Abstract
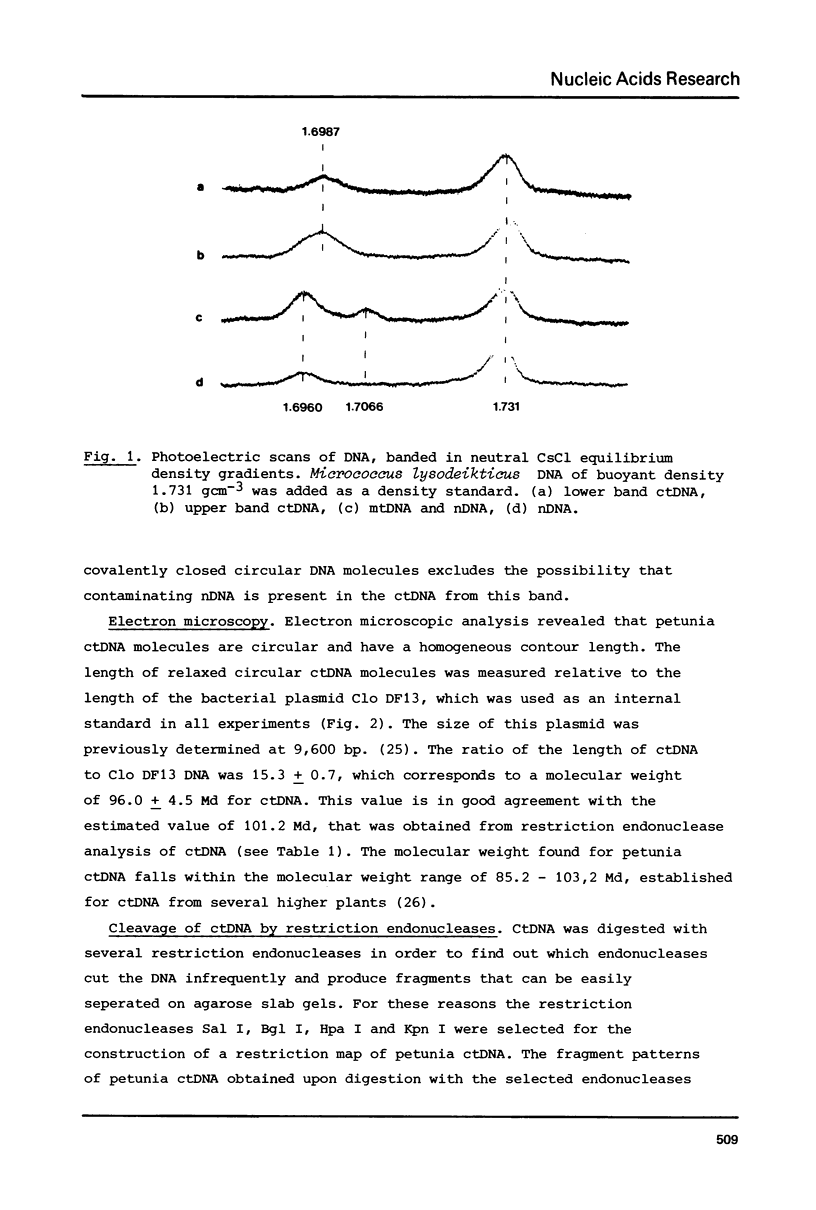
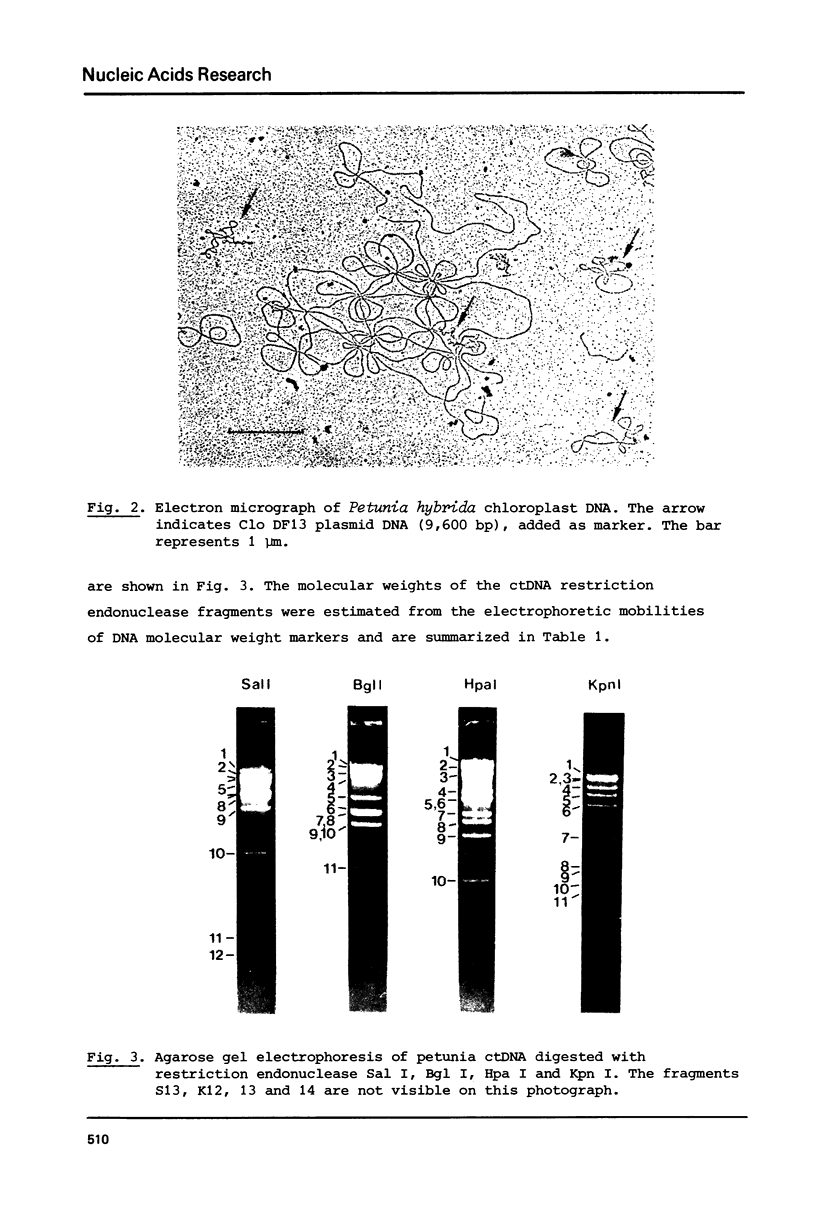
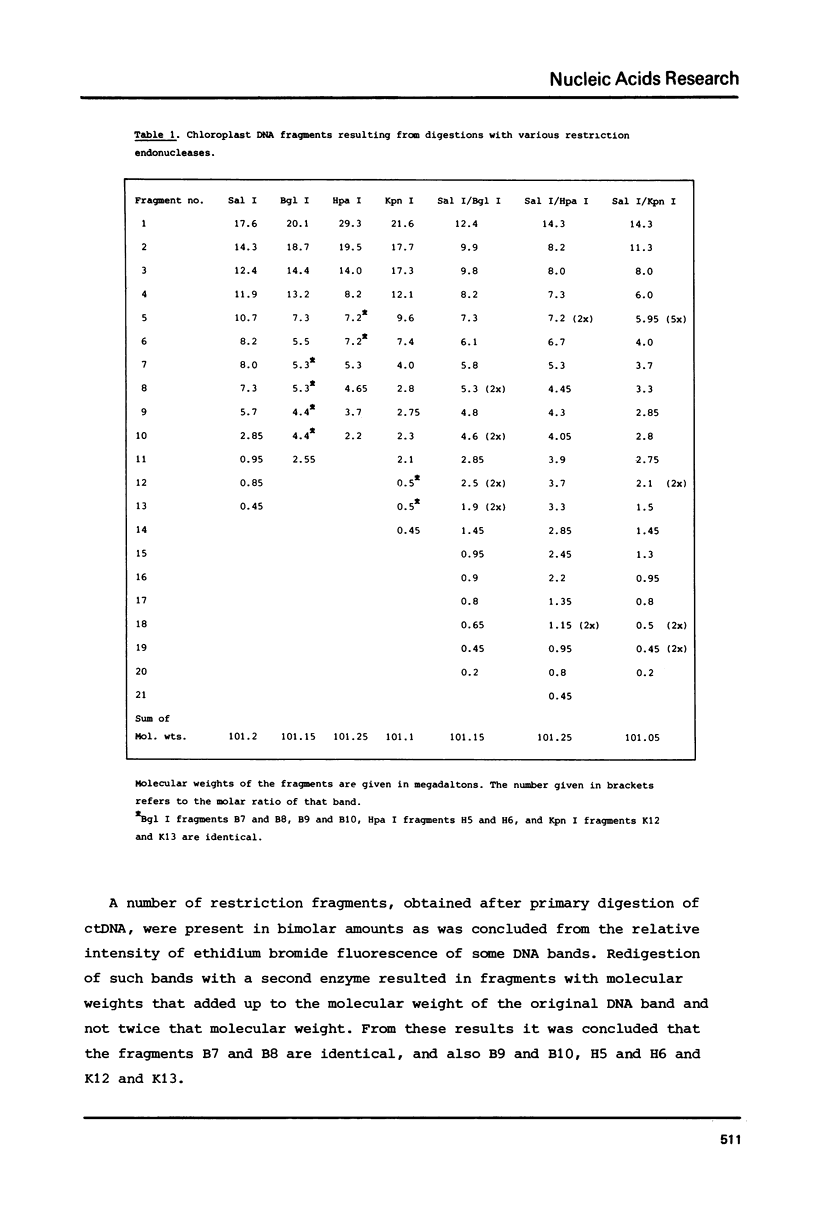
A procedure is developed for the isolation of intact chloroplast DNA (ctDNA) from Petunia hybrida. The molecular weight, calculated from contour length measurements, is 96.0 +/- 4.5 x 10(6) daltons. This value is in good agreement with the value of 101.2 x 10(6) daltons that was estimated from the electrophoretic mobilities of restriction endonuclease fragments of ctDNA. Analysis of petunia ctDNA in neutral CsCl gradients revealed the presence of only one type of DNA at a buoyant density of 1.6987 +/- 0.0005 gcm-3. This corresponds with a GC-content of 39.3 +/- 0.5%. A physical map of petunia ctDNA was constructed by using the restriction endonucleases Sal I, Bgl I, Hpa I and Kpn I. The map indicates that petunia ctDNA contains two copies of a sequence in an inverted orientation. The inverted repeat regions have a minimum length of 10 x 10(6) daltons. Hybridization data indicate that part of the inverted repeat regions contain the genes for chloroplast ribosomal RNAs.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bedbrook J. R., Bogorad L. Endonuclease recognition sites mapped on Zea mays chloroplast DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4309–4313. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedbrook J. R., Kolodner R., Bogorad L. Zea mays chloroplast ribosomal RNA genes are part of a 22,000 base pair inverted repeat. Cell. 1977 Aug;11(4):739–749. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90288-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. W., Hallick R. B. Restriction endonuclease map of Euglena gracilis chloroplast DNA. Biochemistry. 1977 Apr 19;16(8):1665–1671. doi: 10.1021/bi00627a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann R. G., Whitfeld P. R., Bottomley W. Construction of a SalI/PstI restriction map of spinach chloroplast DNA using low-gelling-temperature-agarose electrophoresis. Gene. 1980 Jan;8(2):179–191. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90036-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jurgenson J. E., Bourque D. P. Mapping of rRNA genes in an inverted repeat in Nicotiana tabacum chloroplast DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 25;8(16):3505–3516. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.16.3505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodner R., Tewari K. K. Inverted repeats in chloroplast DNA from higher plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):41–45. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodner R., Tewari K. K. The molecular size and conformation of the chloroplast DNA from higher plants. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Sep 1;402(3):372–390. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90273-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kool A. J., Pols C., Nijkamp H. J. Bacteriocinogenic Clo DF13 minicells of Escherichia coli synthesize a protein that accounts for immunity to bacteriocin Clo DF13: purification and characterization of the immunity protein. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Jul;8(1):67–75. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochaix J. D., Malnoe P. Anatomy of the chloroplast ribosomal DNA of Chlamydomonas reinhardii. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):661–670. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90034-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochaix J. D. Restriction endonuclease map of the chloroplast DNA of Chlamydomonas reinhardii. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 25;126(4):597–617. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHILDKRAUT C. L., MARMUR J., DOTY P. Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its buoyant density in CsCl. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jun;4:430–443. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitfeld P. R., Herrmann R. G., Bottomley W. Mapping of the ribosomal RNA genes on spinach chloroplast DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jun;5(6):1741–1751. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.6.1741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]