Abstract
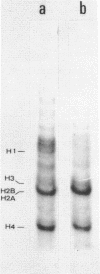
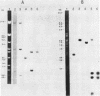
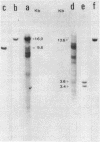
Using a cDNA clone for the histone H3 we have isolated, from two genomic libraries of Xenopus laevis and Xenopus tropicalis, clones containing four different histone gene clusters. The structural organization of X. laevis histone genes has been determined by restriction mapping, Southern blot hybridization and translation of the mRNAs which hybridize to the various restriction fragments. The arrangement of the histone genes in X. tropicalis has been determined by Southern analysis using X. laevis genomic fragments, containing individual genes, as probes. Histone genes are clustered in the genome of X. laevis and X. tropicalis and, compared to invertebrates, show a higher organization heterogeneity as demonstrated by structural analysis of the four genomic clones. In fact, the order of the genes within individual clusters is not conserved.
Full text
PDF







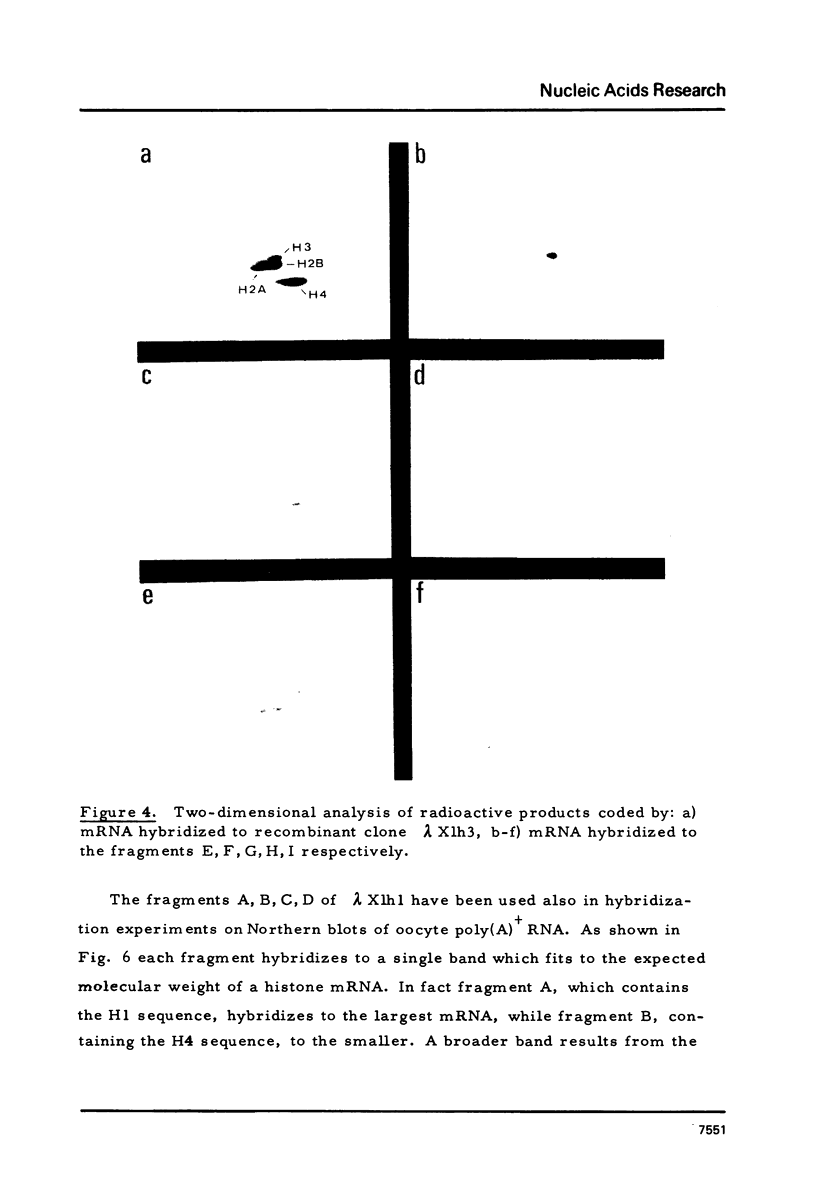
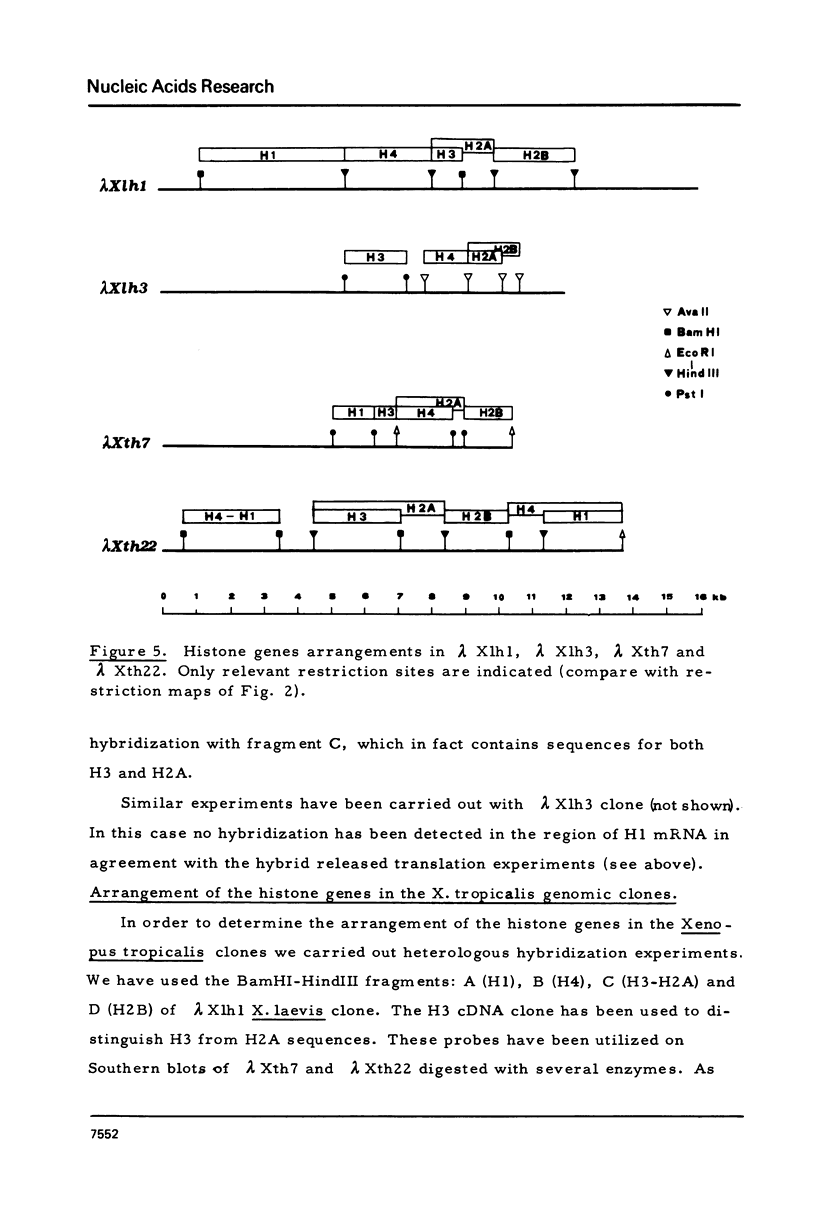

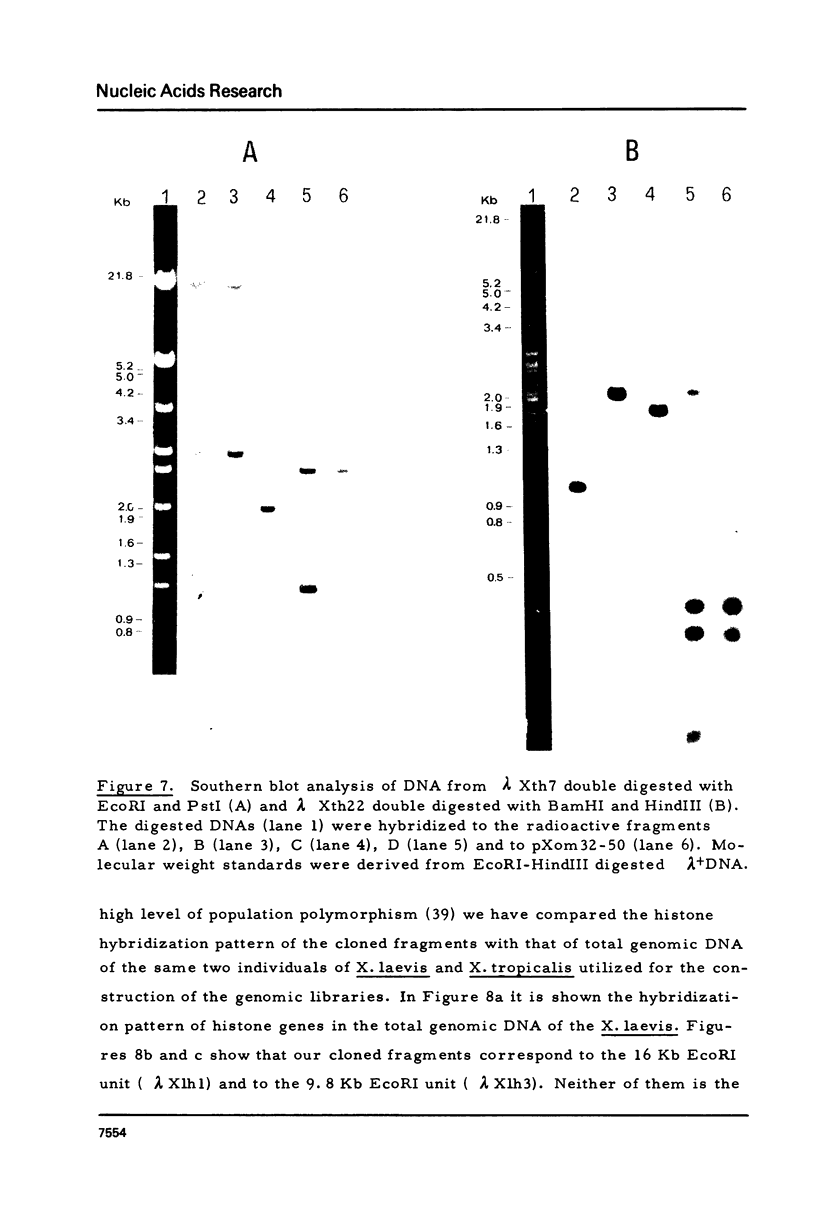





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alton T. H., Lodish H. F. Developmental changes in messenger RNAs and protein synthesis in Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev Biol. 1977 Oct 1;60(1):180–206. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amaldi F., Beccari E., Bozzoni I., Luo Z. X., Pierandrei-Amaldi P. Nucleotide sequences of cloned cDNA fragments specific for six Xenopus laevis ribosomal proteins. Gene. 1982 Mar;17(3):311–316. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90147-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattner F. R., Williams B. G., Blechl A. E., Denniston-Thompson K., Faber H. E., Furlong L., Grunwald D. J., Kiefer D. O., Moore D. D., Schumm J. W. Charon phages: safer derivatives of bacteriophage lambda for DNA cloning. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):161–169. doi: 10.1126/science.847462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozzoni I., Beccari E., Luo Z. X., Amaldi F. Xenopus laevis ribosomal protein genes: isolation of recombinant cDNA clones and study of the genomic organization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 11;9(5):1069–1086. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.5.1069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buongiorno-Nardelli M., Amaldi F., Beccari E., Junakovic N. Size of ribosomal DNA repeating units in Xenopus laevis: limited individual heterogeneity and extensive population polymorphism. J Mol Biol. 1977 Feb 15;110(1):105–117. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80101-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busslinger M., Portmann R., Irminger J. C., Birnstiel M. L. Ubiquitous and gene-specific regulatory 5' sequences in a sea urchin histone DNA clone coding for histone protein variants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Mar 11;8(5):957–977. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.5.957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. J., Krieg P. A., Wells J. R. Isolation of a clone containing human histone genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 10;9(7):1583–1590. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.7.1583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstratiadis A., Maniatis T., Kafatos F. C., Jeffrey A., Vournakis J. N. Full length and discrete partial reverse transcripts of globin and chorion mRNAs. Cell. 1975 Apr;4(4):367–378. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90157-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel J. D., Dodgson J. B. Histone genes are clustered but not tandemly repeated in the chicken genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2856–2860. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N., Zernik M., Roeder R. G. The structure of the human histone genes: clustered but not tandemly repeated. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):661–668. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90092-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel C. C., Birnstiel M. L. The organization and expression of histone gene families. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):301–313. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hereford L., Fahrner K., Woolford J., Jr, Rosbash M., Kaback D. B. Isolation of yeast histone genes H2A and H2B. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1261–1271. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90237-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hereford L., Fahrner K., Woolford J., Jr, Rosbash M., Kaback D. B. Isolation of yeast histone genes H2A and H2B. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1261–1271. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90237-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob E. Histone-gene reiteration in the genome of mouse. Eur J Biochem. 1976 May 17;65(1):275–284. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10415.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob E., Malacinski G., Birnstiel M. L. Reiteration frequency of the histone genes in the genome of the amphibian, Xenopus laevis. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Oct 1;69(1):45–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10856.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedes L. H., Birnstiel M. L. Reiteration and clustering of DNA sequences complementary to histone messenger RNA. Nat New Biol. 1971 Apr 7;230(14):165–169. doi: 10.1038/newbio230165a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedes L. H. Histone genes and histone messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:837–870. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levenson R. G., Marcu K. B. On the existence of polyadenylated histone mRNA in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Cell. 1976 Oct;9(2):311–322. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90121-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifton R. P., Goldberg M. L., Karp R. W., Hogness D. S. The organization of the histone genes in Drosophila melanogaster: functional and evolutionary implications. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):1047–1051. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moorman A. F., de Laaf R. T., Destrée O. H., Telford J., Birnstiel M. L. Histone genes from Xenopus laevis: molecular cloning and initial characterization. Gene. 1980 Aug;10(3):185–193. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90048-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panyim S., Chalkley R. High resolution acrylamide gel electrophoresis of histones. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Mar;130(1):337–346. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierandrei-Amaldi P., Beccari E. Messenger RNA for ribosomal proteins in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1980 May;106(2):603–611. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04608.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierandrei-Amaldi P., Campioni N., Beccari E., Bozzoni I., Amaldi F. Expression of ribosomal-protein genes in Xenopus laevis development. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):163–171. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90022-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portmann R., Schaffner W., Birnstiel M. Partial denaturation mapping of cloned histone DNA from the sea urchin Psammechinus miliaris. Nature. 