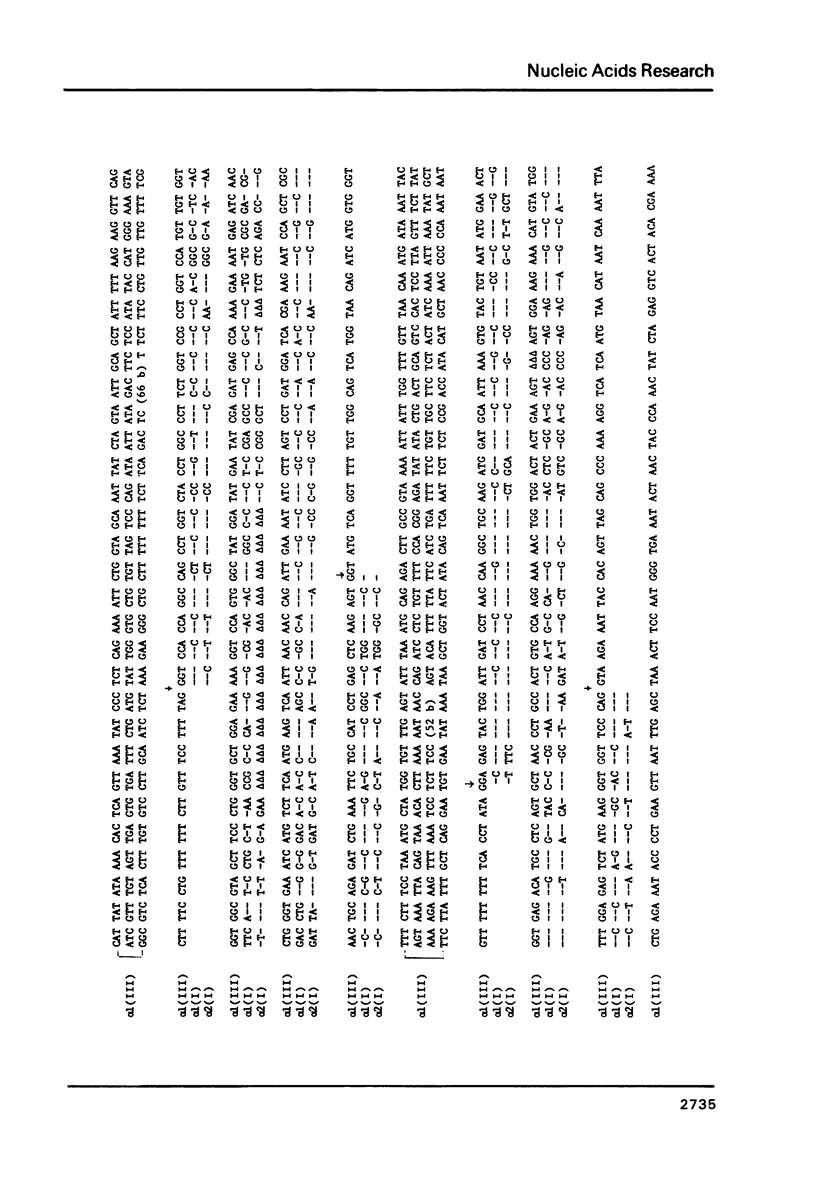
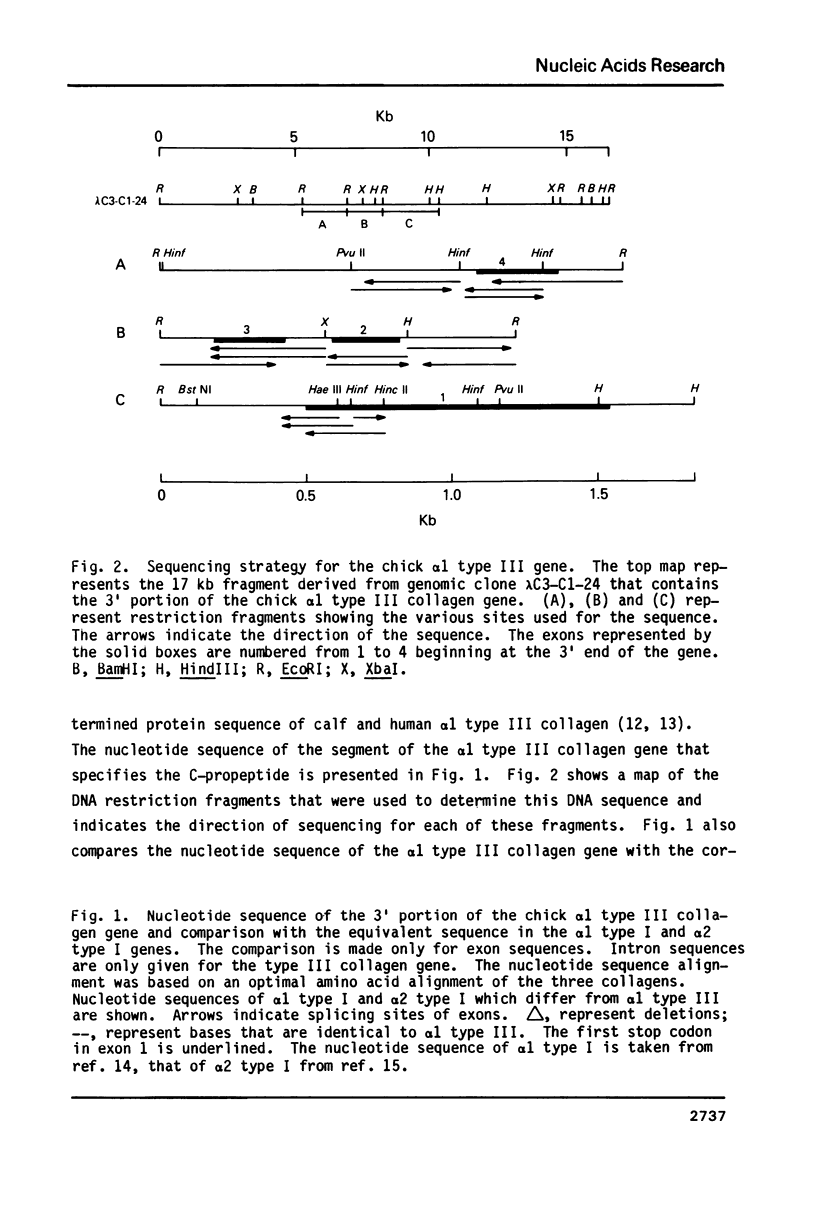
The nucleotide sequence of a segment of the chick alpha 1 type III collagen gene which codes for the C-propeptide was determined and compared with the corresponding sequence in the alpha 1 type I and alpha 2 type I collagen genes. As in the alpha 2 type I gene the coding information for the C-propeptide of the type III collagen gene is subdivided in four exons. Similarly, the amino proximal exon contains sequences for both the carboxy terminal end of the alpha-helical segment of collagen and for the beginning of the C-propeptide in both genes. Therefore, this organization of exons must have been established before these two collagen genes arose by duplication of a common ancestor. In several subsegments the deduced amino acid sequence for the C-propeptide of type III collagen shows a strong homology with the corresponding amino acid sequence in alpha 1 and alpha 2 type I. For one of these homologous amino acid sequences, however, the nucleotide sequence is much better conserved than for the others. It is possible that a mechanism of gene conversion has maintained the homogeneity of this nucleotide sequence among the interstitial collagen genes. Alternatively, the conserved nucleotide sequence may represent a regulatory signal which could function either in the DNA or in the RNA.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allmann H., Fietzek P. P., Glanville R. W., Kühn K. The covalent structure of calf skin type III collagen. VI. The amino acid sequence of the carboxyterminal cyanogen bromide peptide alpha 1(III)CB9B (position 928--1028). Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1979 Jul;360(7):861–868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D. Gene conversion: some implications for immunoglobulin genes. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):592–594. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein P., Sage H. Structurally distinct collagen types. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:957–1003. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.004521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson L. A., Ninomiya Y., Bernard M. P., Pesciotta D. M., Parsons J., Green G., Eikenberry E. F., de Crombrugghe B., Vogeli G., Pastan I. The exon/intron structure of the 3'-region of the pro alpha 2(I) collagen gene. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8407–8415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller F., Boedtker H. Sequence determination and analysis of the 3' region of chicken pro-alpha 1(I) and pro-alpha 2(I) collagen messenger ribonucleic acids including the carboxy-terminal propeptide sequences. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 17;20(4):996–1006. doi: 10.1021/bi00507a054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber J. E., Rogers D. T., McCusker J. H. Homothallic conversions of yeast mating-type genes occur by intrachromosomal recombination. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):277–289. