Abstract
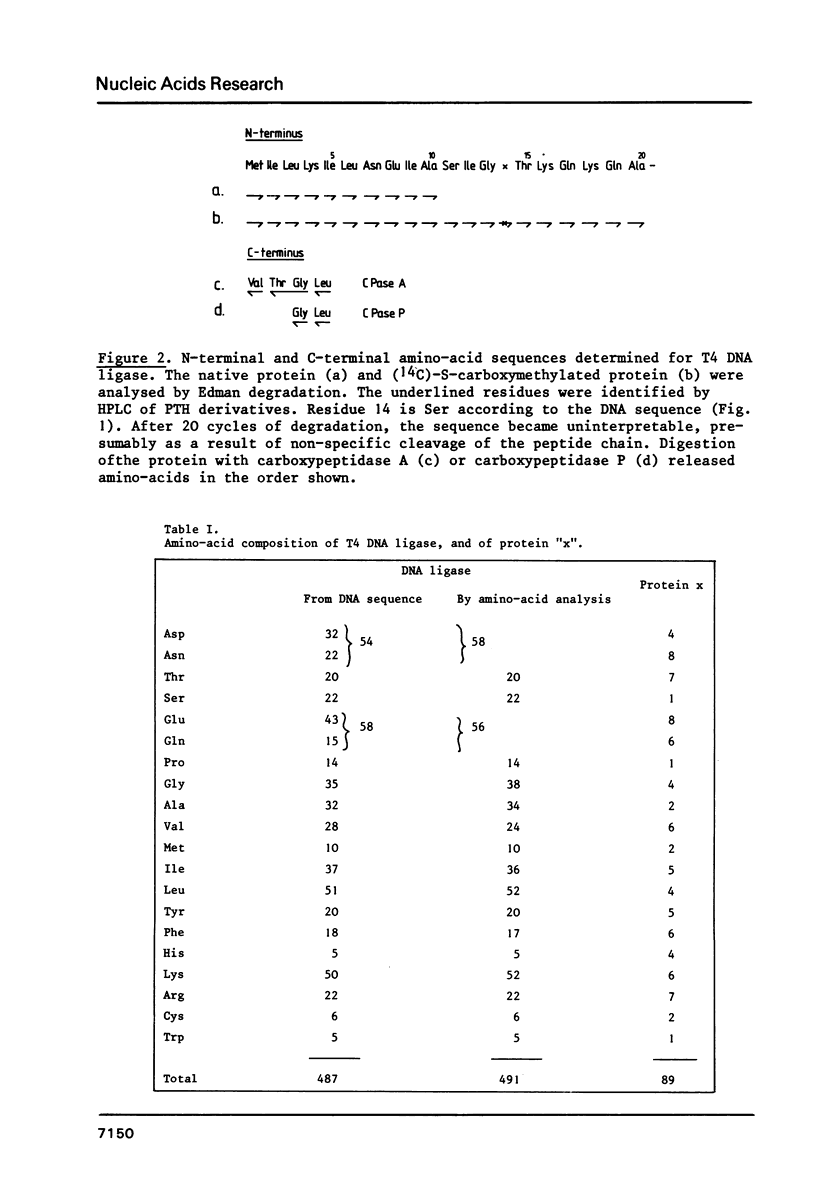
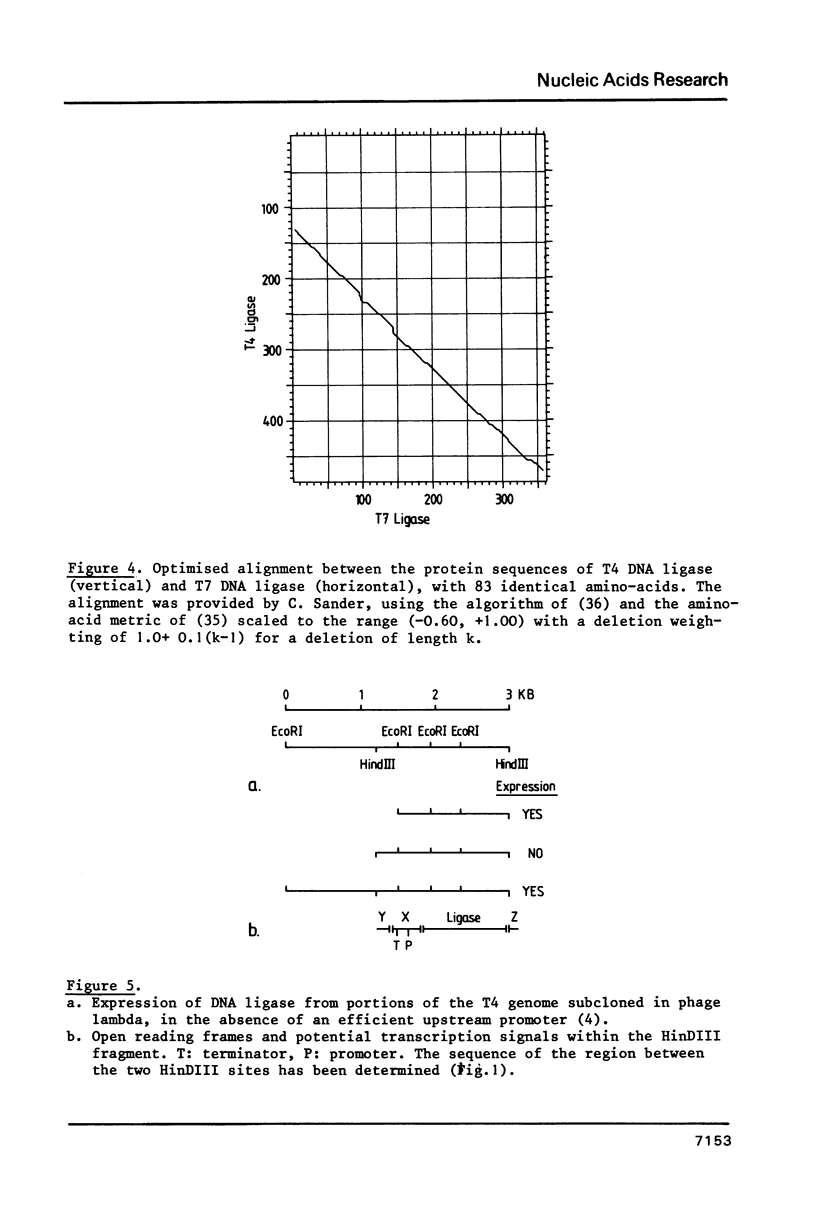
The primary structure of phage T4 DNA ligase has been determined by DNA sequencing of a cloned restriction fragment containing its gene, and partial amino acid sequence analysis of the protein. The molecule has a Mr of 55,230, and contains 487 amino acids. The DNA sequence may also encode all of one and parts of two other, hitherto unidentified, T4 proteins. The four genes are closely packed, with overlaps between terminator and initiator codons of adjacent genes. Potential terminator and promoter sites for transcription are located within the coding sequence of one of the genes.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Betlach M. C., Boyer H. W. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. I. Ampicillin-resistant derivatives of the plasmid pMB9. Gene. 1977;2(2):75–93. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(77)90074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broker T. R., Doermann A. H. Molecular and genetic recombination of bacteriophage T4. Annu Rev Genet. 1975;9:213–244. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.09.120175.001241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Nucleotide sequence from the genetic left end of bacteriophage T7 DNA to the beginning of gene 4. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 5;148(4):303–330. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90178-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukada K., Abelson J. DNA sequence of a T4 transfer RNA gene cluster. J Mol Biol. 1980 May 25;139(3):377–391. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90136-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garoff H., Ansorge W. Improvements of DNA sequencing gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Aug;115(2):450–457. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90031-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gumport R. I., Lehman I. R. Structure of the DNA ligase-adenylate intermediate: lysine (epsilon-amino)-linked adenosine monophosphoramidate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Oct;68(10):2559–2563. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.10.2559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRS C. H. The oxidation of ribonuclease with performic acid. J Biol Chem. 1956 Apr;219(2):611–621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knopf K. W. Simple isolation method and assay for T4 DNA ligase and characterization of the purified enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Feb 15;73(1):33–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11289.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kröger M., Hobom G. A chain of interlinked genes in the ninR region of bacteriophage lambda. Gene. 1982 Nov;20(1):25–38. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90084-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulbe K. D. Micropolyamide thin-layer chromatography of phenylthiohydantoin amino acids (PTH) at subnanomolar level. A rapid microtechnique for simultaneous multisample identification after automated Edman degradations. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jun;59(2):564–573. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90310-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan A. D. Tests for comparing related amino-acid sequences. Cytochrome c and cytochrome c 551 . J Mol Biol. 1971 Oct 28;61(2):409–424. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90390-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray N. E., Bruce S. A., Murray K. Molecular cloning of the DNA ligase gene from bacteriophage T4. II. Amplification and preparation of the gene product. J Mol Biol. 1979 Aug 15;132(3):493–505. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90271-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt T., Yanofsky C. An intercistronic region and ribosome-binding site in bacterial messenger RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2399–2403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt D., Laws P., Griffith J. Complex of bacteriophage M13 single-stranded DNA and gene 5 protein. J Mol Biol. 1974 Feb 5;82(4):425–439. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90239-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remaut E., Tsao H., Fiers W. Improved plasmid vectors with a thermoinducible expression and temperature-regulated runaway replication. Gene. 1983 Apr;22(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90069-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Hong G. F., Hill D. F., Petersen G. B. Nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage lambda DNA. J Mol Biol. 1982 Dec 25;162(4):729–773. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90546-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffler J. J., Tsugita A., Linden G., Schweitz H., Lazdunski M. The amino acid sequence of toxin V from Anemonia sulcata. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jul 16;107(1):272–278. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91700-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schürmann P., Maeda K., Tsugita A. Isomers in thioredoxins of spinach chloroplasts. Eur J Biochem. 1981 May;116(1):37–45. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05297.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sgaramella V., Van de Sande J. H., Khorana H. G. Studies on polynucleotides, C. A novel joining reaction catalyzed by the T4-polynucleotide ligase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1468–1475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Simpson R. B., Gilbert W. E. coli RNA polymerase interacts homologously with two different promoters. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):269–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90613-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. F., Waterman M. S. Identification of common molecular subsequences. J Mol Biol. 1981 Mar 25;147(1):195–197. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90087-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. A new computer method for the storage and manipulation of DNA gel reading data. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 25;8(16):3673–3694. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.16.3673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarr G. E., Beecher J. F., Bell M., McKean D. J. Polyquarternary amines prevent peptide loss from sequenators. Anal Biochem. 1978 Feb;84(2):622–7?0=ENG. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90086-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsugita A., Scheffler J. J. A rapid method for acid hydrolysis of protein with a mixture of trifluoroacetic acid and hydrochloric acid. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Jun;124(3):585–588. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06634.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson G. G., Murray N. E. Molecular cloning of the DNA ligase gene from bacteriophage T4. I. Characterisation of the recombinants. J Mol Biol. 1979 Aug 15;132(3):471–491. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90270-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittmann-Liebold B. Amino acid sequence studies on ten ribosomal proteins of Escherichia coli with an improved sequenator equipped with an automatic conversion device. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1973 Oct-Nov;354(10-11):1415–1431. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1973.354.2.1415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


