Abstract
A library of cloned cDNAs representative of lymphocyte total poly(A)+ RNA was screened with total DNA probes at high clone density. 10% of the recombinants showed the presence of sequences which are repeated in the genome. Further analysis of six such isolated cDNA clones indicated that they contain different families of repetitive sequences with reiteration frequencies of between 150 and 45,000 copies per haploid genomes. Five of the six clones were found to contain single copy sequences as well as a repetitive sequence. cDNA clones containing repetitive sequences have been found to be derived from high, intermediate and low abundance classes of lymphocyte poly(A)+ RNA.
Full text
PDF




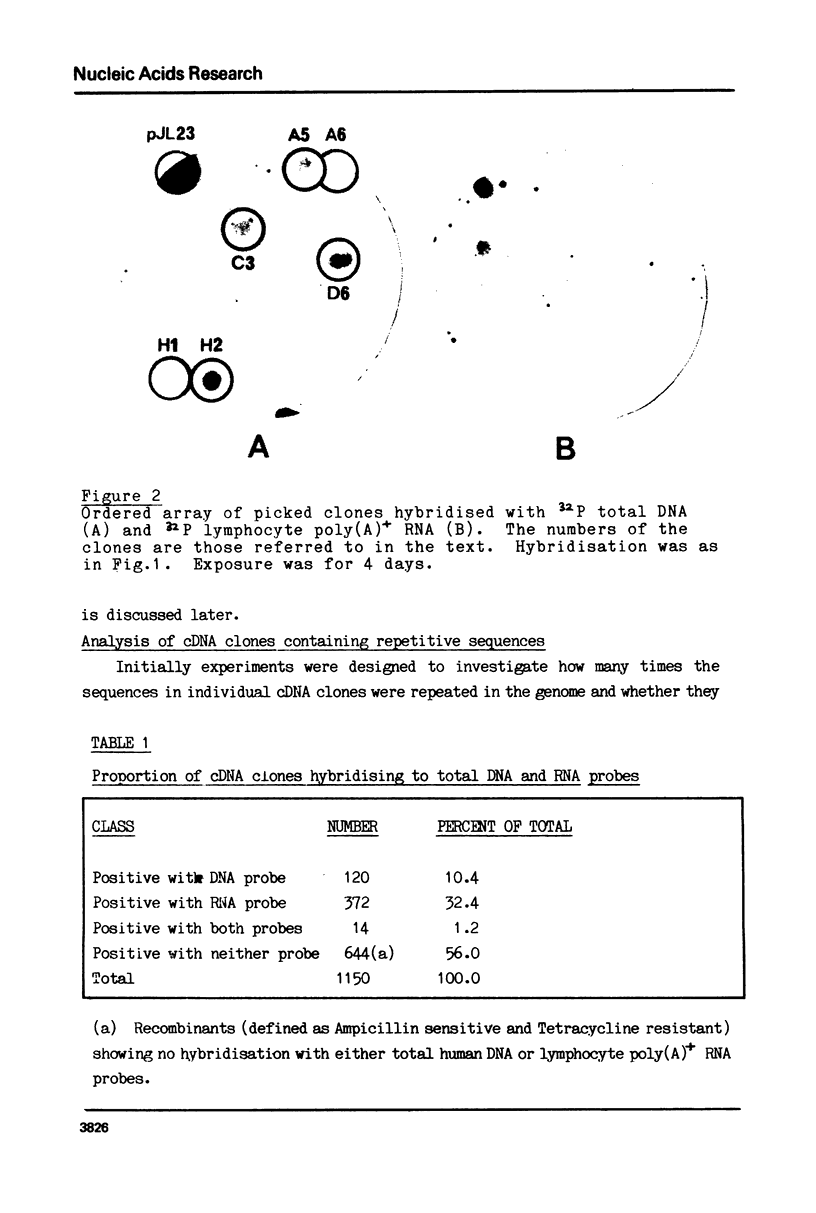

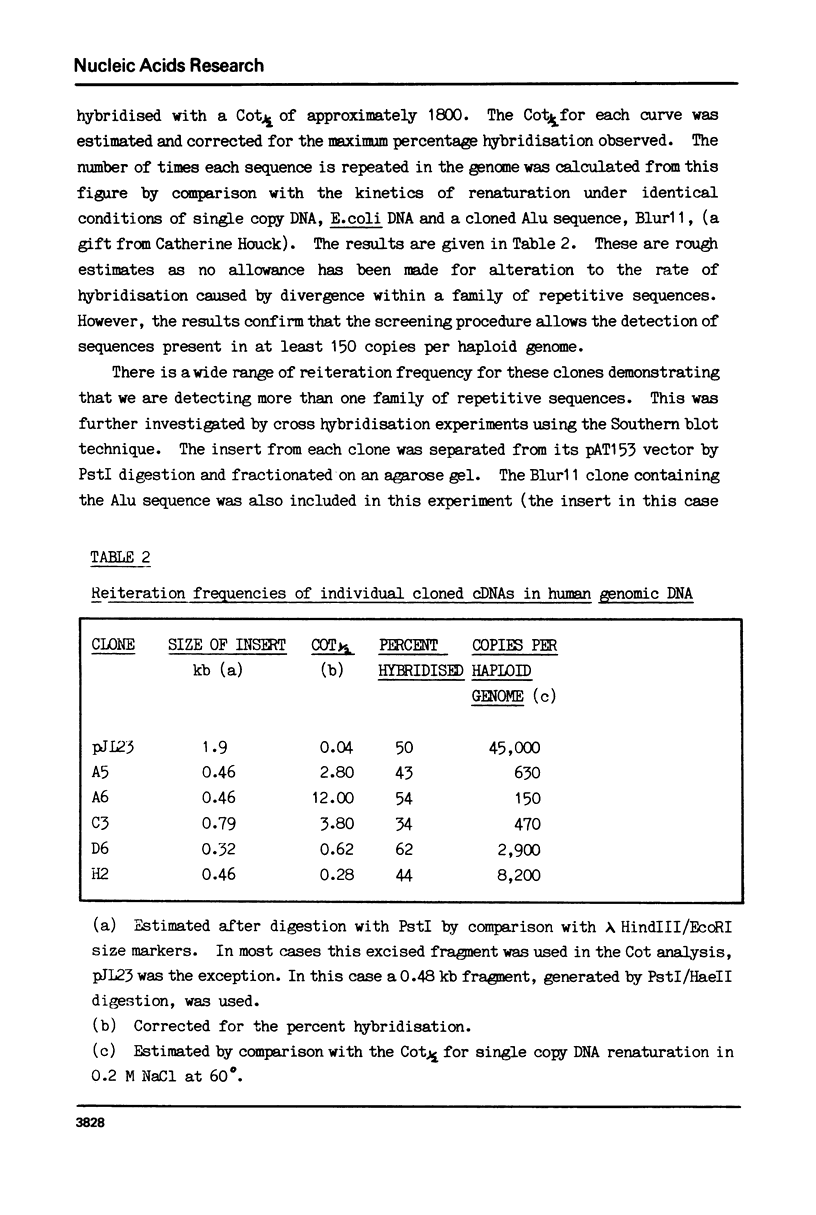






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Britten R. J., Graham D. E., Eden F. C., Painchaud D. M., Davidson E. H. Evolutionary divergence and length of repetitive sequences in sea urchin DNA. J Mol Evol. 1976 Dec 31;9(1):1–23. doi: 10.1007/BF01796119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarkson S. G., Birnstiel M. L., Serra V. Reiterated transfer RNA genes of Xenopus laevis. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 15;79(2):391–410. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Supercoiled circular DNA-protein complex in Escherichia coli: purification and induced conversion to an opern circular DNA form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1159–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke H. J., Hindley J. Cloning of human satellite III DNA: different components are on different chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jul 25;6(10):3177–3197. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.10.3177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costantini F. D., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Message sequences and short repetitive sequences are interspersed in sea urchin egg poly(A)+ RNAs. Nature. 1980 Sep 11;287(5778):111–117. doi: 10.1038/287111a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crampton J., Humphries S., Woods D., Williamson R. The isolation of cloned cDNA sequences which are differentially expressed in human lymphocytes and fibroblasts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):6007–6017. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.6007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. H., Britten R. J. Organization, transcription, and regulation in the animal genome. Q Rev Biol. 1973 Dec;48(4):565–613. doi: 10.1086/407817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. H., Britten R. J. Regulation of gene expression: possible role of repetitive sequences. Science. 1979 Jun 8;204(4397):1052–1059. doi: 10.1126/science.451548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. H., Hough B. R., Amenson C. S., Britten R. J. General interspersion of repetitive with non-repetitive sequence elements in the DNA of Xenopus. J Mol Biol. 1973 Jun 15;77(1):1–23. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90359-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawid I. B., Brown D. D., Reeder R. H. Composition and structure of chromosomal and amplified ribosomal DNA's of Xenopus laevis. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jul 28;51(2):341–360. