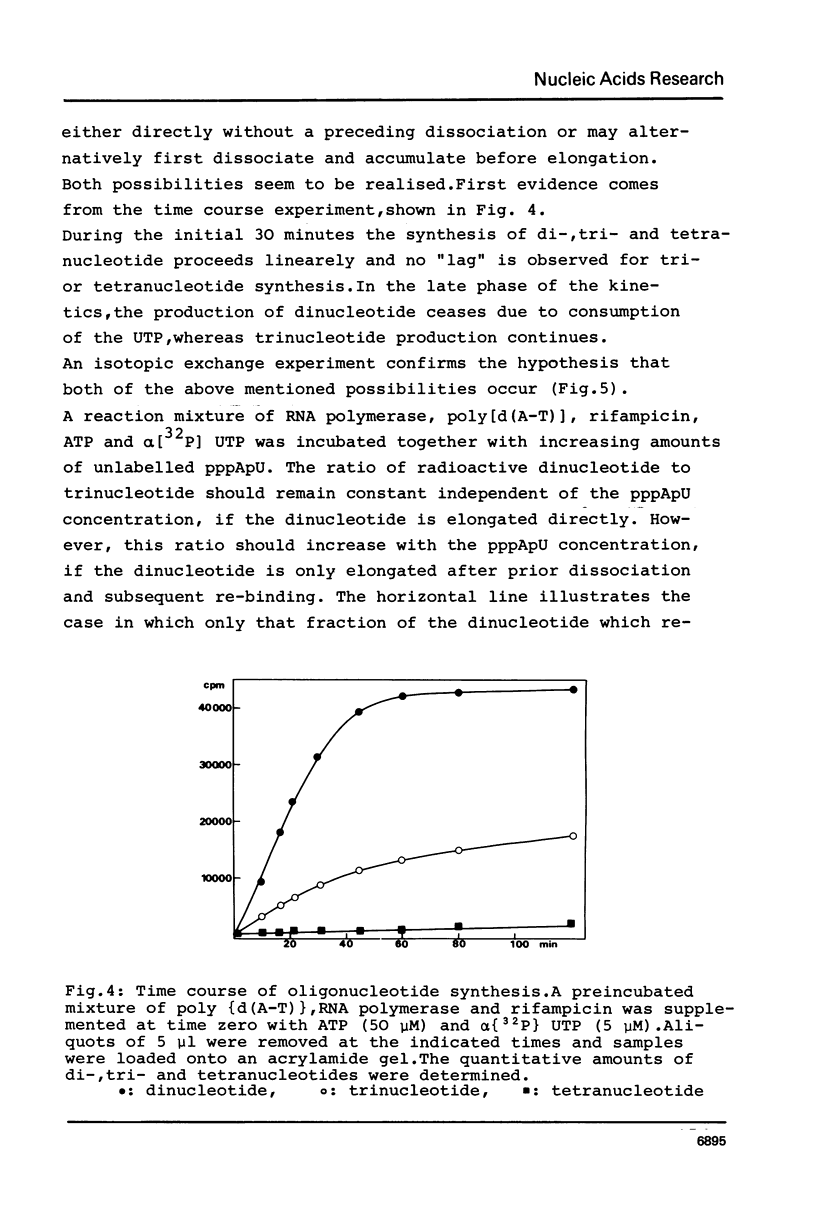
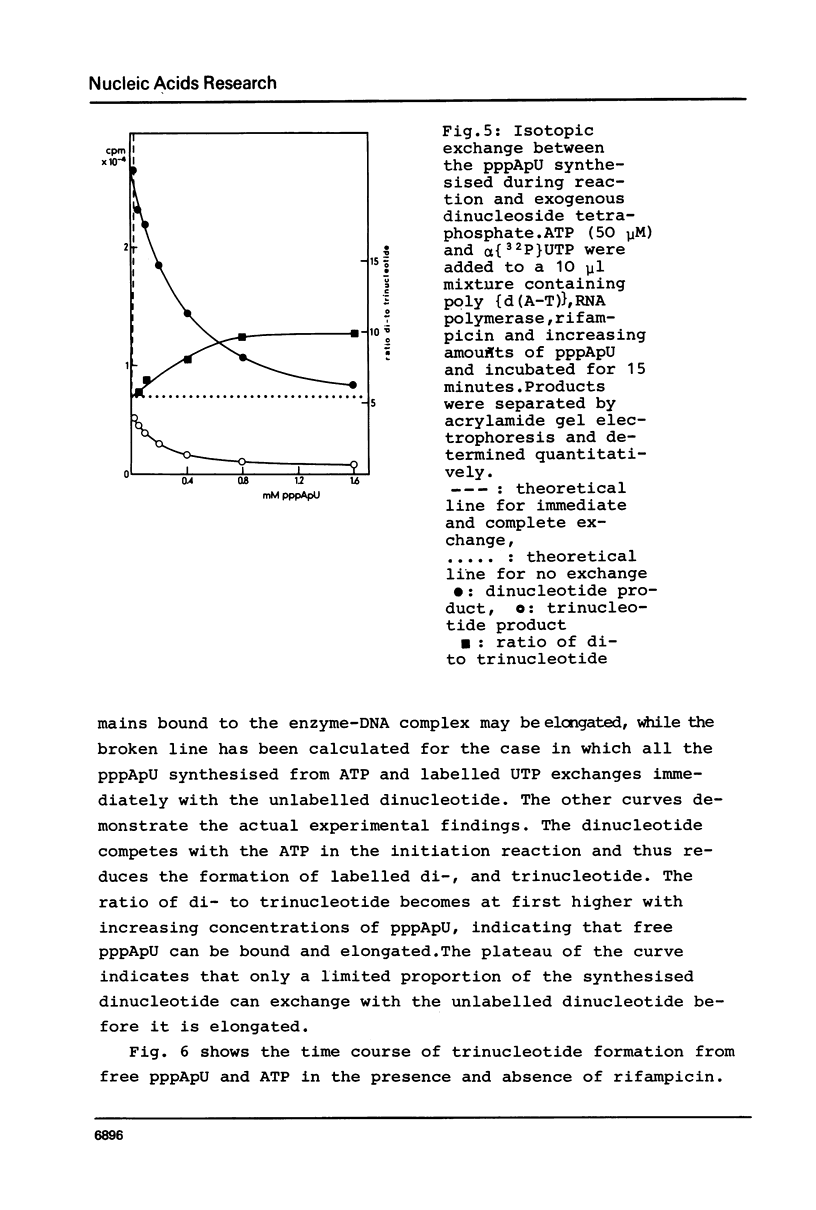
