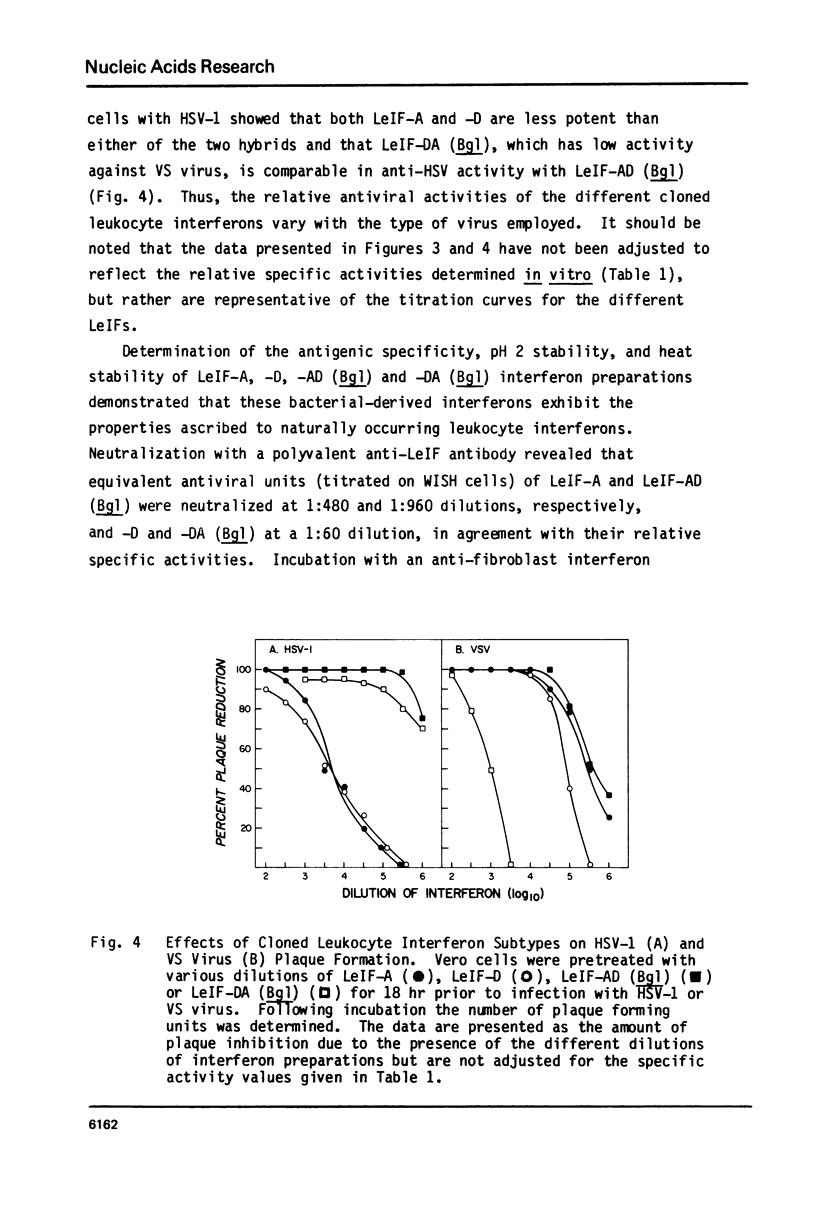
Abstract
Four hybrid human leukocyte interferon (LeIF or IFN-alpha) genes have been constructed by in vitro recombination of LeIF-A (IFN-alpha 2) and LeIF-D (IFN-alpha 1) genes at common restriction endonuclease sites located within their coding regions. These hybrid genes have been expressed in E. coli under trp promoter control. The interferons produced [LeIF-AD (BglII), -AD (PvuII), -DA (BglII), -DA (PvuII)] have antiviral properties distinct from the parental molecules LeIF-A and -D, varying considerably in their abilities to inhibit plaque formation by different viruses in a range of mammalian cells. All six of the cloned LeIFs exhibit the heat stability, pH 2 stability and antigenic specificity of natural leukocyte interferons.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ankel H., Krishnamurti C., Besançon F., Stefanos S., Falcoff E. Mouse fibroblast (type I) and immune (type II) interferons: pronounced differences in affinity for gangliosides and in antiviral and antigrowth effects on mouse leukemia L-1210R cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2528–2532. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baglioni C. Interferon-induced enzymatic activities and their role in the antriviral state. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):255–264. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90151-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell J. B., Grunberger T., Kochman M. A., White S. L. A microplaque reduction assay for human and mouse interferon. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Aug;21(8):1247–1253. doi: 10.1139/m75-186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czarniecki C. W., Sreevalsan T., Friedman R. M., Panet A. Dissociation of interferon effects on murine leukemia virus and encephalomyocarditis virus replication in mouse cells. J Virol. 1981 Feb;37(2):827–831. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.2.827-831.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goeddel D. V., Kleid D. G., Bolivar F., Heyneker H. L., Yansura D. G., Crea R., Hirose T., Kraszewski A., Itakura K., Riggs A. D. Expression in Escherichia coli of chemically synthesized genes for human insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):106–110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goeddel D. V., Leung D. W., Dull T. J., Gross M., Lawn R. M., McCandliss R., Seeburg P. H., Ullrich A., Yelverton E., Gray P. W. The structure of eight distinct cloned human leukocyte interferon cDNAs. Nature. 1981 Mar 5;290(5801):20–26. doi: 10.1038/290020a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goeddel D. V., Shepard H. M., Yelverton E., Leung D., Crea R., Sloma A., Pestka S. Synthesis of human fibroblast interferon by E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 25;8(18):4057–4074. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.18.4057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goeddel D. V., Yelverton E., Ullrich A., Heyneker H. L., Miozzari G., Holmes W., Seeburg P. H., Dull T., May L., Stebbing N. Human leukocyte interferon produced by E. coli is biologically active. Nature. 