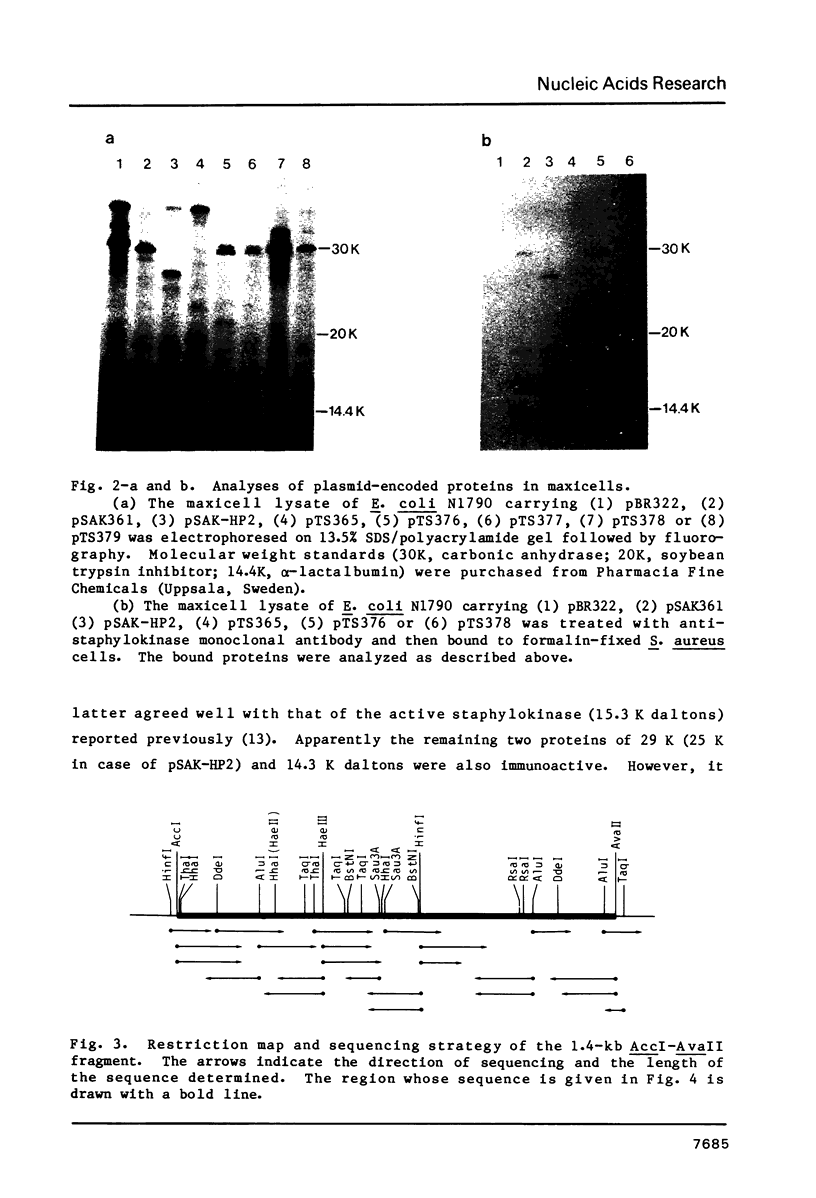
Abstract
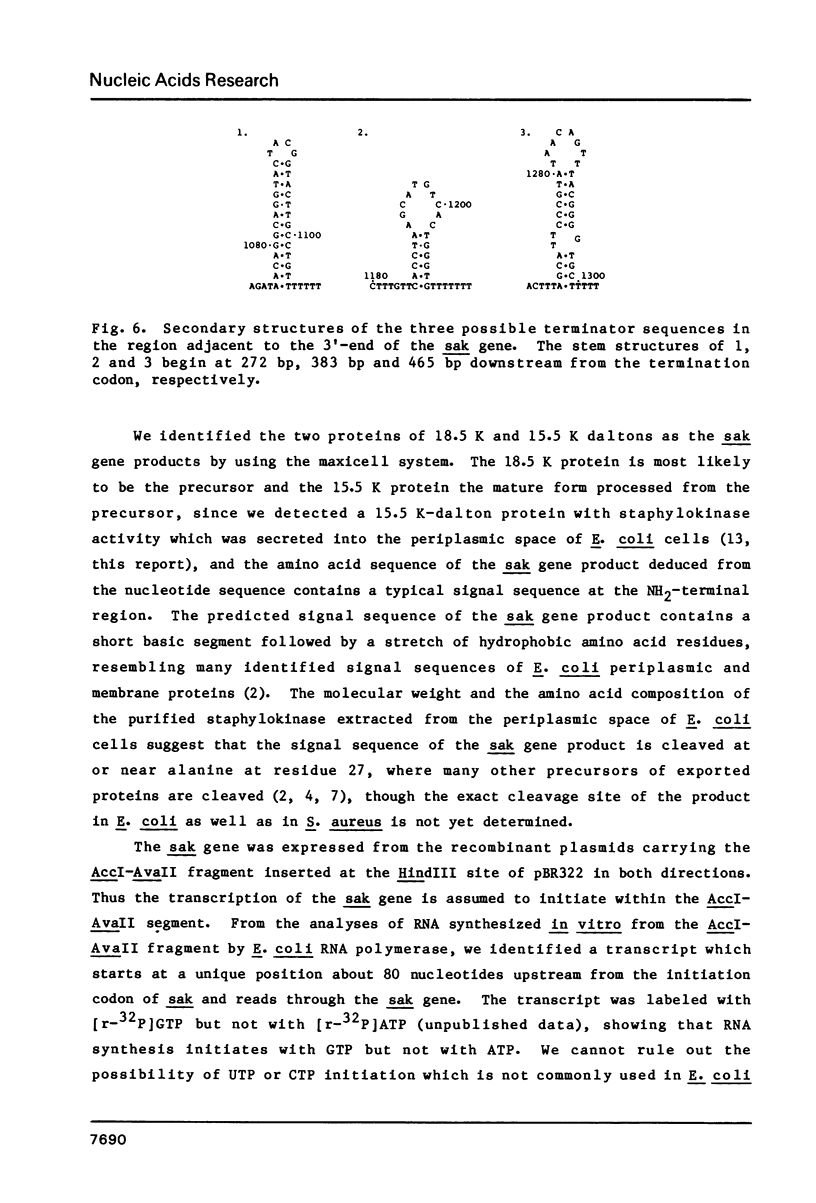
We have determined the entire nucleotide sequence of a 1,4-kilobase segment containing the staphylokinase gene, sak, molecularly cloned from the bacteriophage S phi-C genome of Staphylococcus aureus. The probable coding region is 489 base pairs long and these base pairs are translated into a polypeptide of 163 amino acid residues (Mr = 18,490) with a presumed signal sequence of 27 amino acid residues at the NH2-terminal end. In regions adjacent to the sak structural gene a possible promoter sequence and three possible terminator sequences for transcription were found about 100 base pairs upstream from the initiation codon and about 300, 400, and 500 base pairs downstream from the termination codon, respectively; they are active in an in vitro transcription system using Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. The immunoactive 18,500-dalton and 15,500-dalton proteins corresponding to a precursor form before secretion and a mature form after secretion of the sak gene products, respectively, were identified by the E. coli maxicell system.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B. D., Tai P. C. The mechanism of protein secretion across membranes. Nature. 1980 Jan 31;283(5746):433–438. doi: 10.1038/283433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayhoff M. O., Barker W. C., Hunt L. T. Establishing homologies in protein sequences. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:524–545. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91049-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duggleby C. J., Jones S. A. Cloning and expression of the Staphylococcus aureus protein A gene in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 25;11(10):3065–3076. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.10.3065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emr S. D., Hall M. N., Silhavy T. J. A mechanism of protein localization: the signal hypothesis and bacteria. J Cell Biol. 1980 Sep;86(3):701–711. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.3.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray O., Chang S. Molecular cloning and expression of Bacillus licheniformis beta-lactamase gene in Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):422–428. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.422-428.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2237–2255. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horii T., Ogawa T., Ogawa H. Nucleotide sequence of the lexA gene of E. coli. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):689–697. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90432-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson K. W., Tang J. Complete amino acid sequence of streptokinase and its homology with serine proteases. Biochemistry. 1982 Dec 21;21(26):6620–6625. doi: 10.1021/bi00269a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroyer J., Chang S. The promoter-proximal region of the Bacillus licheniformis penicillinase gene: Nucleotide sequence and predicted leader peptide sequence. Gene. 1981 Dec;15(4):343–347. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90177-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löfdahl S., Guss B., Uhlén M., Philipson L., Lindberg M. Gene for staphylococcal protein A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):697–701. