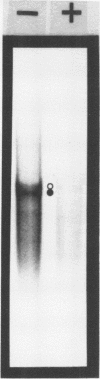
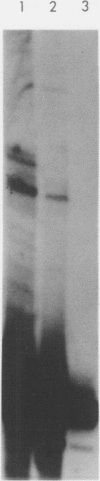
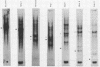
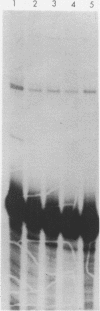
Abstract
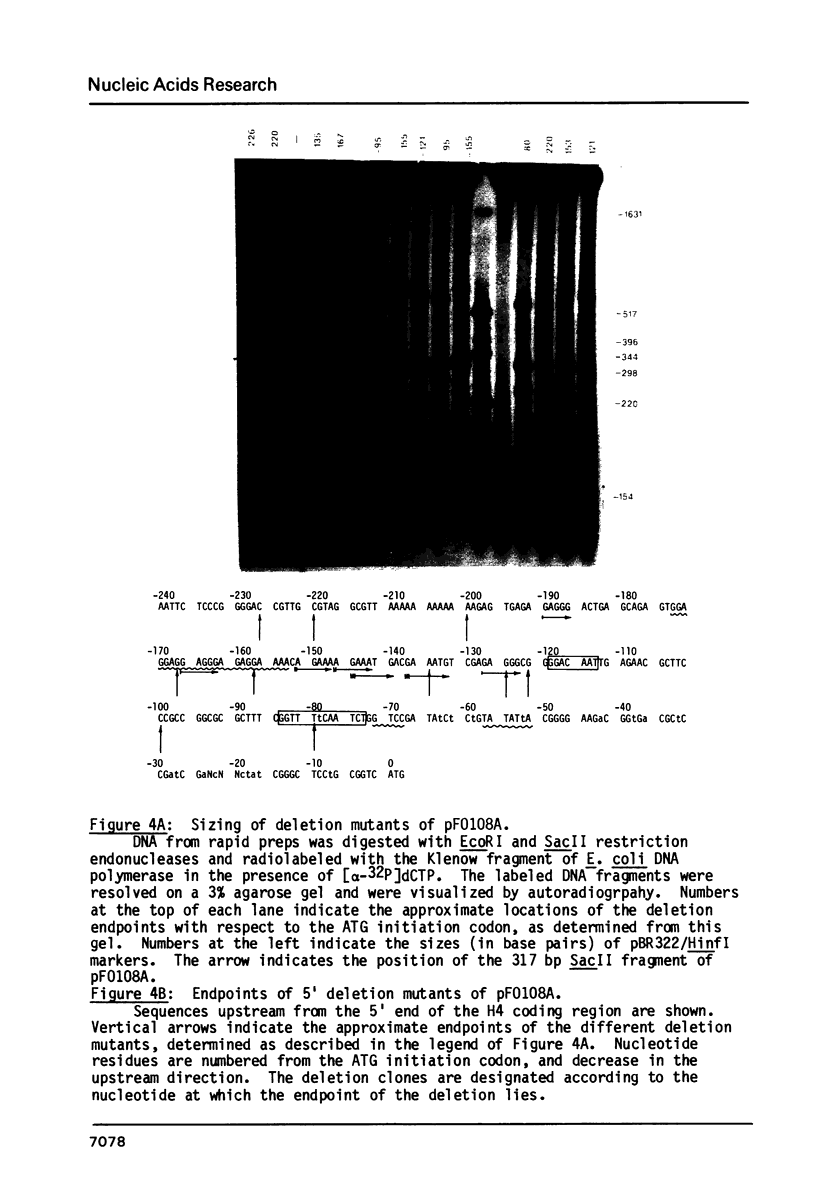
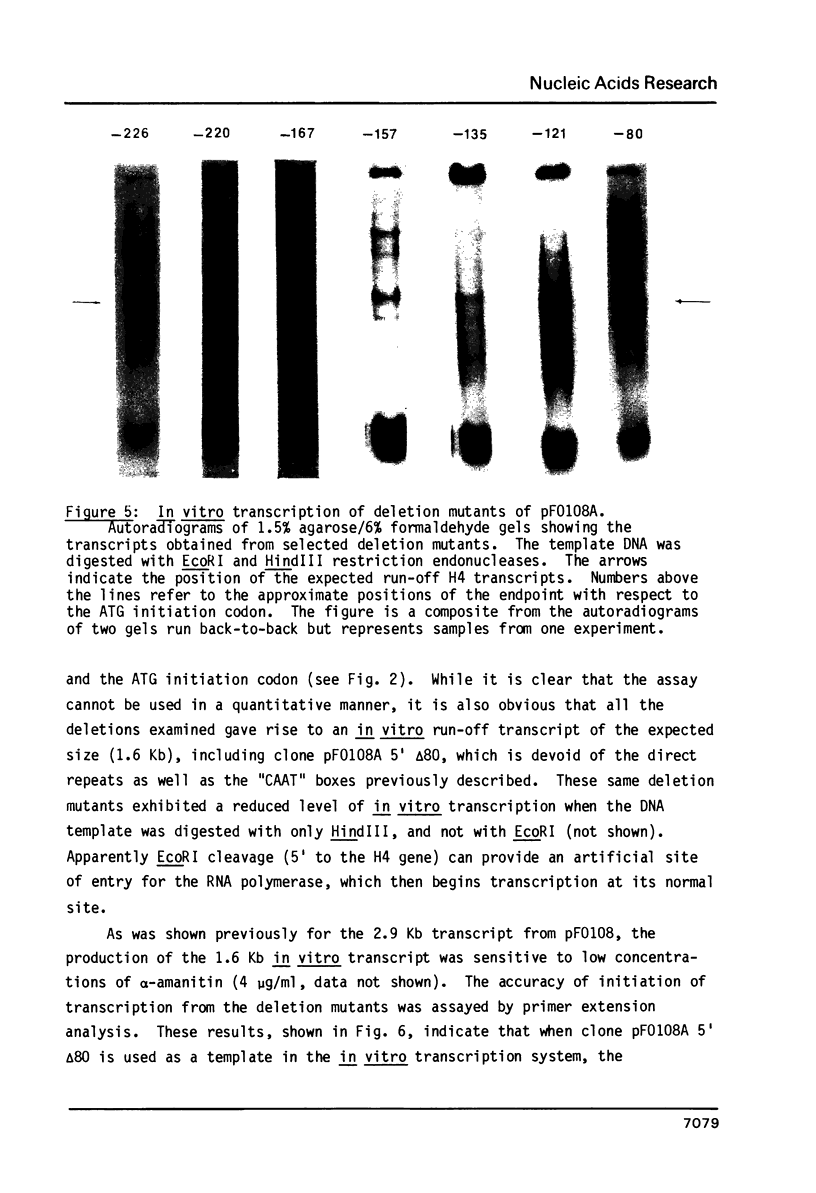
A human H4 histone gene was isolated and the nucleotide sequences of the mRNA coding as well as the 5' and 3' flanking regions were determined. No intervening sequences were found in this gene. A series of sequences which have been assigned putative regulatory roles in histone genes and/or in other genes were identified both upstream and downstream from the H4 histone protein coding region. Deletion mutants were constructed by BAL-31 nuclease digestion of sequences in the 5' flanking region of this H4 histone gene and were assayed in an in vitro transcription system. No regions upstream from the TATA box were required for site specific initiation in vitro. Data are presented which suggest that sequences located downstream from the 3' end of the coding region may influence the in vitro transcription of this human H4 histone gene.
Full text
PDF















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benoist C., Chambon P. In vivo sequence requirements of the SV40 early promotor region. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):304–310. doi: 10.1038/290304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., O'Hare K., Breathnach R., Chambon P. The ovalbumin gene-sequence of putative control regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):127–142. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calabretta B., Robberson D. L., Maizel A. L., Saunders G. F. mRNA in human cells contains sequences complementary to the Alu family of repeated DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6003–6007. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Properties of a supercoiled deoxyribonucleic acid-protein relaxation complex and strand specificity of the relaxation event. Biochemistry. 1970 Oct 27;9(22):4428–4440. doi: 10.1021/bi00824a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detke S., Stein J. L., Stein G. S. Synthesis of histone messenger RNAs by RNA polymerase II in nuclei from S phase HeLa S3 cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 May;5(5):1515–1528. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.5.1515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstratiadis A., Posakony J. W., Maniatis T., Lawn R. M., O'Connell C., Spritz R. A., DeRiel J. K., Forget B. G., Weissman S. M., Slightom J. L. The structure and evolution of the human beta-globin gene family. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):653–668. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90429-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. T., Pan J., Duncan C. H., Weissman S. M. Transcriptional analysis of interspersed repetitive polymerase III transcription units in human DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 11;9(5):1171–1189. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.5.1171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel J. D., Dodgson J. B. Histone genes are clustered but not tandemly repeated in the chicken genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2856–2860. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gall J. G., Stephenson E. C., Erba H. P., Diaz M. O., Barsacchi-Pilone G. Histone genes are located at the sphere loci of newt lampbrush chromosomes. Chromosoma. 1981;84(2):159–171. doi: 10.1007/BF00399128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray H. B., Jr, Ostrander D. A., Hodnett J. L., Legerski R. J., Robberson D. L. Extracellular nucleases of Pseudomonas BAL 31. I. Characterization of single strand-specific deoxyriboendonuclease and double-strand deoxyriboexonuclease activities. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Sep;2(9):1459–1492. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.9.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. Delimitation of far upstream sequences required for maximal in vitro transcription of an H2A histone gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):297–301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. Spacer DNA sequences upstream of the T-A-T-A-A-A-T-A sequence are essential for promotion of H2A histone gene transcription in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7102–7106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld G. C., Shewmaker C. K., Jat P., Flavell R. A. Localization of DNA sequences necessary for transcription of the rabbit beta-globin gene in vitro. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):215–226. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90246-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruss P., Dhar R., Khoury G. Simian virus 40 tandem repeated sequences as an element of the early promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):943–947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. P., Wells J. R. Isolation of a genomal clone containing chicken histone genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 11;7(7):1787–1798. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.7.1787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N., Zernik M., Roeder R. G. The structure of the human histone genes: clustered but not tandemly repeated. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):661–668. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90092-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel C. C., Birnstiel M. L. The organization and expression of histone gene families. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):301–313. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedes L. H. Histone genes and histone messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:837–870. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Robins A. J., Gait M. J., Titmas R. C., Wells J. R. Chicken histone H5: selection of a cDNA recombinant using an extended synthetic primer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 11;10(5):1495–1502. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.5.1495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtler A. C., Detke S., Phillips I. R., Stein G. S., Stein J. L. Multiple forms of H4 histone mRNA in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1942–1946. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtler A. C., Sierra F., Clark S., Wells J. R., Stein J. L., Stein G. S. Multiple H4 histone mRNAs of HeLa cells are encoded in different genes. Nature. 1982 Jul 8;298(5870):195–198. doi: 10.1038/298195a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Colozzo M. T. Synthesis in vitro of an exceptionally long RNA transcript promoted by an AluI sequence. Nature. 1982 Nov 25;300(5890):376–379. doi: 10.1038/300376a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Cano A., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. DNA-dependent transcription of adenovirus genes in a soluble whole-cell extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3855–3859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonell M. W., Simon M. N., Studier F. W. Analysis of restriction fragments of T7 DNA and determination of molecular weights by electrophoresis in neutral and alkaline gels. J Mol Biol. 1977 Feb 15;110(1):119–146. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80102-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon P., Parker V., Gluzman Y., Maniatis T. Identification of DNA sequences required for transcription of the human alpha 1-globin gene in a new SV40 host-vector system. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):279–288. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90411-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overton G. C., Weinberg E. S. Length and sequence heterogeneity of the histone gene repeat unit of the sea urchin, S. purpuratus. Cell. 1978 Jun;14(2):247–257. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90111-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan J., Elder J. T., Duncan C. H., Weissman S. M. Structural analysis of interspersed repetitive polymerase III transcription units in human DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 11;9(5):1151–1170. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Shander M. H., Manley J. L., Gefter M. L., Maniatis T. Structure and in vitro transcription of human globin genes. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1329–1336. doi: 10.1126/science.6158093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rave N., Crkvenjakov R., Boedtker H. Identification of procollagen mRNAs transferred to diazobenzyloxymethyl paper from formaldehyde agarose gels. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 10;6(11):3559–3567. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.11.3559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler-Tuyns A., Birnstiel M. L. Structure and expression in L-cells of a cloned H4 histone gene of the mouse. J Mol Biol. 1981 Oct 5;151(4):607–625. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90426-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sierra F., Leza A., Marashi F., Plumb M., Rickles R., Van Dyke T., Clark S., Wells J., Stein G. S., Stein J. L. Human histone genes are interspersed with members of the Alu family and with other transcribed sequences. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jan 29;104(2):785–792. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90706-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sierra F., Lichtler A., Marashi F., Rickles R., Van Dyke T., Clark S., Wells J., Stein G., Stein J. Organization of human histone genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1795–1799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tullis R. H., Rubin H. Calcium protects DNase I from proteinase K: a new method for the removal of contaminating RNase from DNase I. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):260–264. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90519-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Shine J., Chirgwin J., Pictet R., Tischer E., Rutter W. J., Goodman H. M. Rat insulin genes: construction of plasmids containing the coding sequences. Science. 1977 Jun 17;196(4296):1313–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.325648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahli W., Ryffel G. U., Wyler T., Jaggi F. B., Weber R., Dawid I. B. Cloning and characterization of synthetic sequences from the Xenopus iaevis vitellogenin structural gene. Dev Biol. 1978 Dec;67(2):371–383. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90207-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Kédinger C., Corden J., Brison O., Chambon P. Specific in vitro initiation of transcription on conalbumin and ovalbumin genes and comparison with adenovirus-2 early and late genes. Nature. 1980 Jun 5;285(5764):367–373. doi: 10.1038/285367a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zernik M., Heintz N., Boime I., Roeder R. G. Xenopus laevis histone genes: variant H1 genes are present in different clusters. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):807–815. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90557-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dongen W., de Laaf L., Zaal R., Moorman A., Destrée O. The organization of the histone genes in the genome of Xenopus laevis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 25;9(10):2297–2311. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.10.2297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]