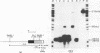Abstract
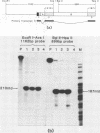
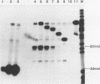
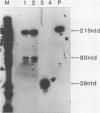
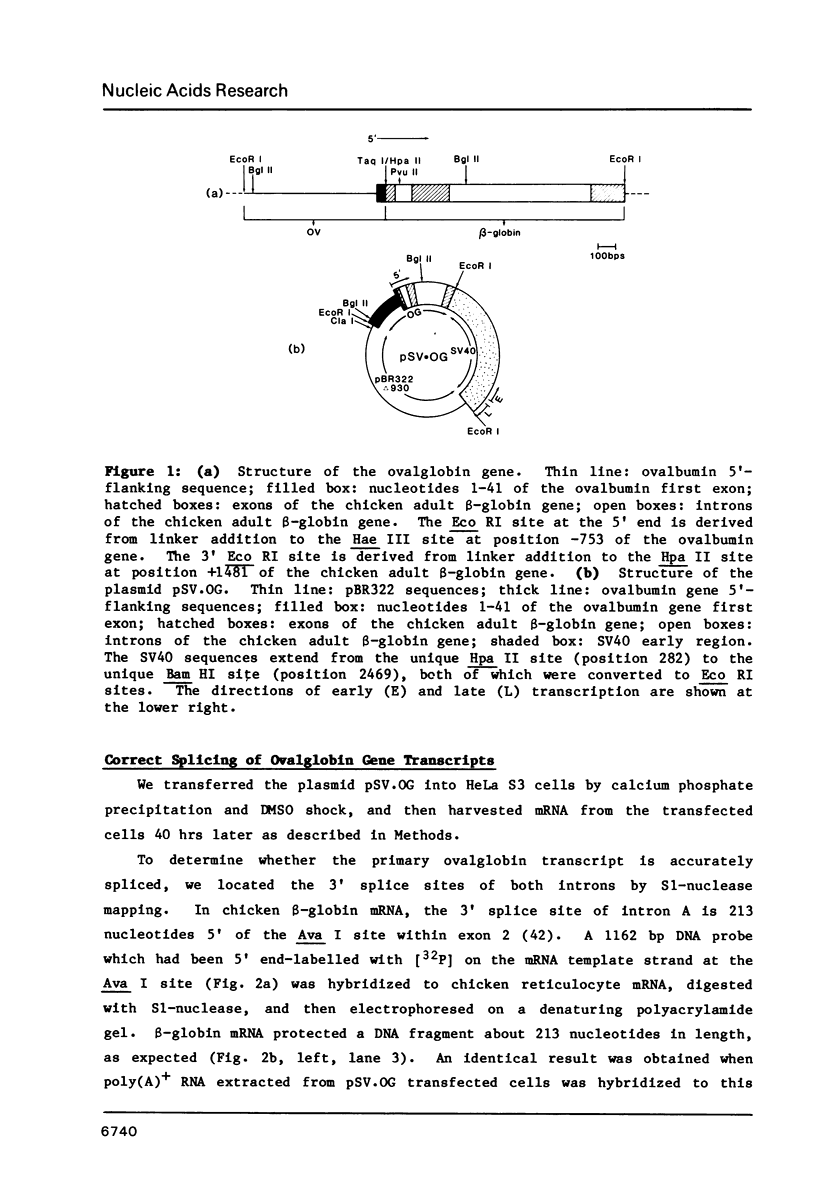
In order to study the initiation of transcription from the ovalbumin gene promoter, we constructed a hybrid gene (ovalglobin) in which 753 bps of ovalbumin gene 5'-flanking sequence were joined to the chicken adult beta-globin gene. When transfected into HeLa S3 cells, ovalglobin gene transcription initiated at the ovalbumin gene cap site, as measured by S1 nuclease and primer extension analysis. Deletion of 5'-flanking sequences to position -95 had little effect on transcription; deletion to -77 reduced transcription to about 20% of the wild type level and deletion to -48 reduced the level to about 2%. A deletion to -24, removing the sequence TATATAT, abolished transcription entirely. Hormonal regulation of the ovalglobin gene was observed when primary oviduct cells were used as recipients for DNA transfection. Under these conditions, addition of progesterone increased the level of ovalglobin transcripts to more than 10 times the uninduced level.
