Abstract
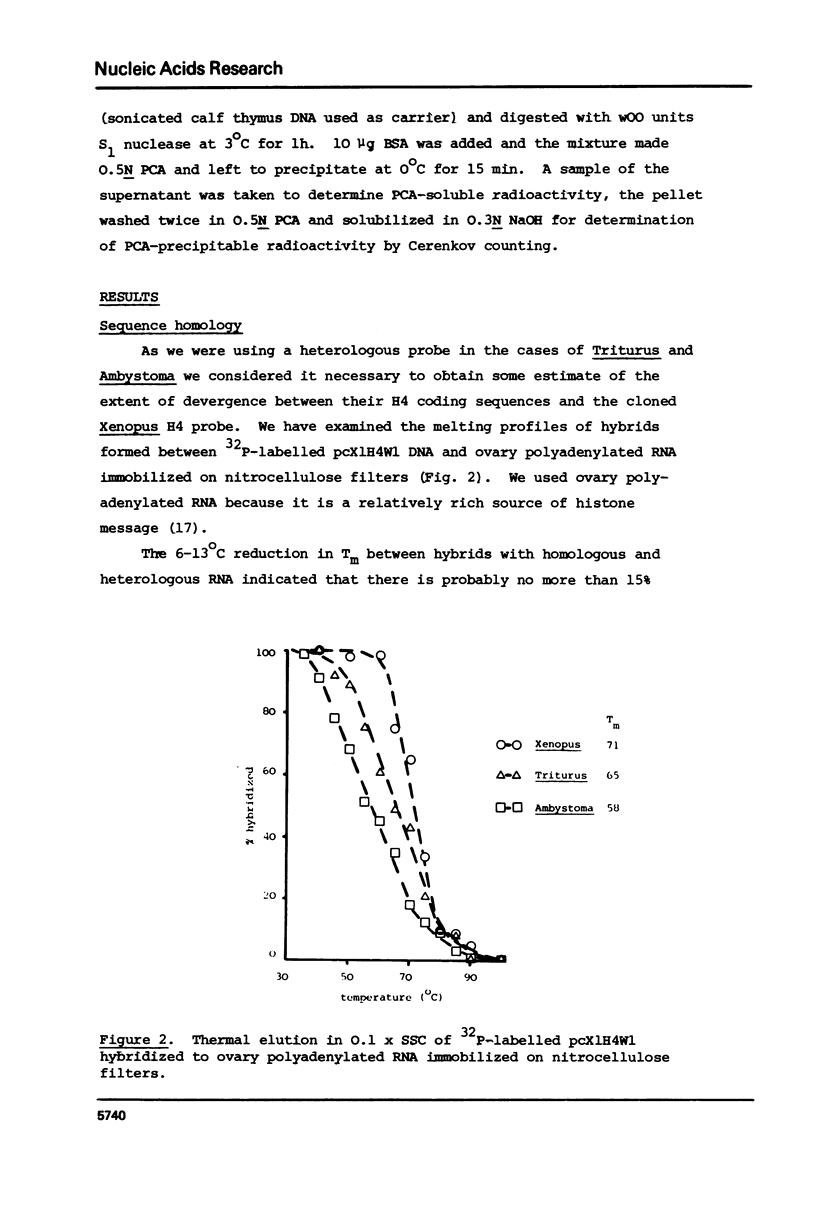
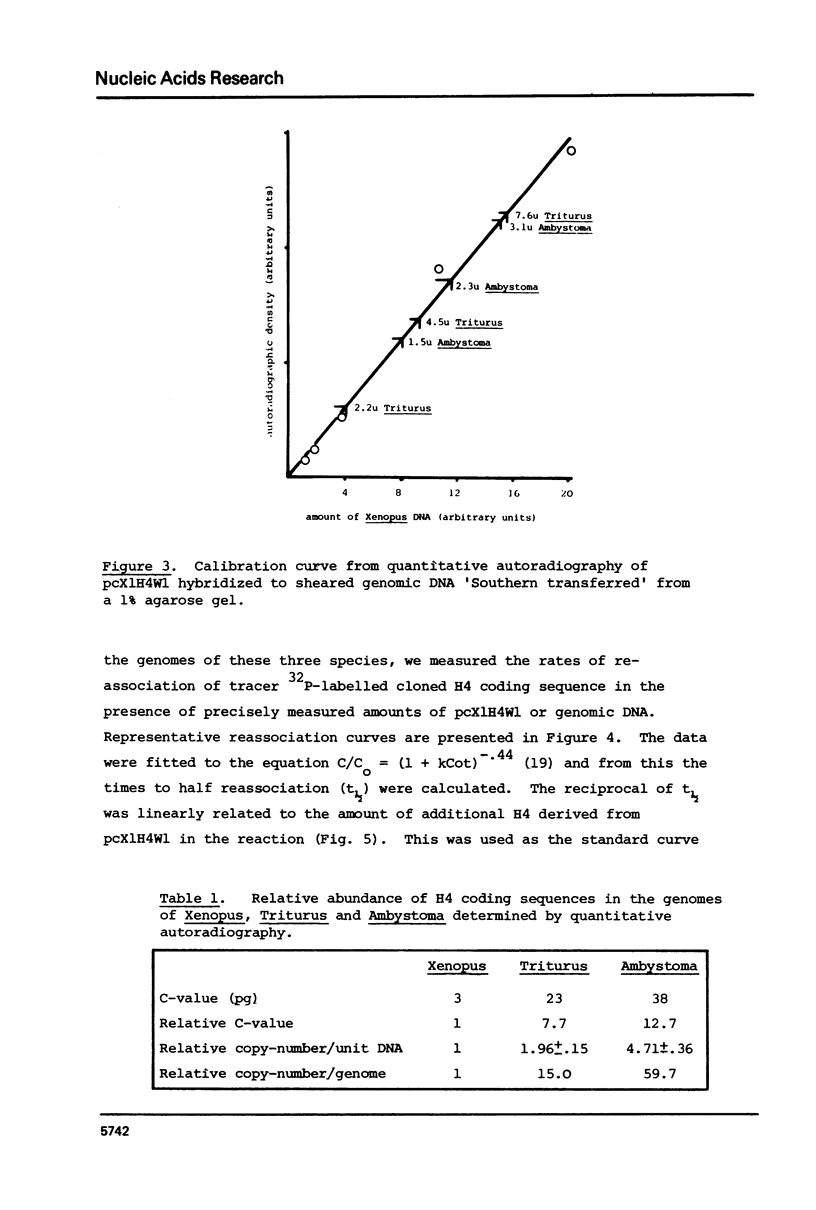
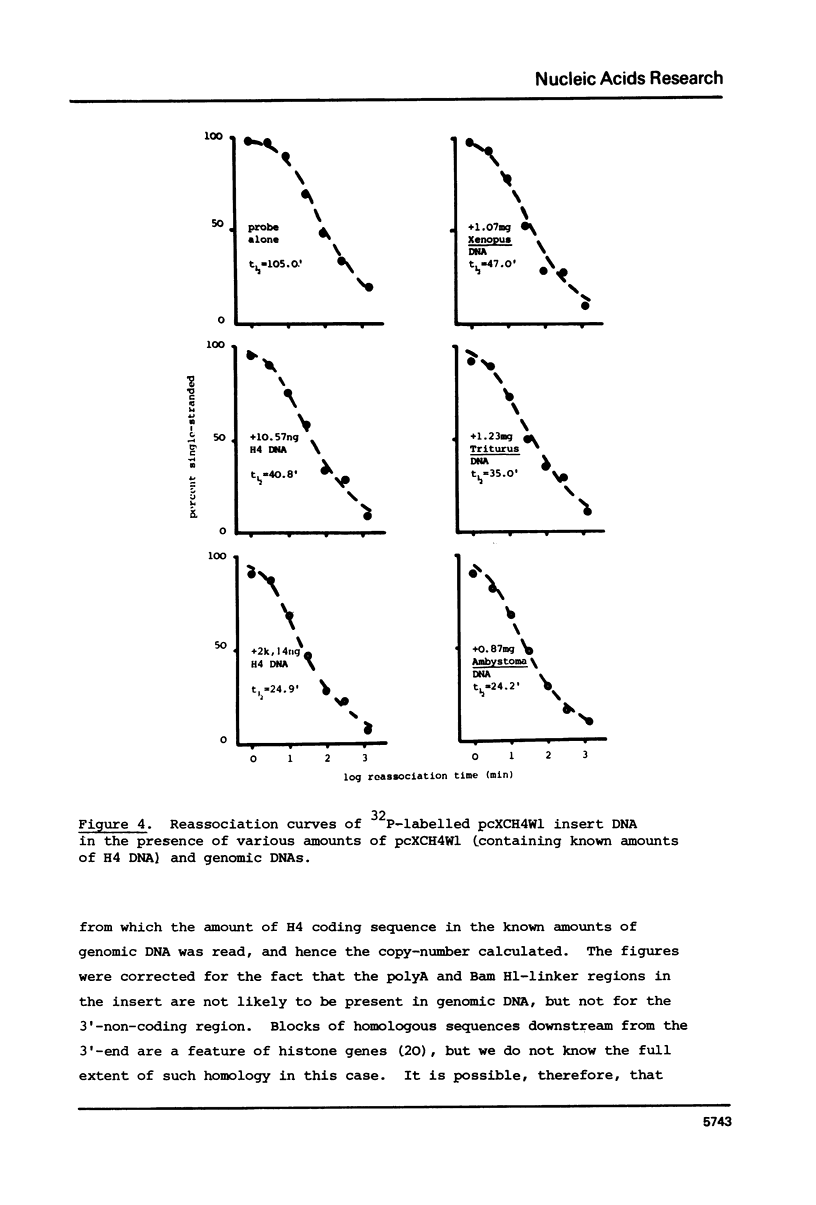
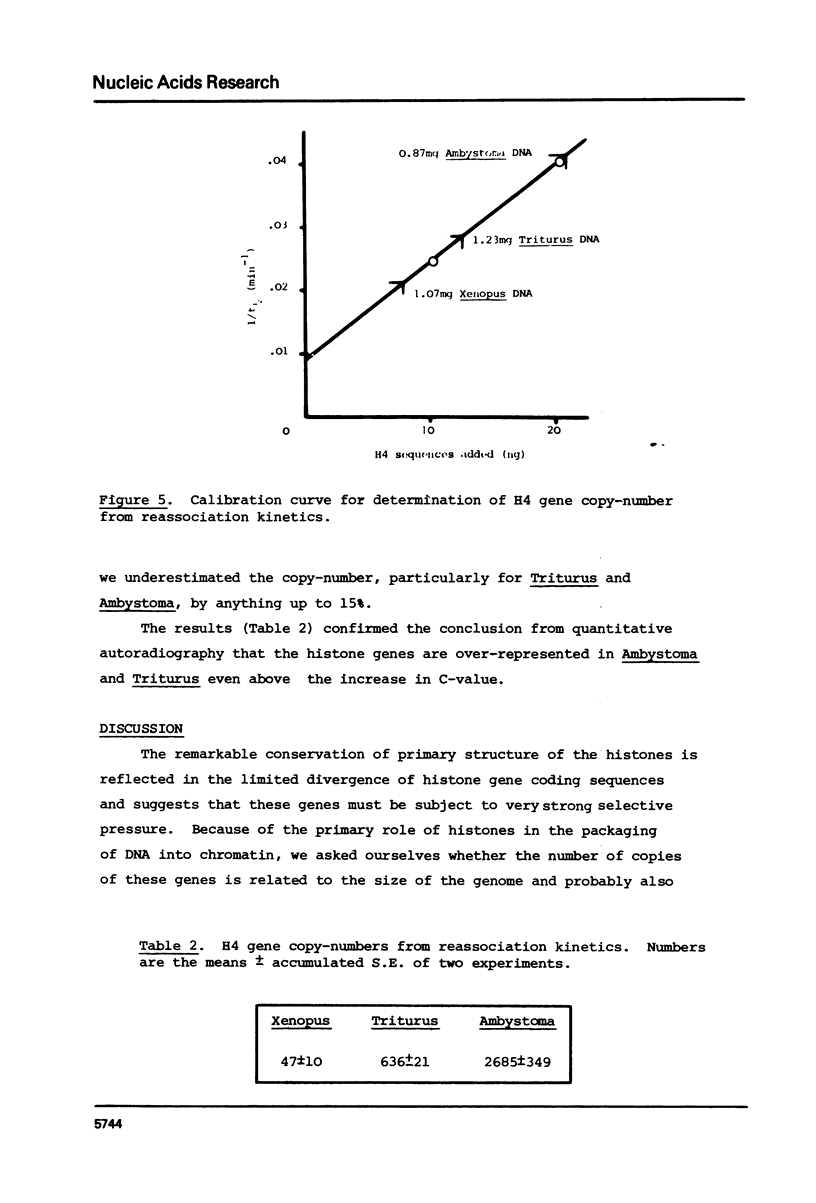
We have compared the number of copies of sequences complementary to a cloned Xenopus histone H4 coding sequence in the genomes of Xenopus, Triturus and Ambystoma, amphibian species with widely different C-values (3, 23 and 38pg DNA/haploid genome respectively). Quantitative autoradiography indicates that H4 sequence constitute a greater proportion of the genome the larger that genome is. Measurement of the absolute copy-number by reassociation kinetic analysis indicated 47 +/- 10, 636 +/- 21 2685 +/- 349 copies per haploid genome each in Xenopus, Triturus and Ambystoma respectively. Whilst this confirms a trend of increasing copy-number with increasing C-value, the two are not directly proportional and some other factors must contribute to determining the number of copies of these genes.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann K. Feulgen slope determinations of urodele nuclear DNA amounts. Histochemie. 1970;22(4):289–293. doi: 10.1007/BF00277456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman A., Byers M. J., Primrose S. B., Lyons A. Rapid purification of plasmid DNAs by hydroxyapatite chromatography. