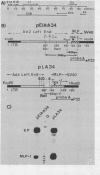
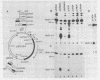
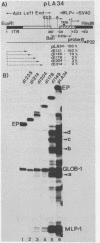
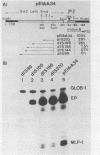
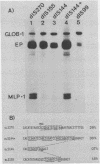
Abstract
A chimeric recombinant, containing the 270 bp left-terminal fragment of Adenovirus-2 (Ad2) inserted upstream from the -34 to +33 Ad2 major late promoter (Ad2MLP) element, has been used to characterize the transcription stimulatory element which is located at least 231 bp upstream from the E1A capsite in the left-end of Ad2 (Ref. 1). We demonstrate that this element, which acts in cis, possesses several properties characteristic of transcriptional enhancers. Firstly, it potentiates initiation of transcription from the capsite of the heterologous Ad2MLP and from "cryptic" sites often preceded by TATA box-like sequences. Secondly, although there is no critical distance requirement between the enhancer element and the Ad2MLP, the extent of stimulation decreases as the distance between the two element increases. However, in contrast to the other known viral or cellular enhancers which are bidirectional, the Ad2 enhancer is unidirectional, i.e. it potentiates the Ad2MLP element only when it is inserted in its "natural" orientation with respect to the direction of transcription. Using two convergent series of deletions, we have localized the Ad2 enhancer element within a 24 bp segment located at approximately 160 bp from the Ad2 left-end, i.e. 340 bp upstream from the E1A capsite. This 24 bp segment contains a sequence which exhibits a striking homology with the consensus sequence of several viral and cellular enhancers.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banerji J., Olson L., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific cellular enhancer is located downstream of the joining region in immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):729–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerji J., Rusconi S., Schaffner W. Expression of a beta-globin gene is enhanced by remote SV40 DNA sequences. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):299–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90413-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., Chambon P. In vivo sequence requirements of the SV40 early promotor region. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):304–310. doi: 10.1038/290304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler V. L., Maler B. A., Yamamoto K. R. DNA sequences bound specifically by glucocorticoid receptor in vitro render a heterologous promoter hormone responsive in vivo. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):489–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90430-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Howley P. M., Levinson A. D., Seeburg P. H. The primary structure and genetic organization of the bovine papillomavirus type 1 genome. Nature. 1982 Oct 7;299(5883):529–534. doi: 10.1038/299529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhar R., McClements W. L., Enquist L. W., Vande Woude G. F. Nucleotide sequences of integrated Moloney sarcoma provirus long terminal repeats and their host and viral junctions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3937–3941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dierks P., van Ooyen A., Cochran M. D., Dobkin C., Reiser J., Weissmann C. Three regions upstream from the cap site are required for efficient and accurate transcription of the rabbit beta-globin gene in mouse 3T6 cells. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):695–706. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies S. D., Morrison S. L., Oi V. T., Tonegawa S. A tissue-specific transcription enhancer element is located in the major intron of a rearranged immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gingeras T. R., Sciaky D., Gelinas R. E., Bing-Dong J., Yen C. E., Kelly M. M., Bullock P. A., Parsons B. L., O'Neill K. E., Roberts R. J. Nucleotide sequences from the adenovirus-2 genome. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13475–13491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearing P., Shenk T. The adenovirus type 5 E1A transcriptional control region contains a duplicated enhancer element. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):695–703. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hen R., Sassone-Corsi P., Corden J., Gaub M. P., Chambon P. Sequences upstream from the T-A-T-A box are required in vivo and in vitro for efficient transcription from the adenovirus serotype 2 major late promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7132–7136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriegler M., Botchan M. Enhanced transformation by a simian virus 40 recombinant virus containing a Harvey murine sarcoma virus long terminal repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;3(3):325–339. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.3.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Khoury G., Gorman C., Howard B., Gruss P. Host-specific activation of transcription by tandem repeats from simian virus 40 and Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6453–6457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Berg L., Weiher H., Botchan M. Bovine papilloma virus contains an activator of gene expression at the distal end of the early transcription unit. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):1108–1122. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.1108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. Transcriptional control signals of a eukaryotic protein-coding gene. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):316–324. doi: 10.1126/science.6283634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercola M., Wang X. F., Olsen J., Calame K. Transcriptional enhancer elements in the mouse immunoglobulin heavy chain locus. Science. 1983 Aug 12;221(4611):663–665. doi: 10.1126/science.6306772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau P., Hen R., Wasylyk B., Everett R., Gaub M. P., Chambon P. The SV40 72 base repair repeat has a striking effect on gene expression both in SV40 and other chimeric recombinants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):6047–6068. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.6047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne T. F., Berk A. J. Far upstream initiation sites for adenovirus early region 1A transcription are utilized after the onset of viral DNA replication. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):594–599. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.594-599.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Baltimore D. Immunoglobulin gene transcription is activated by downstream sequence elements. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):741–748. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeda E., Arrand J. R., Smolar N., Griffin B. E. Sequence from early region of polyoma virus DNA containing viral replication origin and encoding small, middle and (part of) large T antigens. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):357–370. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90162-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Augereau P., Chambon P. The SV40 72 bp repeat preferentially potentiates transcription starting from proximal natural or substitute promoter elements. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):503–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90470-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Matthes H., Wintzerith M., Chambon P. Transcription from the SV40 early-early and late-early overlapping promoters in the absence of DNA replication. EMBO J. 1983;2(9):1605–1611. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01631.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiher H., König M., Gruss P. Multiple point mutations affecting the simian virus 40 enhancer. Science. 1983 Feb 11;219(4585):626–631. doi: 10.1126/science.6297005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaniv M. Enhancing elements for activation of eukaryotic promoters. Nature. 1982 May 6;297(5861):17–18. doi: 10.1038/297017a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Villiers J., Olson L., Tyndall C., Schaffner W. Transcriptional 'enhancers' from SV40 and polyoma virus show a cell type preference. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 20;10(24):7965–7976. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.24.7965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ormondt H., Maat J., Dijkema R. Comparison of nucleotide sequences of the early E1a regions for subgroups A, B and C of human adenoviruses. Gene. 1980 Dec;12(1-2):63–76. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90016-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]