1976 Nov 4;264(5581):31–34. doi: 10.1038/264031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts B. E., Paterson B. M. Efficient translation of tobacco mosaic virus RNA and rabbit globin 9S RNA in a cell-free system from commercial wheat germ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler-Tuyns A., Birnstiel M. L. Structure and expression in L-cells of a cloned H4 histone gene of the mouse. J Mol Biol. 1981 Oct 5;151(4):607–625. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90426-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sittman D. B., Chiu I. M., Pan C. J., Cohn R. H., Kedes L. H., Marzluff W. F. Isolation of two clusters of mouse histone genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4078–4082. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Birnstiel M. L. A simple method for DNA restriction site mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2387–2398. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson E. C., Erba H. P., Gall J. G. Histone gene clusters of the newt notophthalmus are separated by long tracts of satellite DNA. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):639–647. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90090-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver C. A., Gordon D. F., Kemper B. Introduction by molecular cloning of artifactual inverted sequences at the 5' terminus of the sense strand of bovine parathyroid hormone cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4073–4077. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wienand U., Schwarz Z., Feix G. Electrophoretic elution of nucleic acids from gels adapted for subsequent biological tests. Application for analysis of mRNAs from maize endosperm. FEBS Lett. 1979 Feb 15;98(2):319–323. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80208-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zernik M., Heintz N., Boime I., Roeder R. G. Xenopus laevis histone genes: variant H1 genes are present in different clusters. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):807–815. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90557-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dongen W., de Laaf L., Zaal R., Moorman A., Destrée O. The organization of the histone genes in the genome of Xenopus laevis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 25;9(10):2297–2311. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.10.2297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]