Full text
PDF




















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerji J., Rusconi S., Schaffner W. Expression of a beta-globin gene is enhanced by remote SV40 DNA sequences. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):299–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90413-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., Chambon P. In vivo sequence requirements of the SV40 early promotor region. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):304–310. doi: 10.1038/290304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., O'Hare K., Breathnach R., Chambon P. The ovalbumin gene-sequence of putative control regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):127–142. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao M. V., Mellon P., Charnay P., Maniatis T., Axel R. The regulated expression of beta-globin genes introduced into mouse erythroleukemia cells. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):483–493. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90468-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton J. G., Schrader W. T., O'Malley B. W. DNA sequence preference of the progesterone receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):16–20. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagert M., Ehrlich S. D. Prolonged incubation in calcium chloride improves the competence of Escherichia coli cells. Gene. 1979 May;6(1):23–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. H., Jacobs H. T., Britten R. J. Very short repeats and coordinate induction of genes. Nature. 1983 Feb 10;301(5900):468–470. doi: 10.1038/301468a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dierks P., van Ooyen A., Cochran M. D., Dobkin C., Reiser J., Weissmann C. Three regions upstream from the cap site are required for efficient and accurate transcription of the rabbit beta-globin gene in mouse 3T6 cells. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):695–706. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolan M., Dodgson J. B., Engel J. D. Analysis of the adult chicken beta-globin gene. Nucleotide sequence of the locus, microheterogeneity at the 5'-end of beta-globin mRNA, and aberrant nuclear RNA species. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3983–3990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald M., Shenk T. The sequence 5'-AAUAAA-3'forms parts of the recognition site for polyadenylation of late SV40 mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90521-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman H. M., MacDonald R. J. Cloning of hormone genes from a mixture of cDNA molecules. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:75–90. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68007-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray H. B., Jr, Ostrander D. A., Hodnett J. L., Legerski R. J., Robberson D. L. Extracellular nucleases of Pseudomonas BAL 31. I. Characterization of single strand-specific deoxyriboendonuclease and double-strand deoxyriboexonuclease activities. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Sep;2(9):1459–1492. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.9.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. Delimitation of far upstream sequences required for maximal in vitro transcription of an H2A histone gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):297–301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. Identification of regulatory sequences in the prelude sequences of an H2A histone gene by the study of specific deletion mutants in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1432–1436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Wasylyk B., Chambon P., Birnstiel M. L. Point mutation in the TATA box curtails expression of sea urchin H2A histone gene in vivo. Nature. 1981 Nov 12;294(5837):178–180. doi: 10.1038/294178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld G. C., Koster A., Flavell R. A. A transcription map for the rabbit beta-globin gene. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):573–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld G. C., Rosenthal A., Flavell R. A. Sequence requirements for the transcription of the rabbit beta-globin gene in vivo: the -80 region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 25;10(16):4951–4971. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.16.4951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld G. C., Shewmaker C. K., Jat P., Flavell R. A. Localization of DNA sequences necessary for transcription of the rabbit beta-globin gene in vitro. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):215–226. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90246-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld G. C., de Boer E., Shewmaker C. K., Flavell R. A. DNA sequences necessary for transcription of the rabbit beta-globin gene in vivo. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):120–126. doi: 10.1038/295120a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruss P., Dhar R., Khoury G. Simian virus 40 tandem repeated sequences as an element of the early promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):943–947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamer D. H., Kaehler M., Leder P. A mouse globin gene promoter is functional in SV40. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):697–708. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90433-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hen R., Sassone-Corsi P., Corden J., Gaub M. P., Chambon P. Sequences upstream from the T-A-T-A box are required in vivo and in vitro for efficient transcription from the adenovirus serotype 2 major late promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7132–7136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz K. B., Mockus M. B., Lessey B. A. Variant T47D human breast cancer cells with high progesterone-receptor levels despite estrogen and antiestrogen resistance. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):633–642. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90218-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes N. E., Groner B., Sippel A. E., Nguyen-Huu M. C., Schütz G. mRNA complexity and egg white protein mRNA content in mature and hormone-withdrawn oviduct. Cell. 1977 Aug;11(4):923–932. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90303-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knoll B. J., Woo S. L., Beattie W., O'Malley B. W. Identification and sequence analysis of the 5' domain of the X and Y pseudo-ovalbumin genes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7949–7953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz D. T. Hormonal inducibility of rat alpha 2u globulin genes in transfected mouse cells. Nature. 1981 Jun 25;291(5817):629–631. doi: 10.1038/291629a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. C., McKnight G. S., Palmiter R. D. The action of estrogen and progesterone on the expression of the transferrin gene. A comparison of the response in chick liver and oviduct. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 25;253(10):3494–3503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. Inhibition of SV40 replication in simian cells by specific pBR322 DNA sequences. Nature. 1981 Sep 3;293(5827):79–81. doi: 10.1038/293079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malek L. T., Eschenfeldt W. H., Munns T. W., Rhoads R. E. Heterogeneity of the 5' terminus of hen ovalbumin messenger ribonucleic acid. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 10;9(7):1657–1673. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.7.1657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Cano A., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. DNA-dependent transcription of adenovirus genes in a soluble whole-cell extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3855–3859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight G. S., Pennequin P., Schimke R. T. Induction of ovalbumin mRNA sequences by estrogen and progesterone in chick oviduct as measured by hybridization to complementary DNA. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 25;250(20):8105–8110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Gavis E. R. Expression of the herpes thymidine kinase gene in Xenopus laevis oocytes: an assay for the study of deletion mutants constructed in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):5931–5948. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.5931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Gavis E. R., Kingsbury R., Axel R. Analysis of transcriptional regulatory signals of the HSV thymidine kinase gene: identification of an upstream control region. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):385–398. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. Transcriptional control signals of a eukaryotic protein-coding gene. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):316–324. doi: 10.1126/science.6283634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon P., Parker V., Gluzman Y., Maniatis T. Identification of DNA sequences required for transcription of the human alpha 1-globin gene in a new SV40 host-vector system. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):279–288. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90411-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulvihill E. R., LePennec J. P., Chambon P. Chicken oviduct progesterone receptor: location of specific regions of high-affinity binding in cloned DNA fragments of hormone-responsive genes. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):621–632. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90217-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley B. W., McGuire W. L., Kohler P. O., Korenman S. G. Studies on the mechanism of steroid hormone regulation of synthesis of specific proteins. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1969;25:105–160. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571125-8.50006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley B. W., McGuire W. L., Korenman S. G. Estrogen stimulation of synthesis of specific proteins and RNA polymerase activity in the immature chick oviduct. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Aug 22;145(1):204–207. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90679-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley B. W., Means A. R. Female steroid hormones and target cell nuclei. Science. 1974 Feb 15;183(4125):610–620. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4125.610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D. Regulation of protein synthesis in chick oviduct. I. Independent regulation of ovalbumin, conalbumin, ovomucoid, and lysozyme induction. J Biol Chem. 1972 Oct 25;247(20):6450–6461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlakis G. N., Hamer D. H. Regulation of a metallothionein-growth hormone hybrid gene in bovine papilloma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):397–401. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. A regulatory upstream promoter element in the Drosophila hsp 70 heat-shock gene. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):517–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90249-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Schaffner W. Correct transcription of a cloned mouse immunoglobulin gene in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):417–421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purrello M., Balazs I. Direct hybridization of labeled DNA to DNA in agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1983 Feb 1;128(2):393–397. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90391-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renkawitz R., Beug H., Graf T., Matthias P., Grez M., Schütz G. Expression of a chicken lysozyme recombinant gene is regulated by progesterone and dexamethasone after microinjection into oviduct cells. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):167–176. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90416-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roop D. R., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Definition of the 5' and 3' ends of transcripts of the ovalbumin gene. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):63–68. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90388-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen J. M., Woo S. L., Holder J. W., Means A. R., O'Malley B. W. Preparation and preliminary characterization of purified ovalbumin messenger RNA from the hen oviduct. Biochemistry. 1975 Jan 14;14(1):69–78. doi: 10.1021/bi00672a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. W., Tilghman S. M. Transient expression of a mouse alpha-fetoprotein minigene: deletion analyses of promoter function. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;3(7):1295–1309. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.7.1295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., Wilkie N. M. An improved technique for obtaining enhanced infectivity with herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA. J Gen Virol. 1976 Dec;33(3):447–458. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-33-3-447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaneck G. E., Nordstrom J. L., Kreuzaler F., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Effect of estrogen on gene expression in chicken oviduct: evidence for transcriptional control of ovalbumin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1049–1053. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talkington C. A., Nishioka Y., Leder P. In vitro transcription of normal, mutant, and truncated mouse alpha-globin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7132–7136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Orkin S. H., Maniatis T. Specific transcription and RNA splicing defects in five cloned beta-thalassaemia genes. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):591–596. doi: 10.1038/302591a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. Y., Roop D. R., Tsai M. J., Stein J. P., Means A. R., O'Malley B. W. Effect of estrogen on gene expression in the chick oviduct. Regulation of the ovomucoid gene. Biochemistry. 1978 Dec 26;17(26):5773–5780. doi: 10.1021/bi00619a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. Y., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Specific 5' flanking sequences are required for faithful initiation of in vitro transcription of the ovalbumin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):879–883. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Kédinger C., Corden J., Brison O., Chambon P. Specific in vitro initiation of transcription on conalbumin and ovalbumin genes and comparison with adenovirus-2 early and late genes. Nature. 1980 Jun 5;285(5764):367–373. doi: 10.1038/285367a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil P. A., Luse D. S., Segall J., Roeder R. G. Selective and accurate initiation of transcription at the Ad2 major late promotor in a soluble system dependent on purified RNA polymerase II and DNA. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):469–484. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westley B., Rochefort H. A secreted glycoprotein induced by estrogen in human breast cancer cell lines. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):353–362. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90621-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarucki-Schulz T., Tsai S. Y., Itakura K., Soberon X., Wallace R. B., Tsai M. J., Woo S. L., O'Malley B. W. Point mutagenesis of the ovalbumin gene promoter sequence and its effect on in vitro transcription. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):11070–11077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]