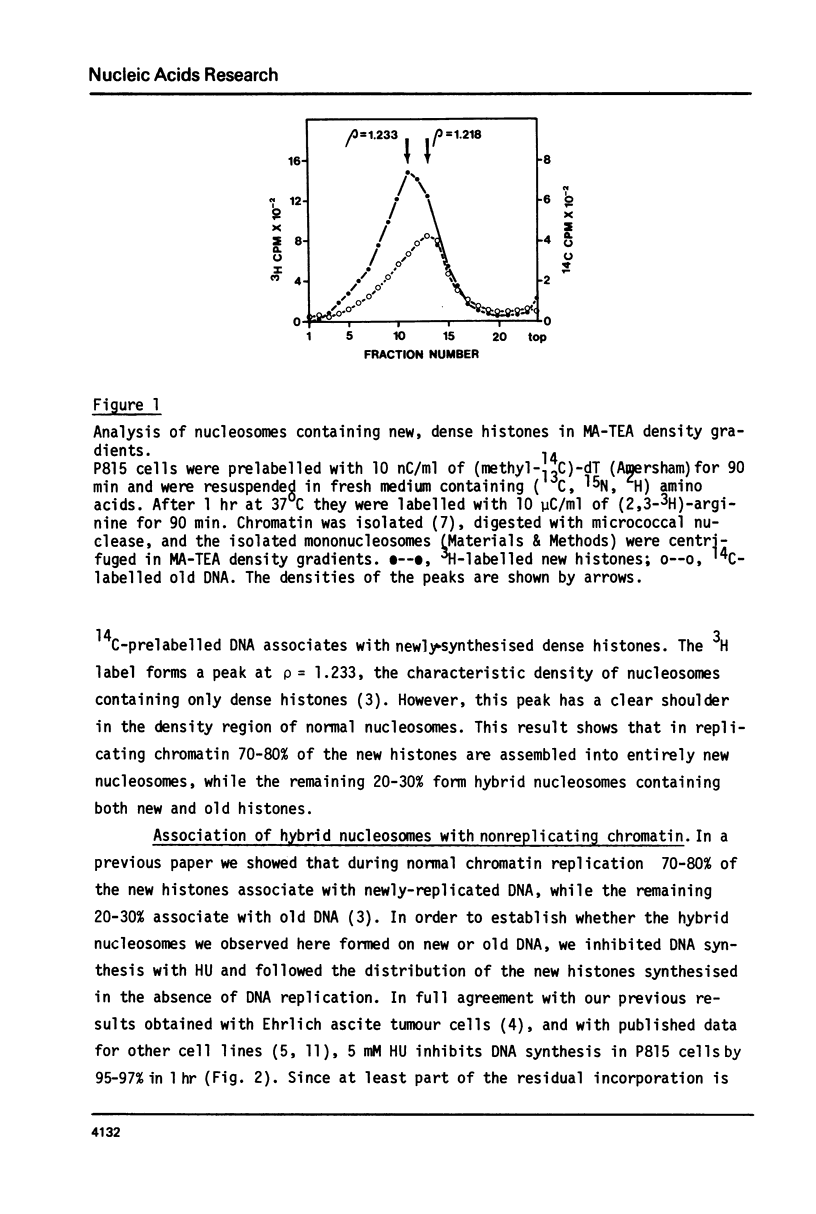
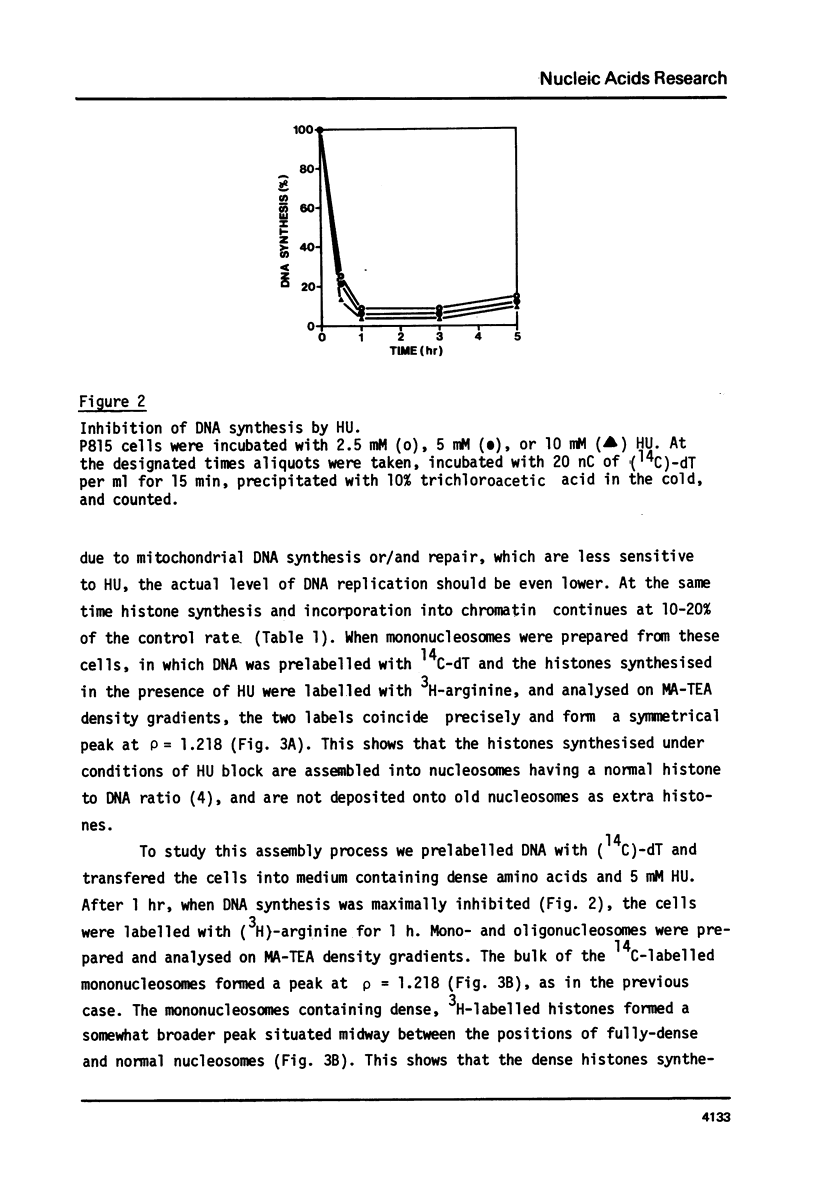
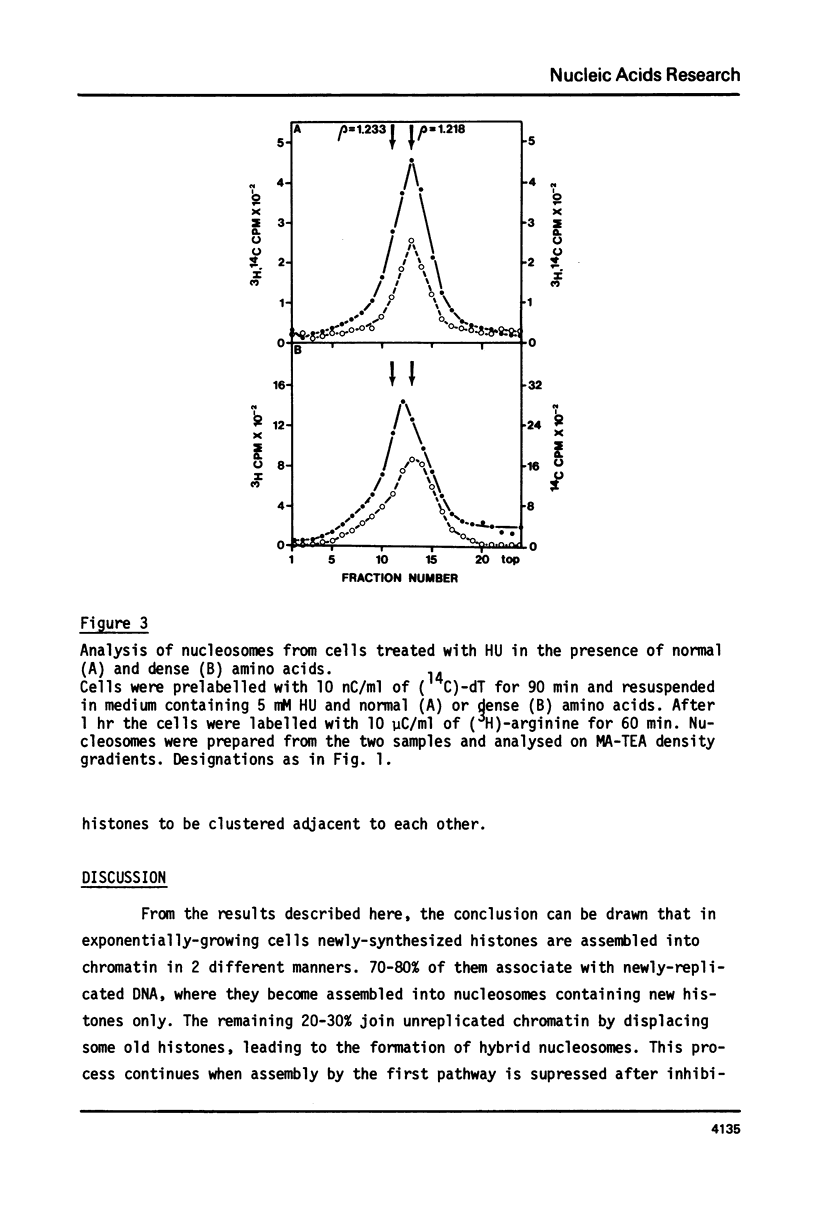
Abstract
5 mM hydroxyurea (HU) inhibits DNA synthesis in mouse P815 cells by 94-97% in less than 1 hr. Nevertheless, histone synthesis continues and newly-synthesised histones are incorporated into non-replicating chromatin at a rate of about 20% of that in control exponentially-growing cells. To study the organization of these histones in chromatin P815 cells were treated with 5 mM HU in medium containing dense (15N, 13C, 2H) - substituted amino acids. After inhibition of DNA synthesis, newly-synthesised histones were labelled with (3H)-arginine. The cells were harvested 90 min later, and mono- and oligonucleosomes were prepared and analysed on metrizamide-triethanolamine (MA-TEA density gradients. Analysis of the distribution of 3H-labelled histones in these gradients shows that they are incorporated into hybrid mononucleosomes containing both new and old histones. It is also shown that these hybrid nucleosomes are not randomly distributed, but show a certain tendency to be clustered in certain chromatin regions.
Full text
PDF