Abstract
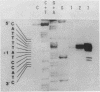
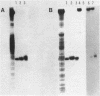
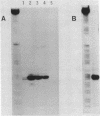
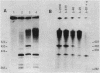
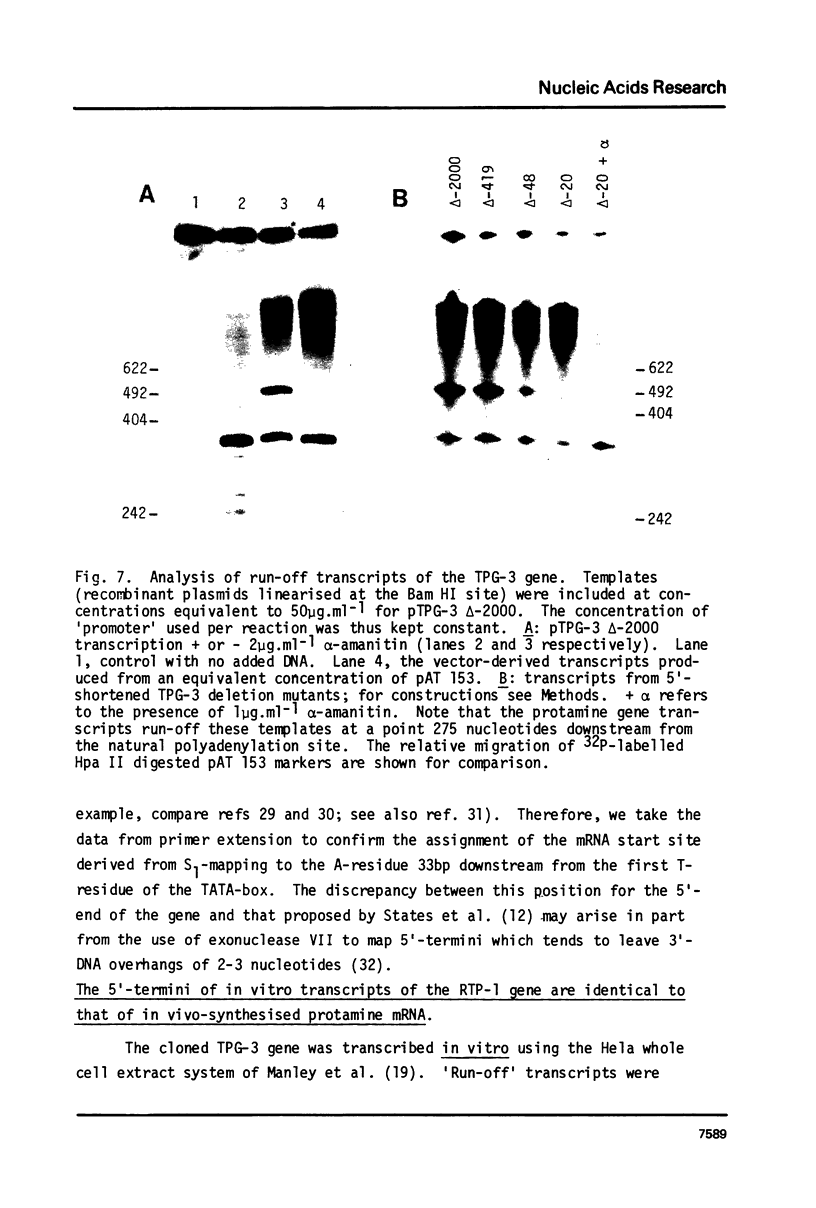
The mRNA start site of a cloned rainbow trout protamine gene (TPG-3) has been localised using S1-nuclease mapping and primer extension of in vivo synthesised trout testis poly A+-RNA. The presumptive cap site occurs within an AT-rich region, only 14 nucleotides from the start of the protein-coding sequence. Transcription of this protamine gene in vitro, using the Hela whole-cell extract system, generates products initiated at the same nucleotide as that used in vivo. In vitro transcription is abolished by deletion of sequences between -20 and -48, within which is a canonical TATA-box having an llbp homology with the strong chick conalbumin and Adenovirus-2 major late promoters (CTATAAAAGGG).
