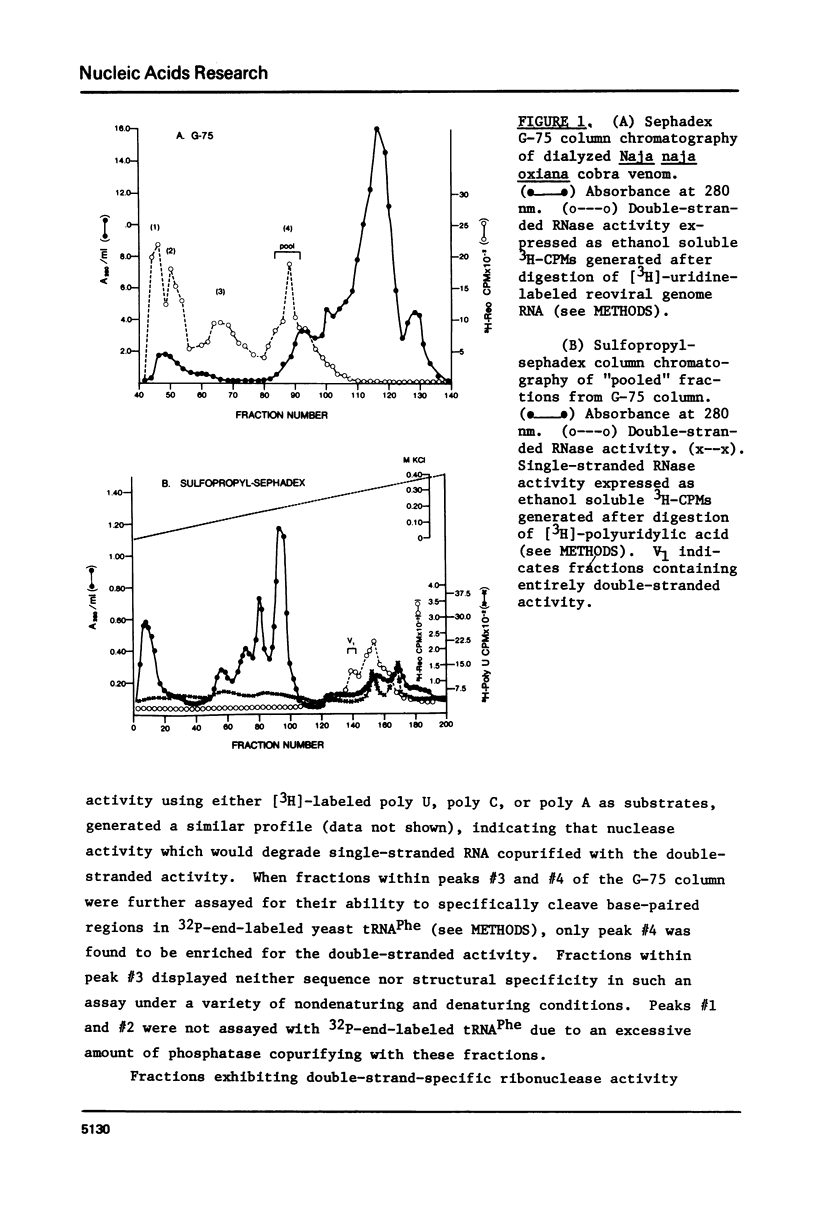
Abstract
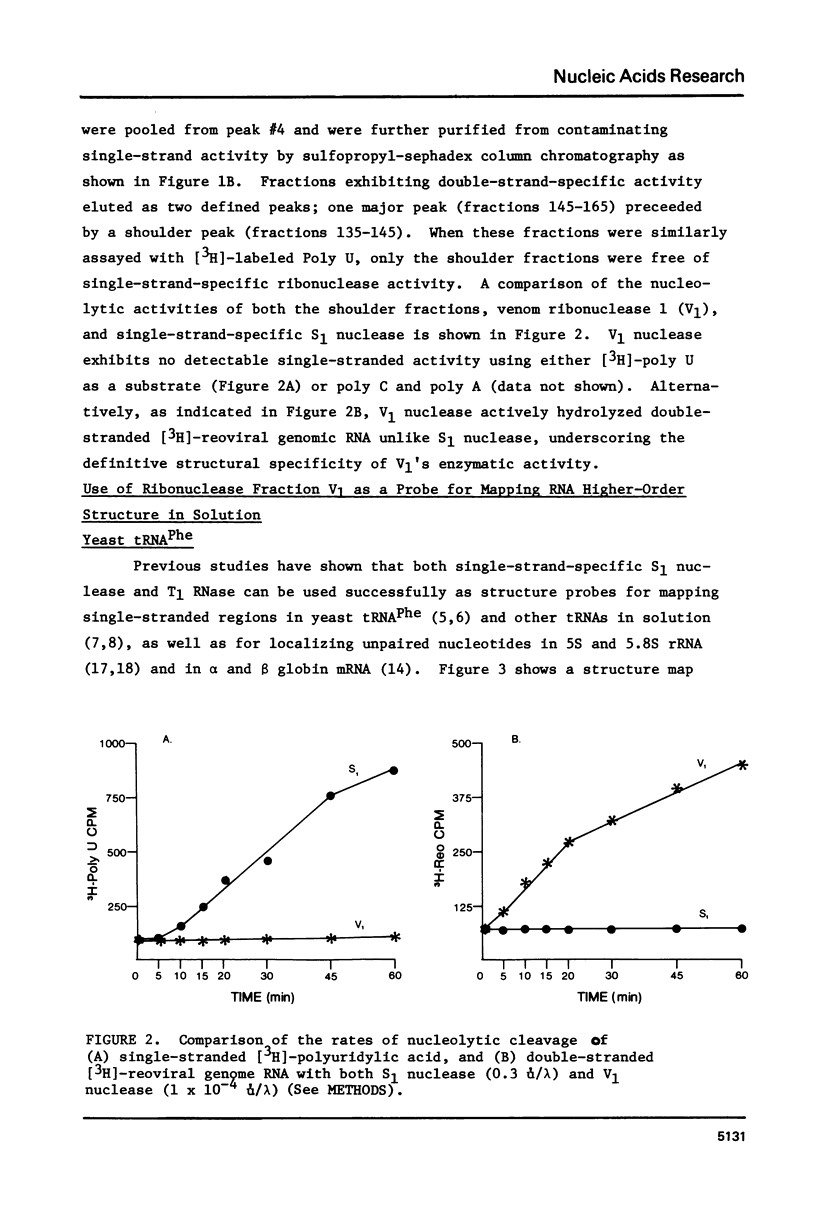
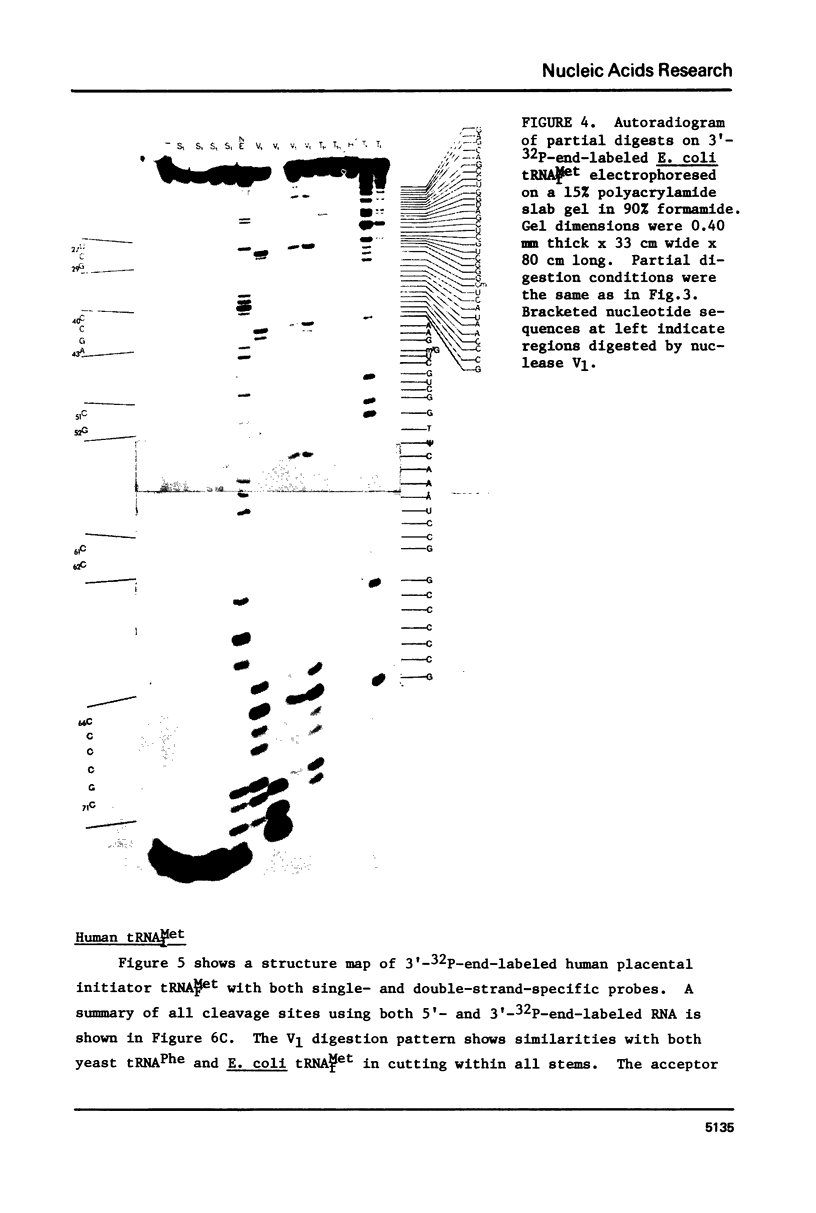
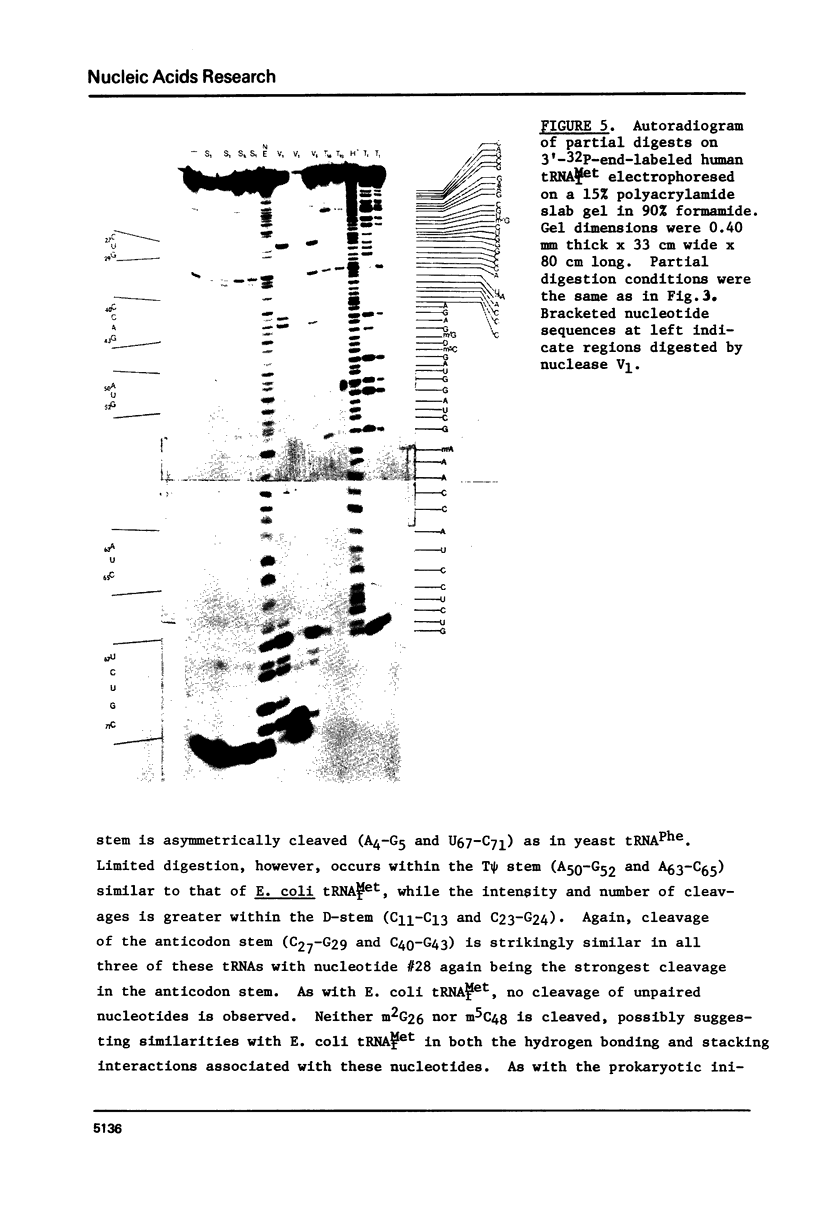
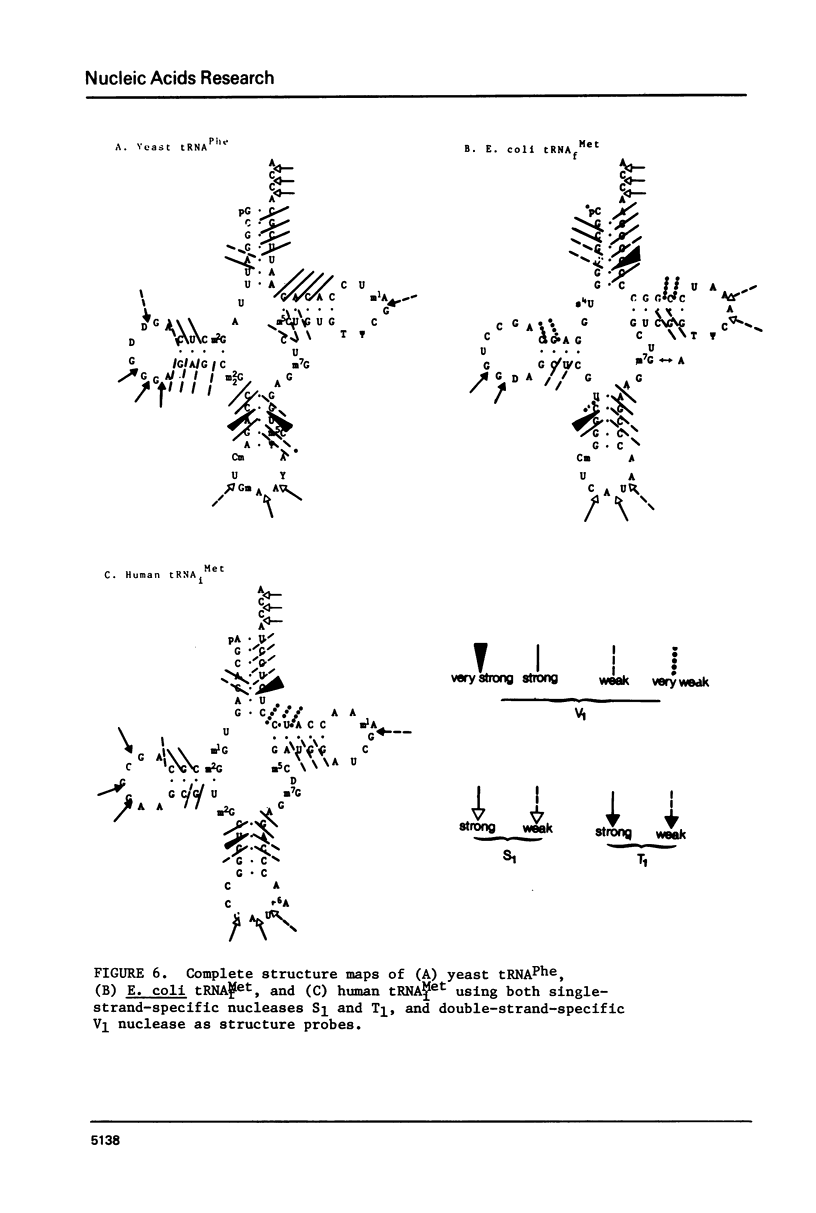
A method for mapping all base-paired stems in both elongation and initiator tRNAs is described using double-stranded-specific ribonuclease V1 from the venom of the cobra Naja naja oxiana. 32p-end-labeled RNA is first partially digested with double-strand-specific V1 nuclease under near physiological conditions, and the resultant fragments are than electrophoretically fractionated by size in adjacent lanes of a polyacrylamide gel run in 90% formamide. After autoradiography, the base-paired nucleotides are definitively located by comparing V1 generated bands with fragments of known length produced by both Neurospora endonuclease and base-specific ribonucleases. Using the substrates yeast tRNAPhe an E, coli tRNAfMet of known three-dimensional structure, we find V1 nuclease to cleave entirely within every base-paired stem. Our studies also reveal that nuclease V1 will digest paired nucleotides not hydrogen-bonded by standard Watson-Crick base-pairing. In yeast tRNAPhe cleavage of both wobble base-pairs and nucleotides involved in tertiary base-base hydrogen bonding is demonstrated.