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90175-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klar A. J., McIndoo J., Strathern J. N., Hicks J. B. Evidence for a physical interaction between the transposed and the substituted sequences during mating type gene transposition in yeast. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):291–298. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90176-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein H. L., Petes T. D. Intrachromosomal gene conversion in yeast. Nature. 1981 Jan 15;289(5794):144–148. doi: 10.1038/289144a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J., Gay S. Collagen: an overview. Methods Enzymol. 1982;82(Pt A):3–32. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)82058-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkubo H., Vogeli G., Mudryj M., Avvedimento V. E., Sullivan M., Pastan I., de Crombrugghe B. Isolation and characterization of overlapping genomic clones covering the chicken alpha 2 (type I) collagen gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7059–7063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paglia L., Wilczek J., de Leon L. D., Martin G. R., Hörlein D., Müller P. Inhibition of procollagen cell-free synthesis by amino-terminal extension peptides. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 30;18(22):5030–5034. doi: 10.1021/bi00589a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. M., Axel R. Gene amplification and gene correction in somatic cells. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):109–119. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90095-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbloom J., Endo R., Harsch M. Termination of procollagen chain synthesis by puromycin. Evidence that assembly and secretion require a COOH-terminal extension. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 10;251(7):2070–2076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seyer J. M., Kang A. H. Covalent structure of collagen: amino acid sequence of alpha 1(III)-CB9 from type III collagen of human liver. Biochemistry. 1981 Apr 28;20(9):2621–2627. doi: 10.1021/bi00512a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiestner M., Krieg T., Hörlein D., Glanville R. W., Fietzek P., Müller P. K. Inhibiting effect of procollagen peptides on collagen biosynthesis in fibroblast cultures. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7016–7023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wozney J., Hanahan D., Tate V., Boedtker H., Doty P. Structure of the pro alpha 2 (I) collagen gene. Nature. 1981 Nov 12;294(5837):129–135. doi: 10.1038/294129a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada Y., Avvedimento V. E., Mudryj M., Ohkubo H., Vogeli G., Irani M., Pastan I., de Crombrugghe B. The collagen gene: evidence for its evolutinary assembly by amplification of a DNA segment containing an exon of 54 bp. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):887–892. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90565-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


