Abstract
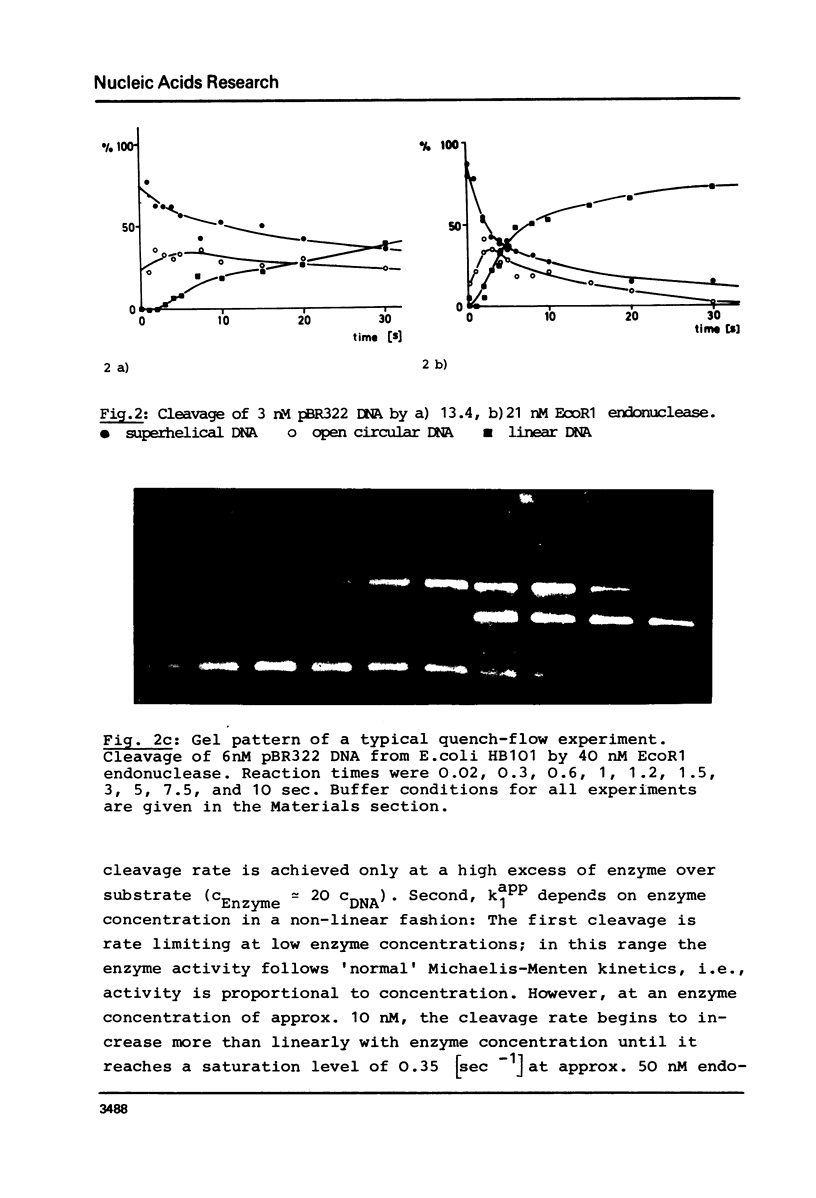
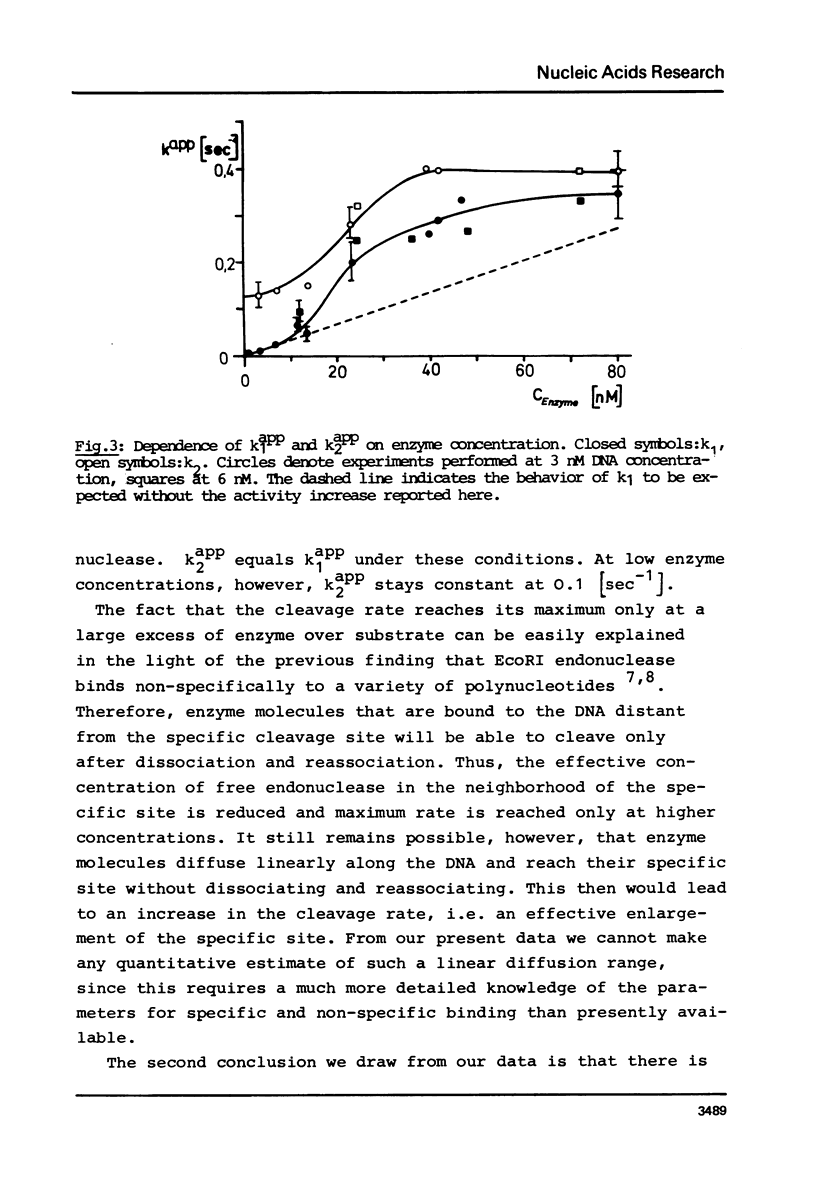
We report measurements of the cleavage rate of pBR 322 plasmid DNA by the restriction endonuclease Eco RI as a function of enzyme and DNA concentration. The reaction, which at high excess of enzyme over DNA occurs between 0.2 and 5 seconds, was studied by the means of a microprocessor controlled pulsed quench-flow apparatus. Enzyme concentrations were between 1 and 100 nM with DNA concentrations being 3 to 6 nM (specific Eco RI sites). The catalytic constants for cleavage of the first and second phosphodiester bonds as measured at high enzyme concentration both have the same value of 0.35 sec-1 and 21 degrees C. At enzyme concentrations comparable to or less than DNA concentration, the rate of the first cleavage is proportional to enzyme concentration, while the second step is independent of concentration. At approx. 10 nM Eco RI endonuclease concentration, a rate increase shows up in both the first and the second cleavage. We suggest that this increase is due to the tetramerization reported by Modrich & Zabel1, which occurs in this concentration range.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Goppelt M., Pingoud A., Maass G., Mayer H., Köster H., Frank R. The interaction of the EcoRI restriction endonuclease with its substrate. A physico-chemical study employing natural and synthetic oligonucleotides and polynucleotides. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Feb;104(1):101–107. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04405.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halford S. E., Johnson N. P., Grinsted J. The EcoRI restriction endonuclease with bacteriophage lambda DNA. Kinetic studies. Biochem J. 1980 Nov 1;191(2):581–592. doi: 10.1042/bj1910581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langowski J., Pingoud A., Goppelt M., Maass G. Inhibition of Eco RI action by polynucleotides. A characterization of the non-specific binding of the enzyme to DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Oct 24;8(20):4727–4736. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.20.4727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modrich P., Zabel D. EcoRI endonuclease. Physical and catalytic properties of the homogenous enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 10;251(19):5866–5874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodbury C. P., Jr, Hagenbüchle O., von Hippel P. H. DNA site recognition and reduced specificity of the Eco RI endonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 10;255(23):11534–11548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodhead J. L., Bhave N., Malcolm A. D. Cation dependence of restriction endonuclease EcoRI activity. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Apr;115(2):293–296. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05237.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