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corden J., Wasylyk B., Buchwalder A., Sassone-Corsi P., Kedinger C., Chambon P. Promoter sequences of eukaryotic protein-coding genes. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1406–1414. doi: 10.1126/science.6251548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P. L., Dixon G. H., Simoncsits A., Brownlee G. C. Sequences of large T1 ribonuclease-resistant oligoribonucleotides from protamine mRNA: the overall architecture of protamine mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 20;7(8):2323–2345. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.8.2323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favaloro J., Treisman R., Kamen R. Transcription maps of polyoma virus-specific RNA: analysis by two-dimensional nuclease S1 gel mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):718–749. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gedamu L., Chaconas G., van de Sande J. H., Dixon G. H. Studies on the heterogeneity of the 5' ends of the protamine mRNAs from rainbow trout testis. Biosci Rep. 1981 Jan;1(1):61–70. doi: 10.1007/BF01115150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gedamu L., Wosnick M. A., Connor W., Watson D. C., Dixon G. H., Iatrou K. Molecular analysis of the protamine multi-gene family in rainbow trout testis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 25;9(6):1463–1482. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.6.1463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Reddy V. B., Piatak M., Lebowitz P., Weissman S. M. Determination of RNA sequences by primer directed synthesis and sequencing of their cDNA transcripts. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):580–595. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65061-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Roeder R. G. Definition of a novel promoter for the major adenovirus-associated virus mRNA. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):231–242. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90171-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. Delimitation of far upstream sequences required for maximal in vitro transcription of an H2A histone gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):297–301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. Spacer DNA sequences upstream of the T-A-T-A-A-A-T-A sequence are essential for promotion of H2A histone gene transcription in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7102–7106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld G. C., de Boer E., Shewmaker C. K., Flavell R. A. DNA sequences necessary for transcription of the rabbit beta-globin gene in vivo. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):120–126. doi: 10.1038/295120a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld G. C., de Boer E., Shewmaker C. K., Flavell R. A. DNA sequences necessary for transcription of the rabbit beta-globin gene in vivo. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):120–126. doi: 10.1038/295120a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Diamond K. E., Knoppel E., Grunstein J. E. Comparison of the early histone H4 gene sequence of Strongylocentrotus purpuratus with maternal, early, and late histone H4 mRNA sequences. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 3;20(5):1216–1223. doi: 10.1021/bi00508a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel C., Irminger J. C., Bucher P., Birnstiel M. L. Sea urchin histone mRNA termini are located in gene regions downstream from putative regulatory sequences. Nature. 1980 May 15;285(5761):147–151. doi: 10.1038/285147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins J. R., Bishop J. O., Butterworth P. H. Molecular cloning of three major sequence species from Rainbow trout protamine mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 24;6(12):3805–3819. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.12.3805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins J. R. Sequence divergence of rainbow trout protamine mRNAs; comparison of coding and non-coding nucleotide sequences in three protamine cDNA plasmids. Nature. 1979 Jun 28;279(5716):809–811. doi: 10.1038/279809a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp D. J., Cory S., Adams J. M. Cloned pairs of variable region genes for immunoglobulin heavy chains isolated from a clone library of the entire mouse genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4627–4631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Cano A., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. DNA-dependent transcription of adenovirus genes in a soluble whole-cell extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3855–3859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. Transcriptional control signals of a eukaryotic protein-coding gene. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):316–324. doi: 10.1126/science.6283634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. High-efficiency cloning of full-length cDNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;2(2):161–170. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.2.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai M., Fujii-Kuriyama Y., Saito T., Muramatsu M. Closely related mRNA sequences of protamines in rainbow trout testis. J Biochem. 1981 Jun;89(6):1863–1868. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A., Berk A. J., Berget S. M. Transcription maps of adenovirus. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):750–768. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65071-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Simpson R. B., Gilbert W. E. coli RNA polymerase interacts homologously with two different promoters. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):269–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90613-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Reeder R. H. The nucleotide sequence of the initiation and termination sites for ribosomal RNA transcription in X. laevis. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):485–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- States J. C., Connor W., Wosnick M. A., Aiken J. M., Gedamu L., Dixon G. H. Nucleotide sequence of a protamine component CII gene of Salmo gairdnerii. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 11;10(15):4551–4563. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.15.4551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sures I., Levy S., Kedes L. H. Leader sequences of Strongylocentrotus purpuratus histone mRNAs start at a unique heptanucleotide common to all five histone genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1265–1269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziff E. B., Evans R. M. Coincidence of the promoter and capped 5' terminus of RNA from the adenovirus 2 major late transcription unit. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1463–1475. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90070-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]