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Favorova O. O., Fasiolo F., Keith G., Vassilenko S. K., Ebel J. P. Partial digestion of tRNA--aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase complexes with cobra venom ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 17;20(4):1006–1011. doi: 10.1021/bi00507a055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauss D. H., Grüter F., Sprinzl M. Compilation of tRNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jan;6(1):r1–r19. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs S. T., Shen C. K., Hearst J. E., Rapoport H. Synthesis and characterization of new psoralen derivatives with superior photoreactivity with DNA and RNA. Biochemistry. 1977 Mar 22;16(6):1058–1064. doi: 10.1021/bi00625a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. A., Walseth T. F. The enzymatic preparation of [alpha-32P]ATP, [alpha-32P]GTP, [32P]cAMP, and [32P]cGMP, and their use in the assay of adenylate and guanylate cyclases and cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;10:135–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karathanasis S. K., Champney W. S. Properties of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal ribonucleic acid treated with 4,5',8-trimethylpsoralen and light. Biochemistry. 1979 May 15;18(10):2012–2019. doi: 10.1021/bi00577a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupp G., Gross H. J. Rapid RNA sequencing: nucleases from Staphylococcus aureus and Neurospora crassa discriminate between uridine and cytidine. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 10;6(11):3481–3490. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.11.3481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockard R. E., Alzner-Deweerd B., Heckman J. E., MacGee J., Tabor M. W., RajBhandary U. L. Sequence analysis of 5'[32P] labeled mRNA and tRNA using polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jan;5(1):37–56. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F. Topography of 16S RNA in 30S ribosomal subunits. Nucleotide sequences and location of sites of reaction with kethoxal. Biochemistry. 1974 Nov 5;13(23):4694–4703. doi: 10.1021/bi00720a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlakis G. N., Jordan B. R., Wurst R. M., Vournakis J. N. Sequence and secondary structure of Drosophila melanogaster 5.8S and 2S rRNAs and of the processing site between them. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 20;7(8):2213–2238. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.8.2213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlakis G. N., Lockard R. E., Vamvakopoulos N., Rieser L., RajBhandary U. L., Vournakis J. N. Secondary structure of mouse and rabbit alpha- and beta-globin mRNAs: differential accessibility of alpha and beta initiator AUG codons towards nucleases. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):91–102. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90391-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peattie D. A., Gilbert W. Chemical probes for higher-order structure in RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4679–4682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponomareva R. B., Kavunenko T. N., Kalatcheva T. N., Tikhomirova-Sidorova N. S., Samsonov G. V. [Modification of pancreatic ribonuclease activity in complexes with polyanions]. Biokhimiia. 1975 May-Jun;40(3):468–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley G. J., Rich A. Structural domains of transfer RNA molecules. Science. 1976 Nov 19;194(4267):796–806. doi: 10.1126/science.790568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabin D., Crothers D. M. Analysis of RNA secondary structure by photochemical reversal of psoralen crosslinks. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Oct 10;7(3):689–703. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.3.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich A., RajBhandary U. L. Transfer RNA: molecular structure, sequence, and properties. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:805–860. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.004105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross A., Brimacombe R. Experimental determination of interacting sequences in ribosomal RNA. Nature. 1979 Sep 27;281(5729):271–276. doi: 10.1038/281271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberklang M., Gillum A. M., RajBhandary U. L. The use of nuclease P1 in sequence analysis of end group labeled RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Dec;4(12):4091–4108. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.12.4091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woo N. H., Roe B. A., Rich A. Three-dimensional structure of Escherichia coli initiator tRNAfMet. Nature. 1980 Jul 24;286(5771):346–351. doi: 10.1038/286346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrede P., Rich A. Stability of the unique anticodon loop conformation of E.coli tRNAfMet. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1457–1467. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrede P., Woo N. H., Rich A. Initiator tRNAs have a unique anticodon loop conformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3289–3293. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrede P., Wurst R., Vournakis J., Rich A. Conformational changes of yeast tRNAPhe and E. coli tRNA2Glu as indicated by different nuclease digestion patterns. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9608–9616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurst R. M., Vournakis J. N., Maxam A. M. Structure mapping of 5'-32P-labeled RNA with S1 nuclease. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 17;17(21):4493–4499. doi: 10.1021/bi00614a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]