1980 Oct 2;287(5781):411–416. doi: 10.1038/287411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawn R. M., Adelman J., Dull T. J., Gross M., Goeddel D., Ullrich A. DNA sequence of two closely linked human leukocyte interferon genes. Science. 1981 Jun 5;212(4499):1159–1162. doi: 10.1126/science.6165082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata S., Mantei N., Weissmann C. The structure of one of the eight or more distinct chromosomal genes for human interferon-alpha. Nature. 1980 Oct 2;287(5781):401–408. doi: 10.1038/287401a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen T. W., Wood D. L., Baglioni C. Virus-specific effects of interferon in embryonal carcinoma cells. Nature. 1980 Jul 10;286(5769):178–180. doi: 10.1038/286178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stebbing N., Grantham C. A., Carey N. H. Anti-viral activity of single-stranded homopolynucleotides against encephalomyocarditis virus and Semliki Forest virus in adult mice without interferon induction. J Gen Virol. 1976 Jan;30(1):21–39. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-30-1-21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart W. E., 2nd, Havell E. A. Characterization of a subspecies of mouse interferon cross-reactive on human cells and antigenically related to human leukocyte interferon. Virology. 1980 Feb;101(1):315–318. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90512-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streuli M., Hall A., Boll W., Stewart W. E., 2nd, Nagata S., Weissmann C. Target cell specificity of two species of human interferon-alpha produced in Escherichia coli and of hybrid molecules derived from them. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2848–2852. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streuli M., Nagata S., Weissmann C. At least three human type alpha interferons: structure of alpha 2. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1343–1347. doi: 10.1126/science.6158094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetzel R. Assignment of the disulphide bonds of leukocyte interferon. Nature. 1981 Feb 12;289(5798):606–607. doi: 10.1038/289606a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetzel R., Perry L. J., Estell D. A., Lin N., Levine H. L., Slinker B., Fields F., Ross M. J., Shively J. Properties of a human alpha-interferon purified from E. coli extracts. J Interferon Res. 1981;1(3):381–390. doi: 10.1089/jir.1981.1.381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. N., Hovanessian A. G. Interferon enhances 2-5A synthetase in embryonal carcinoma cells. Nature. 1979 Nov 1;282(5734):74–76. doi: 10.1038/282074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yelverton E., Leung D., Weck P., Gray P. W., Goeddel D. V. Bacterial synthesis of a novel human leukocyte interferon. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 11;9(3):731–741. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.3.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarucki-Schulz T., Jerez C., Goldberg G., Kung H. F., Huang K. H., Brot N., Weissbach H. DNA-directed in vitro synthesis of proteins involved in bacterial transcription and translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6115–6119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


