Abstract
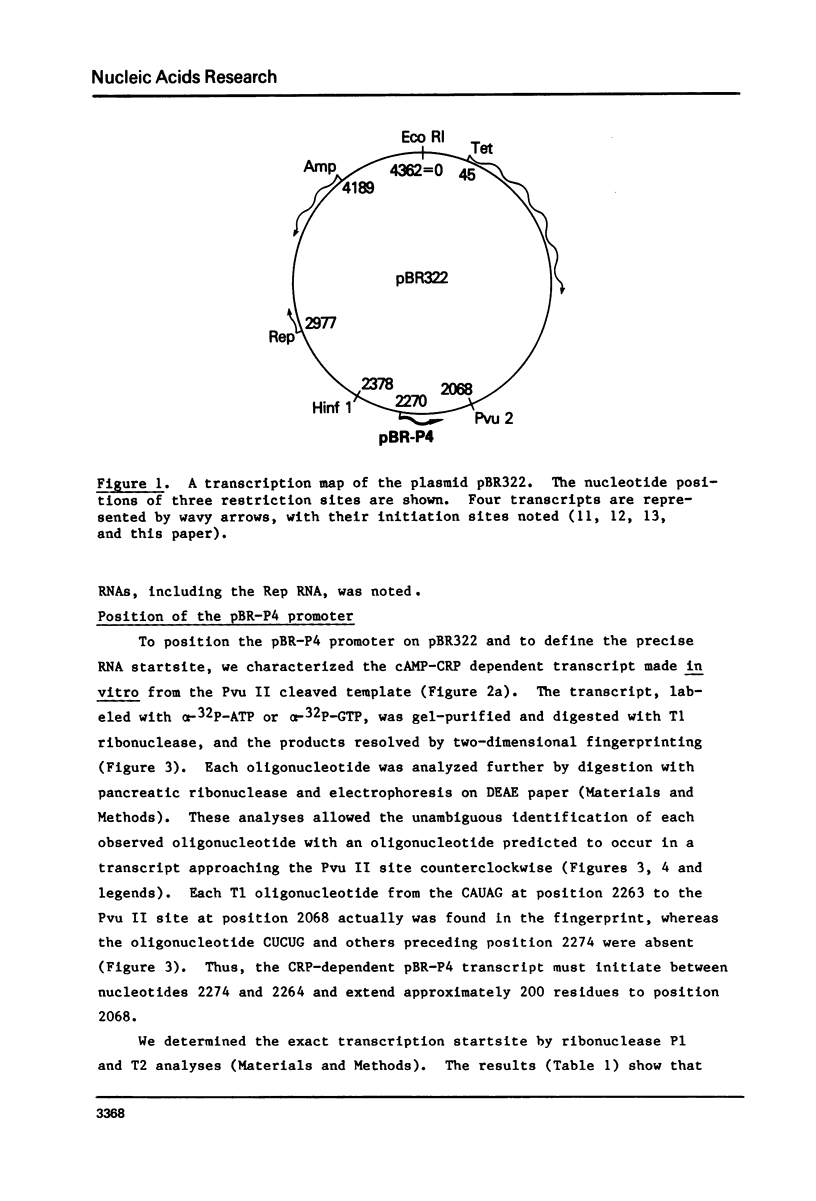
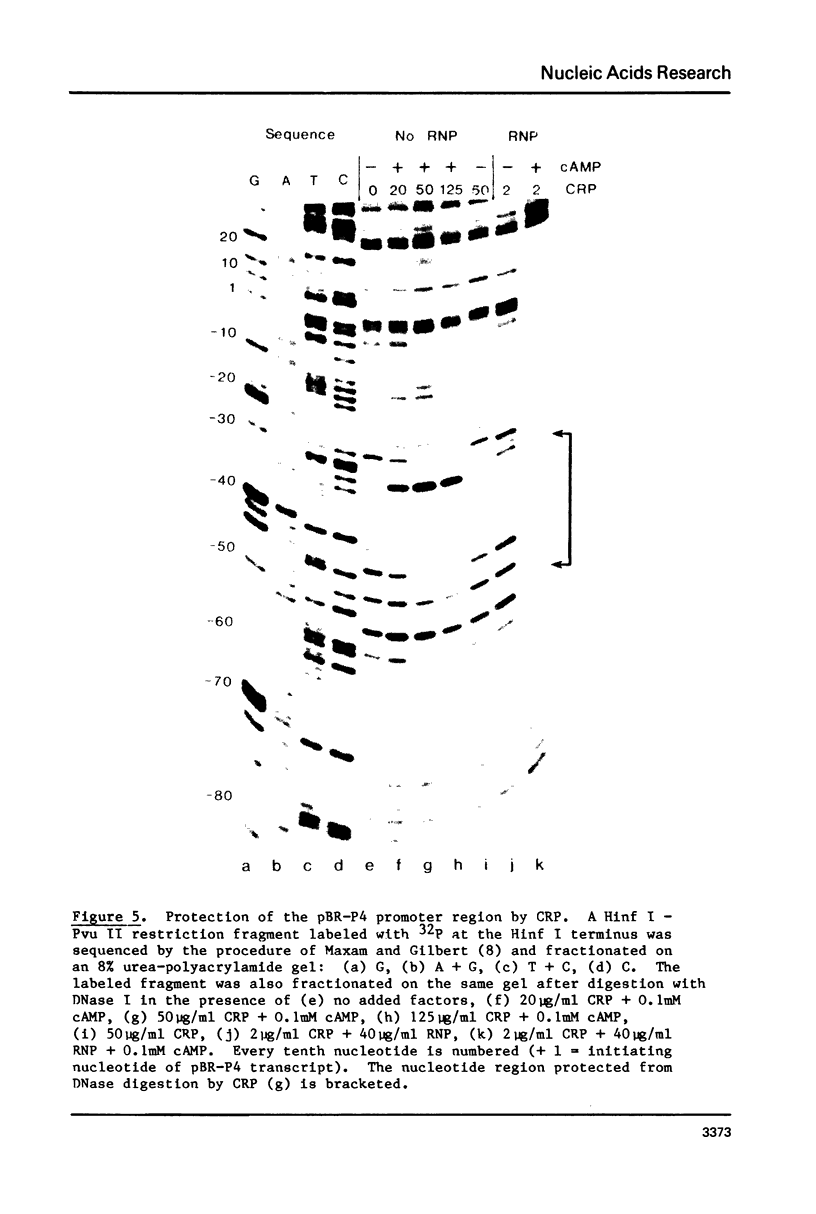
We have demonstrated in vitro the existence on the plasmid pBR322 of a promoter signal that is strictly dependent on cAMP and its receptor protein CRP. Transcription initiates with pppG at nucleotide 2270 and proceeds counterclockwise on the standard pBR322 map. DNase protection studies show that CRP selectively binds to the -35 region of the promoter. This region exhibits strong structural homologies to the binding sites of other CRP-dependent promoters.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dickson R. C., Abelson J., Barnes W. M., Reznikoff W. S. Genetic regulation: the Lac control region. Science. 1975 Jan 10;187(4171):27–35. doi: 10.1126/science.1088926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsh J., Schleif R. The araC promoter: transcription, mapping and interaction with the araBAD promoter. Cell. 1977 Jul;11(3):545–550. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90072-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majors J. Initiation of in vitro mRNA synthesis from the wild-type lac promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4394–4398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maquat L. E., Reznikoff W. S. In vitro analysis of the Escherichia coli RNA polymerase interaction with wild-type and mutant lactose promoters. J Mol Biol. 1978 Nov 15;125(4):467–490. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90311-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita M., Oka A. The structure of a transcriptional unit on colicin E1 plasmid. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jul;97(2):435–443. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13131.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musso R., Di Lauro R., Rosenberg M., de Crombrugghe B. Nucleotide sequence of the operator-promoter region of the galactose operon of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):106–110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi S., Adhya S., Gottesman M., Pastan I. Activation of transcription at specific promoters by glycerol. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4050–4056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nisseley S. P., Anderson W. B., Gottesman M. E., Perlman R. L., Pastan I. In vitro transcription of the gal operon requires cyclic adenosine monophosphate and cyclic adenosine monophosphate receptor protein. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4671–4678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogden S., Haggerty D., Stoner C. M., Kolodrubetz D., Schleif R. The Escherichia coli L-arabinose operon: binding sites of the regulatory proteins and a mechanism of positive and negative regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3346–3350. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka A., Nomura N., Morita M., Sugisaki H., Sugimoto K., Takanami M. Nucleotide sequence of small ColE1 derivatives: structure of the regions essential for autonomous replication and colicin E1 immunity. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 May 4;172(2):151–159. doi: 10.1007/BF00268276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaller H., Gray C., Herrmann K. Nucleotide sequence of an RNA polymerase binding site from the DNA of bacteriophage fd. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):737–741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz A. Cyclic AMP receptor proteins interacts with lactose operator DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):277–292. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Simpson R. B., Gilbert W. E. coli RNA polymerase interacts homologously with two different promoters. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):269–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90613-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. R., Schleif R. Nucleotide sequence of the L-arabinose regulatory region of Escherichia coli K12. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 10;253(19):6931–6933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli plasmid pBR322. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):77–90. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T., O'Neill M., de Crombrugghe B. Interaction site of Escherichia coli cyclic AMP receptor protein on DNA of galactose operon promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5090–5094. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]