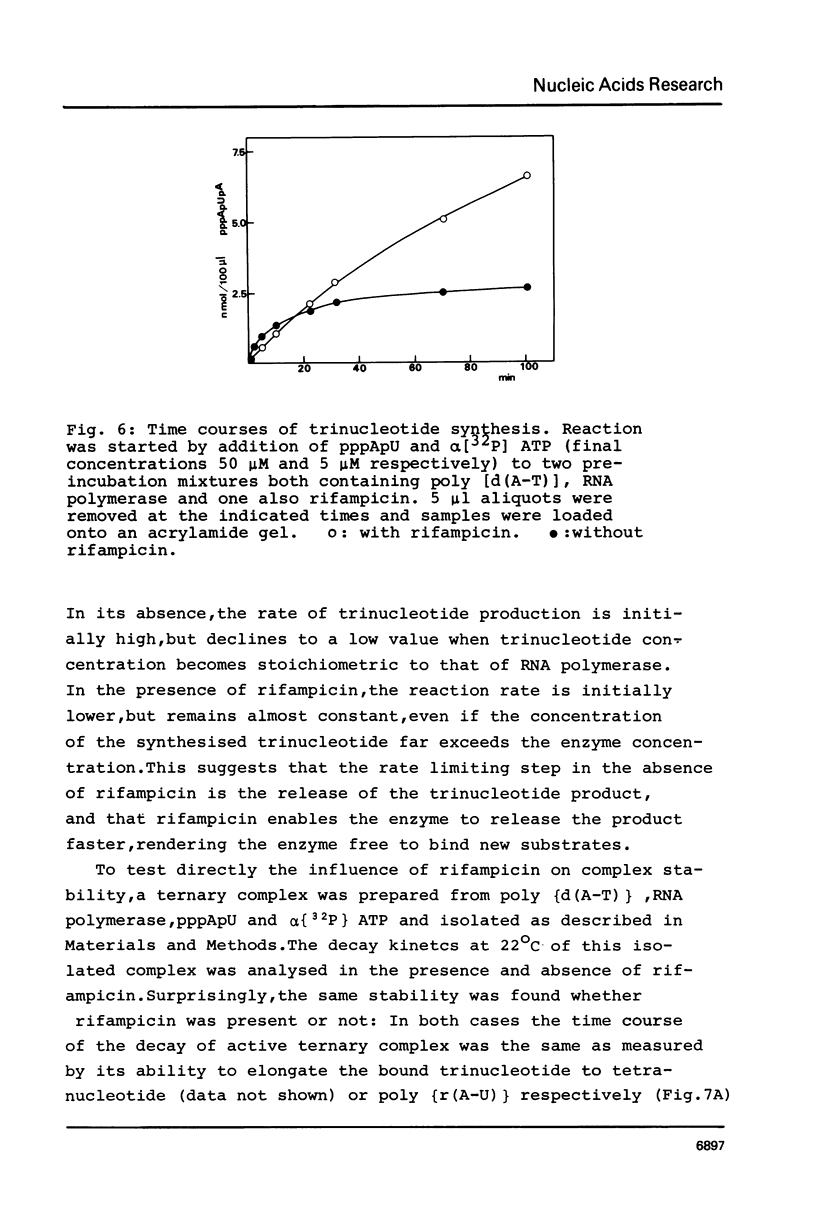
Abstract