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Nov 2;91(1):303–310. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb20966.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford R. J., Krieg P., Harvey R. P., Hewish D. A., Wells J. R. Histone genes are clustered with a 15-kilobase repeat in the chicken genome. Nature. 1979 May 10;279(5709):132–136. doi: 10.1038/279132a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawid I. B. Deoxyribonucleic acid in amphibian eggs. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jul;12(3):581–599. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80313-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel J. D., Dodgson J. B. Histone genes are clustered but not tandemly repeated in the chicken genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2856–2860. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N., Zernik M., Roeder R. G. The structure of the human histone genes: clustered but not tandemly repeated. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):661–668. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90092-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob E., Malacinski G., Birnstiel M. L. Reiteration frequency of the histone genes in the genome of the amphibian, Xenopus laevis. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Oct 1;69(1):45–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10856.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Flavell R. A. A physical map of the DNA regions flanking the rabbit beta-globin gene. Cell. 1977 Oct;12(2):429–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90119-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRBY K. S. ISOLATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF RIBOSOMAL RIBONUCLEIC ACID. Biochem J. 1965 Jul;96:266–269. doi: 10.1042/bj0960266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Felsenfeld G. Nucleosome structure. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:1115–1156. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.005343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazato H., Edmonds M. The isolation and purification of rapidly labeled polysome-bound ribonucleic acid on polythymidylate cellulose. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 25;247(10):3365–3367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruderman J. V., Pardue M. L. Cell-free translation analysis of messenger RNA in echinoderm and amphibian early development. Dev Biol. 1977 Oct 1;60(1):48–68. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90109-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson E. C., Erba H. P., Gall J. G. Histone gene clusters of the newt notophthalmus are separated by long tracts of satellite DNA. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):639–647. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90090-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truett M. A., Jones R. S., Potter S. S. Unusual structure of the FB family of transposable elements in Drosophila. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):753–763. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90101-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodland H. R. Histone synthesis during the development of Xenopus. FEBS Lett. 1980 Nov 17;121(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81252-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dongen W., de Laaf L., Zaal R., Moorman A., Destrée O. The organization of the histone genes in the genome of Xenopus laevis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 25;9(10):2297–2311. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.10.2297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


