Abstract
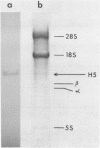
Using 3 overlapping cDNA clones we have determined the nucleotide sequence of chicken histone H5 mRNA. The mRNA does not contain the 23 base conserved sequence element that is present at the 3' end of cell-cycle regulated histone mRNAs. Although the RNA is polyadenylated it lacks the 3' AAUAAA sequence.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Stark G. R. Method for detection of specific RNAs in agarose gels by transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and hybridization with DNA probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5350–5354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appels R., Wells J. R. Synthesis and turnover of DNA-bound histone during maturation of avian red blood cells. J Mol Biol. 1972 Oct 14;70(3):425–434. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90550-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviles F. J., Chapman G. E., Kneale G. G., Crane-Robinson C., Bradbury E. M. The conformation of histone H5. Isolation and characterisation of the globular segment. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Aug 1;88(2):363–371. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12457.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey J. M., Davidson N. Methylmercury as a reversible denaturing agent for agarose gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birchmeier C., Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. Generation of authentic 3' termini of an H2A mRNA in vivo is dependent on a short inverted DNA repeat and on spacer sequences. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):739–745. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briand G., Kmiecik D., Sautiere P., Wouters D., Borie-Loy O., Biserte G., Mazen A., Champagne M. Chicken erythrocyte histone H5. IV. Sequence of the carboxy-termined half of the molecule (96 residues) and complete sequence. FEBS Lett. 1980 Apr 7;112(2):147–151. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80167-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busslinger M., Portmann R., Birnsteil M. L. A regulatory sequence near the 3' end of sea urchin histone genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jul 11;6(9):2997–3008. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.9.2997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald M., Shenk T. The sequence 5'-AAUAAA-3'forms parts of the recognition site for polyadenylation of late SV40 mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90521-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Wallis J. Colony hybridization. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:379–389. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel C. C., Birnstiel M. L. The organization and expression of histone gene families. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):301–313. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobart P., Crawford R., Shen L., Pictet R., Rutter W. J. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNAs encoding two distinct somatostatin precursors found in the endocrine pancreas of anglerfish. Nature. 1980 Nov 13;288(5787):137–141. doi: 10.1038/288137a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedes L. H. Histone genes and histone messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:837–870. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn L. J., Brown D. D. Nucleotide sequence of Xenopus borealis oocyte 5S DNA: comparison of sequences that flank several related eucaryotic genes. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1145–1156. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90042-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Robins A. J., Gait M. J., Titmas R. C., Wells J. R. Chicken histone H5: selection of a cDNA recombinant using an extended synthetic primer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 11;10(5):1495–1502. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.5.1495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald R. J., Crerar M. M., Swain W. F., Pictet R. L., Thomas G., Rutter W. J. Structure of a family of rat amylase genes. Nature. 1980 Sep 11;287(5778):117–122. doi: 10.1038/287117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molgaard H. V., Perucho M., Ruiz-Carrillo A. Histone H5 messenger RNA is polyadenylated. Nature. 1980 Jan 31;283(5746):502–504. doi: 10.1038/283502a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter A. G., Fellner P., Black D. N., Rowlands D. J., Harris T. J., Brown F. 3'-Terminal nucleotide sequences in the genome RNA of picornaviruses. Nature. 1978 Nov 16;276(5685):298–301. doi: 10.1038/276298a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickles R., Marashi F., Sierra F., Clark S., Wells J., Stein J., Stein G. Analysis of histone gene expression during the cell cycle in HeLa cells by using cloned human histone genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):749–753. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Vazquez R., Ruiz-Carillo A. Construction of chimeric plasmids containing histone H5 cDNA from hen erythrocyte. DNA sequence of a fragment derived from the 5' region of H5 mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 25;10(6):2093–2108. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.6.2093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu R. S., Bonner W. M. Separation of basal histone synthesis from S-phase histone synthesis in dividing cells. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):321–330. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90415-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaguchi M., Roy C., Dove M., Seligy V. Amino acid sequence homologies between H1 and H5 histones. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 May 9;76(1):100–106. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91673-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]