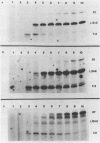
Abstract
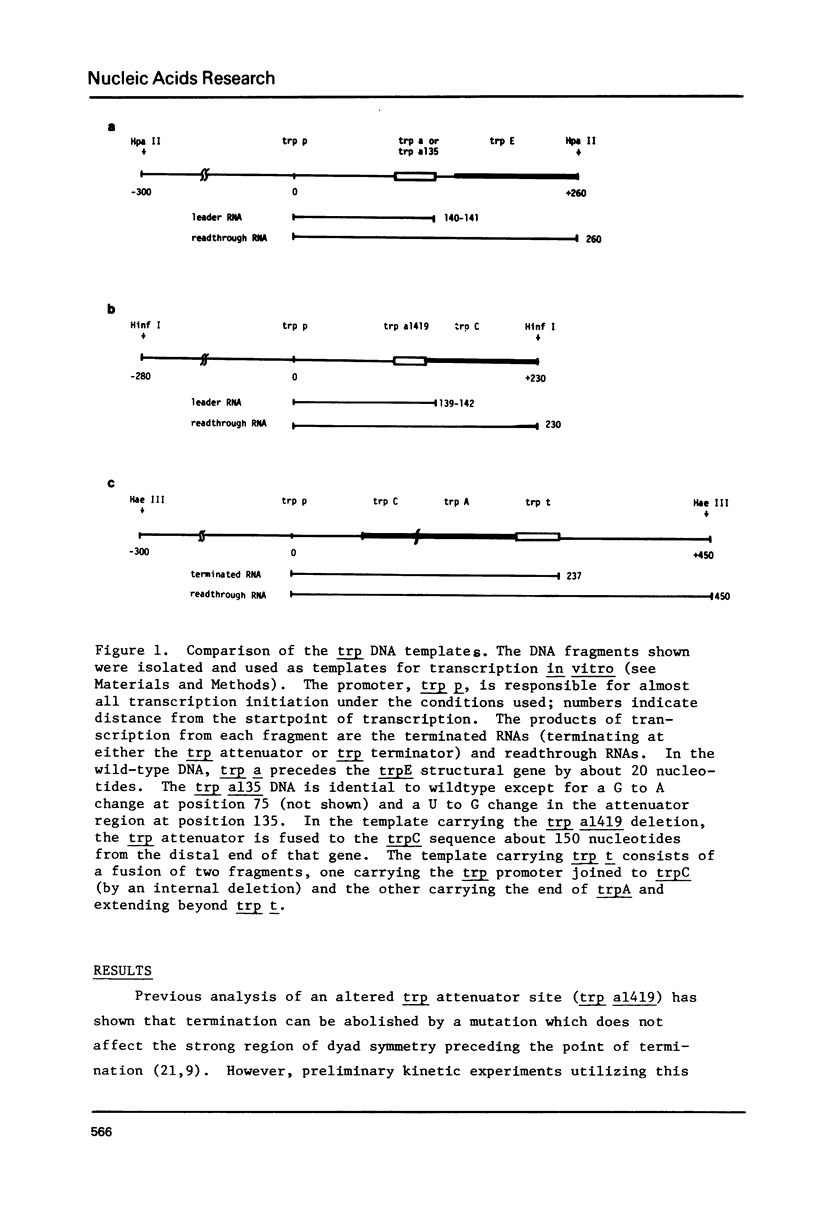
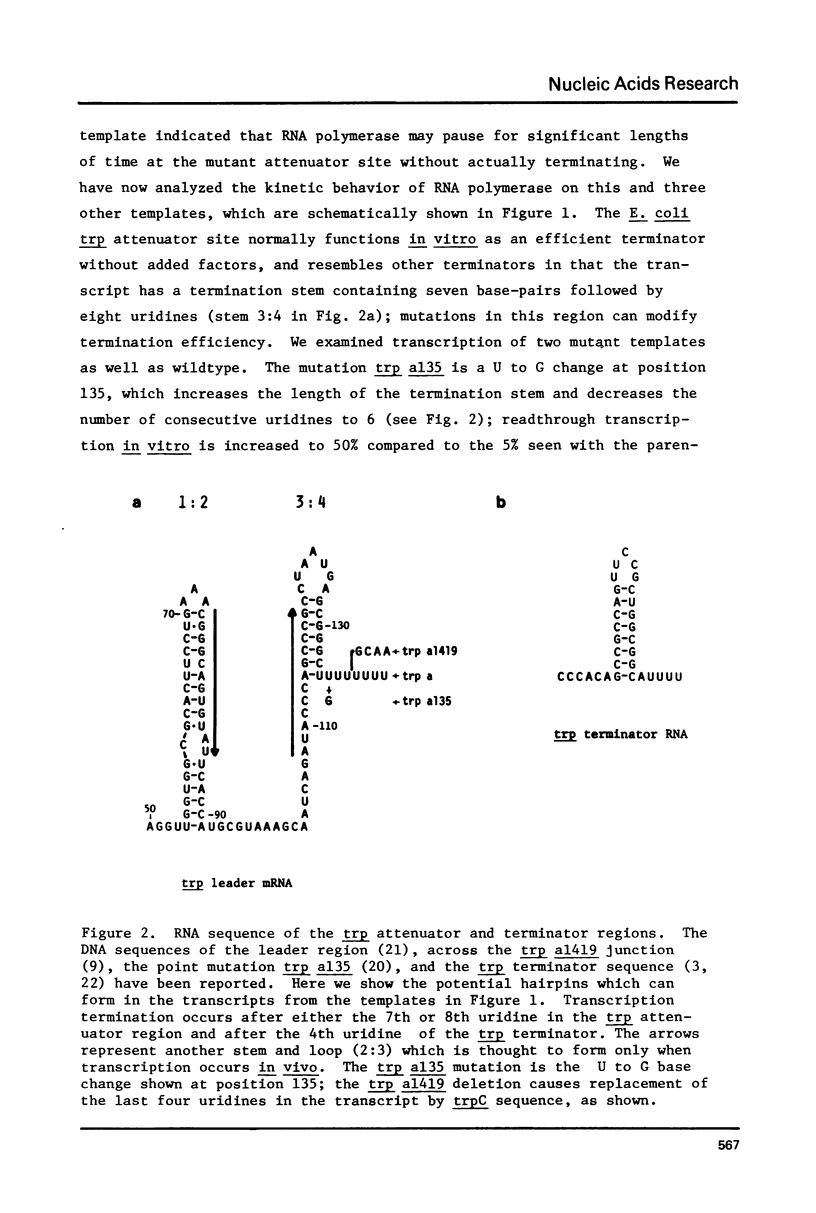
Termination of transcription by RNA polymerase at rho-independent sites appears to depend primarily upon two structural features, a region of GC-rich dyad symmetry in the DNA preceding the stop point and a stretch of uridines at the 3' end of the transcript. The possibility that the former might be responsible for slowing elongation prompted us to perform a kinetic analysis of transcription across the leader and terminator regions of the E. coli tryptophan (trp) operon. Regions where the elongation rate is dramatically slowed or stopped are identifiable because they generate discrete transcript hands on a gel. Species derived from pause sites, unlike those resulting from termination sites, are transient and detectable only within the first two minutes of transcription, since polymerase eventually resumes elongation. At two mutant trp attenuator sites (trp a135 and trp a1419), where termination is incomplete or absent in vitro, a substantial pause is nevertheless observed. Likewise, a significant pause occurs at trp t, the termination site at the end of the operon. Our experiments also reveal a major pause site at about position 90 in the trp leader sequence, just past a region of dyad symmetry. The RNA hairpin corresponding to this site is U-rich, and pausing is strongly enhanced by incorporation of BrUTP. In contrast, this analog does not affect pausing at the attenuator or terminator sites with hairpins that are GC-rich. These results strongly support the hypothesis that pausing of the polymerase is an obligatory prelude to rho-independent termination. Moreover, the termination event evidently results from consecutive but discrete responses to separate structural features of these sites.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adhya S., Gottesman M. Control of transcription termination. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:967–996. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.004535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adhya S., Sarkar P., Valenzuela D., Maitra U. Termination of transcription by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase: influence of secondary structure of RNA transcripts on rho-independent and rho-dependent termination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1613–1617. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand K., Korn L. J., Lee F., Yanofsky C. The attenuator of the tryptophan operon of Escherichia coli. Heterogeneous 3'-OH termini in vivo and deletion mapping of functions. J Mol Biol. 1977 Nov 25;117(1):227–247. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90032-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand K., Squires C., Yanofsky C. Transcription termination in vivo in the leader region of the tryptophan operon of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1976 May 15;103(2):319–337. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90315-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calva E., Burgess R. R. Characterization of a rho-dependent termination site within the cro gene of bacteriophage lambda. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):11017–11022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie G. E., Platt T. Gene structure in the tryptophan operon of Escherichia coli. Nucleotide sequence of trpC and the flanking intercistronic regions. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 5;142(4):519–530. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90261-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlix J. L., Horaist M. Existence and possible roles of transcriptional barriers in T7 DNA early region as shown by electron microscopy. Nature. 1975 Jul 24;256(5515):288–292. doi: 10.1038/256288a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlix J. L. Rho, a factor causing the modulation of early T7 genes transcription. Biochimie. 1974;56(5):693–701. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(74)80040-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnham P. J., Platt T. A model for transcription termination suggested by studies on the trp attenuator in vitro using base analogs. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):739–748. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90320-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. S., Platt T. The attenuator of the tryptophan operon in E.coli: rho-mediated release of RNA polymerase from a transcription termination complex in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Dec;5(12):4613–4623. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard B. H., de Crombrugghe B., Rosenberg M. Transcription in vitro of bacteriophage lambda 4S RNA: studies on termination and rho protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Apr;4(4):827–842. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.4.827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee F., Squires C. L., Squires C., Yanofsky C. Termination of transcription in vitro in the Escherichia coli tryptophan operon leader region. J Mol Biol. 1976 May 15;103(2):383–393. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90318-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee F., Yanofsky C. Transcription termination at the trp operon attenuators of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium: RNA secondary structure and regulation of termination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4365–4369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin F. H., Tinoco I., Jr DNA-RNA hybrid duplexes containing oligo(dA:rU) sequences are exceptionally unstable and may facilitate termination of transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 May 24;8(10):2295–2299. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.10.2295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills D. R., Dobkin C., Kramer F. R. Template-determined, variable rate of RNA chain elongation. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):541–550. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90022-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neff N. F., Chamberlin M. J. Termination of transcription by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase in vitro is affected by ribonucleoside triphosphate base analogs. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 10;253(7):2455–2460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxender D. L., Zurawski G., Yanofsky C. Attenuation in the Escherichia coli tryptophan operon: role of RNA secondary structure involving the tryptophan codon region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5524–5528. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. P., Conaway R. Ribonucleic acid release activity of transcription termination protein rho is dependent on the hydrolysis of nucleoside triphosphates. Biochemistry. 1980 Sep 2;19(18):4293–4299. doi: 10.1021/bi00559a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. W. Termination factor for RNA synthesis. Nature. 1969 Dec 20;224(5225):1168–1174. doi: 10.1038/2241168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D., Shimatake H., Brady C., Wulff D. L. The relationship between function and DNA sequence in an intercistronic regulatory region in phage lambda. Nature. 1978 Mar 30;272(5652):414–423. doi: 10.1038/272414a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shigesada K., Wu C. W. Studies of RNA release reaction catalyzed by E. coli transcription termination factor rho using isolated ternary transcription complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 11;8(15):3355–3369. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.15.3355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauffer G. V., Zurawski G., Yanofsky C. Single base-pair alterations in the Escherichia coli trp operon leader region that relieve transcription termination at the trp attenuator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4833–4837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu A. M., Chapman A. B., Platt T., Guarente L. P., Beckwith J. Deletions of distal sequence after termination of transcription at the end of the tryptophan operon in E. coli. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):829–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90073-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu A. M., Platt T. Transcription termination: nucleotide sequence at 3' end of tryptophan operon in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5442–5446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurawski G., Yanofsky C. Escherichia coli tryptophan operon leader mutations, which relieve transcription termination, are cis-dominant to trp leader mutations, which increase transcription termination. J Mol Biol. 1980 Sep 5;142(1):123–129. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90210-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]