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90147-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan C., Biro P. A., Choudary P. V., Elder J. T., Wang R. R., Forget B. G., de Riel J. K., Weissman S. M. RNA polymerase III transcriptional units are interspersed among human non-alpha-globin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5095–5099. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houck C. M., Rinehart F. P., Schmid C. W. A ubiquitous family of repeated DNA sequences in the human genome. J Mol Biol. 1979 Aug 15;132(3):289–306. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90261-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Flavell R. A. A physical map of the DNA regions flanking the rabbit beta-globin gene. Cell. 1977 Oct;12(2):429–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90119-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek W. R., Toomey T. P., Leinwand L., Duncan C. H., Biro P. A., Choudary P. V., Weissman S. M., Rubin C. M., Houck C. M., Deininger P. L. Ubiquitous, interspersed repeated sequences in mammalian genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1398–1402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L. Chromosomal localization of complex and simple repeated human DNAs. Chromosoma. 1978 Mar 22;66(1):23–32. doi: 10.1007/BF00285813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L., Wu J. C. Homology between human and simian repeated DNA. Nature. 1978 Nov 2;276(5683):92–94. doi: 10.1038/276092a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson H. D., Dickson E., Jelinek W. Determination of nucleotide sequences from double-stranded regions of HeLa cell nuclear RNA. J Mol Biol. 1977 Oct 5;115(4):571–589. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90103-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. M., Houck C. M., Deininger P. L., Friedmann T., Schmid C. W. Partial nucleotide sequence of the 300-nucleotide interspersed repeated human DNA sequences. Nature. 1980 Mar 27;284(5754):372–374. doi: 10.1038/284372a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid U. Bemerkungen zur Atiologie des dyshidrotischen Ekzems von O.P. Hornstein, Hautarzt 29, 170 (1978). Hautarzt. 1979 May;30(5):276–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen C. K., Maniatis T. The organization of repetitive sequences in a cluster of rabbit beta-like globin genes. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):379–391. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90512-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashima M., Calabretta B., Torelli G., Scofield M., Maizel A., Saunders G. F. Presence of a highly repetitive and widely dispersed DNA sequence in the human genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1508–1512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thuring R. W., Sanders J. P., Borst P. A freeze-squeeze method for recovering long DNA from agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1975 May 26;66(1):213–220. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90739-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D., Crampton J., Clarke B., Williamson R. The construction of a recombinant cDNA library representative of the poly(A)+ mRNA population from normal human lymphocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Nov 25;8(22):5157–5168. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.22.5157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