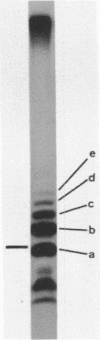
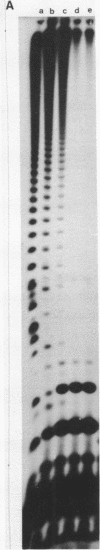
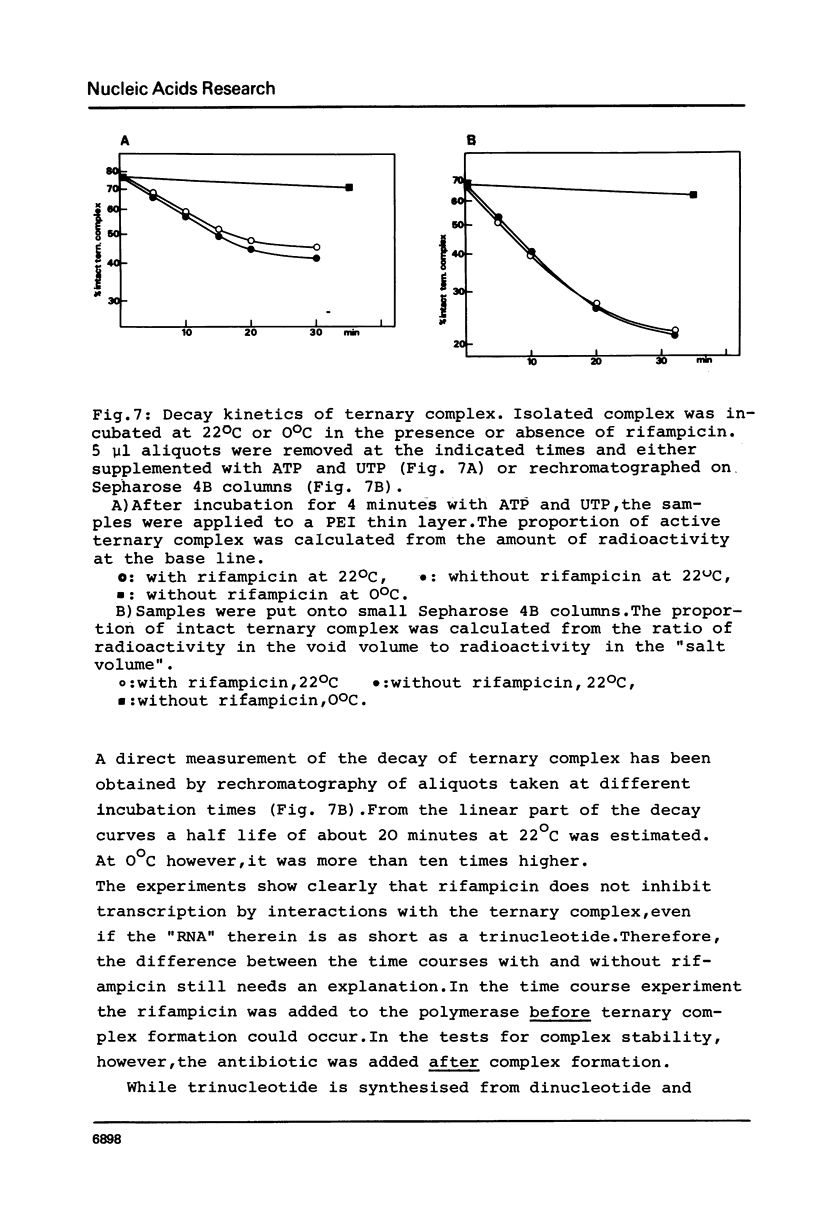