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin J. R., Murray C. L., Rabinowitz J. C. Unique features in the ribosome binding site sequence of the gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus beta-lactamase gene. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11283–11291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelis S., Beckwith J. Mechanism of incorporation of cell envelope proteins in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1982;36:435–465. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.36.100182.002251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran C. P., Jr, Lang N., LeGrice S. F., Lee G., Stephens M., Sonenshein A. L., Pero J., Losick R. Nucleotide sequences that signal the initiation of transcription and translation in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(3):339–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00729452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neugebauer K., Sprengel R., Schaller H. Penicillinase from Bacillus licheniformis: nucleotide sequence of the gene and implications for the biosynthesis of a secretory protein in a Gram-positive bacterium. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 11;9(11):2577–2588. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.11.2577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen J. B., Lampen J. O. Membrane-bound penicillinases in Gram-positive bacteria. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4490–4495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palva I., Pettersson R. F., Kalkkinen N., Lehtovaara P., Sarvas M., Söderlund H., Takkinen K., Käriäinen L. Nucleotide sequence of the promoter and NH2-terminal signal peptide region of the alpha-amylase gene from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Gene. 1981 Oct;15(1):43–51. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90103-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sako T., Sawaki S., Sakurai T., Ito S., Yoshizawa Y., Kondo I. Cloning and expression of the staphylokinase gene of Staphylococcus aureus in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;190(2):271–277. doi: 10.1007/BF00330650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Hack A. M., Rupp W. D. Simple method for identification of plasmid-coded proteins. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):692–693. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.692-693.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimotsu H., Kawamura F., Kobayashi Y., Saito H. Early sporulation gene spo0F: nucleotide sequence and analysis of gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):658–662. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. B. Host specificity of DNA produced by Escherichia coli: bacterial mutations affecting the restriction and modification of DNA. J Mol Biol. 1966 Mar;16(1):118–133. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80267-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang M., Galizzi A., Henner D. Nucleotide sequence of the amylase gene from Bacillus subtilis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 25;11(2):237–249. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.2.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]