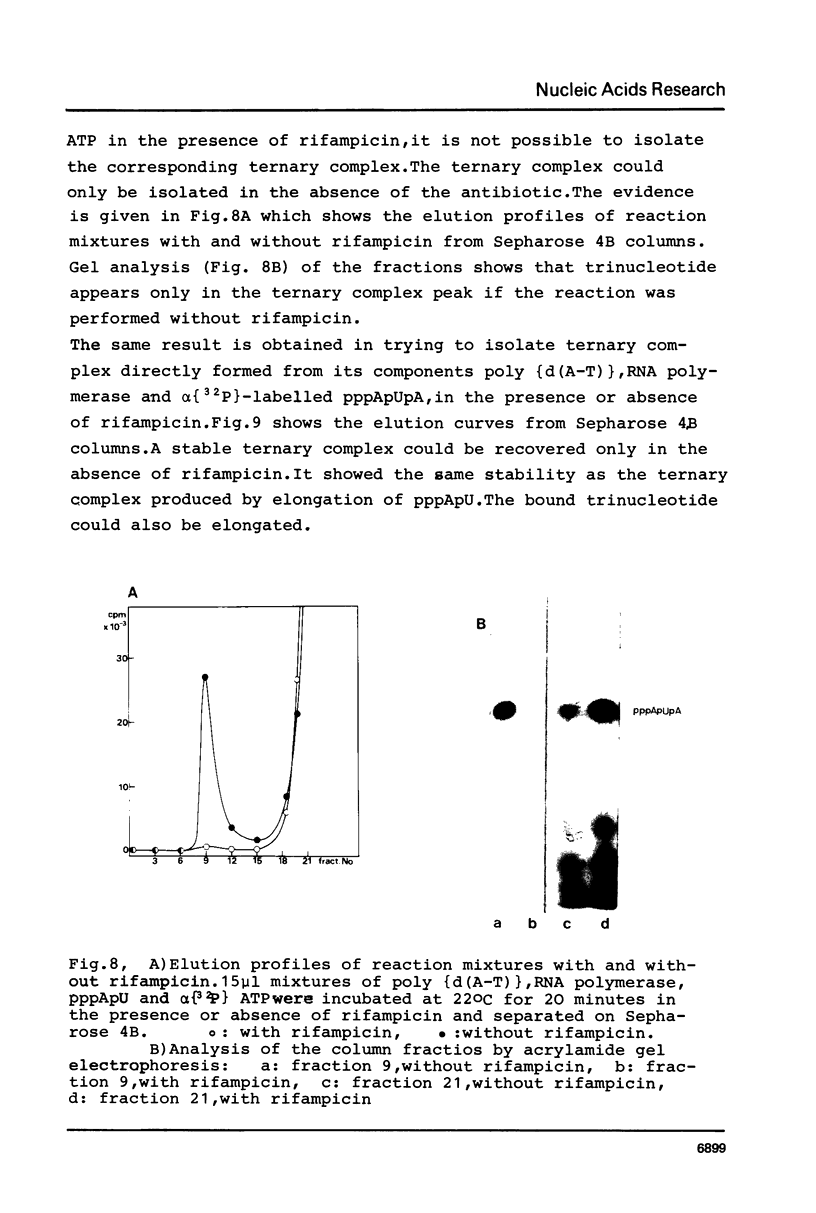
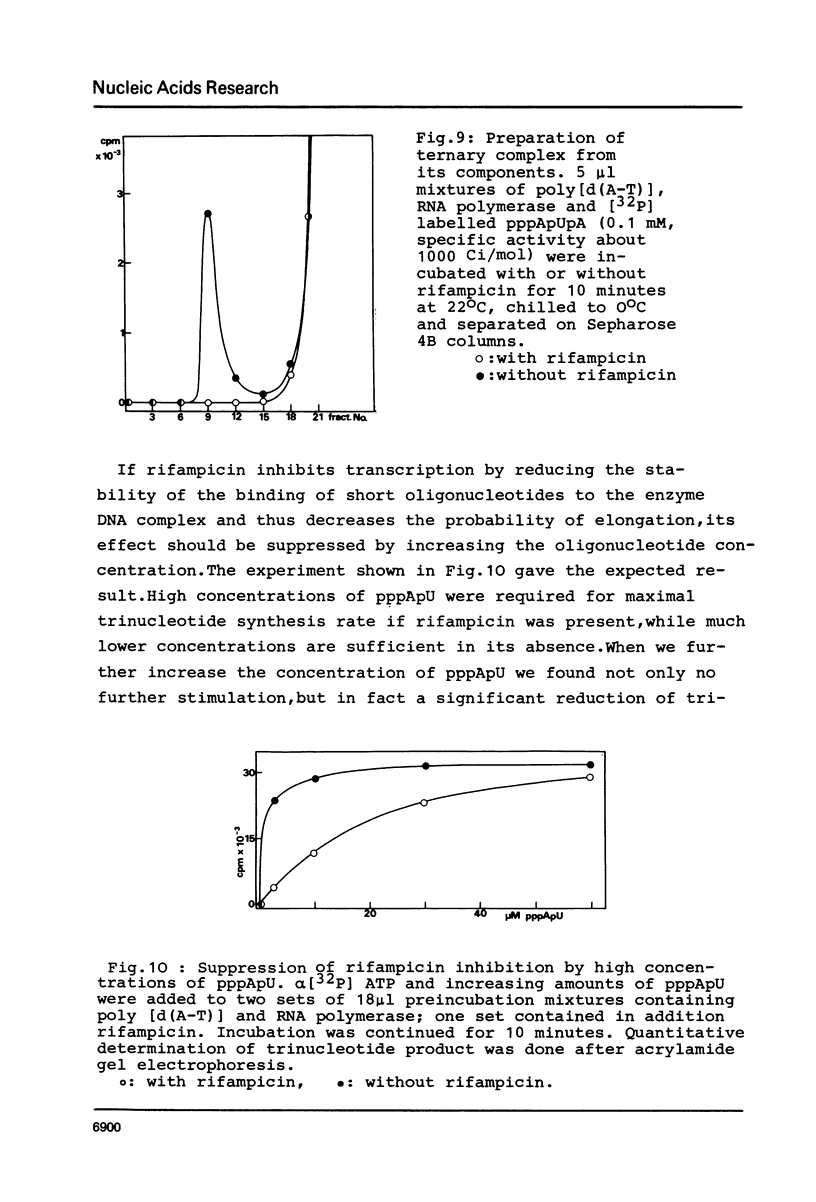
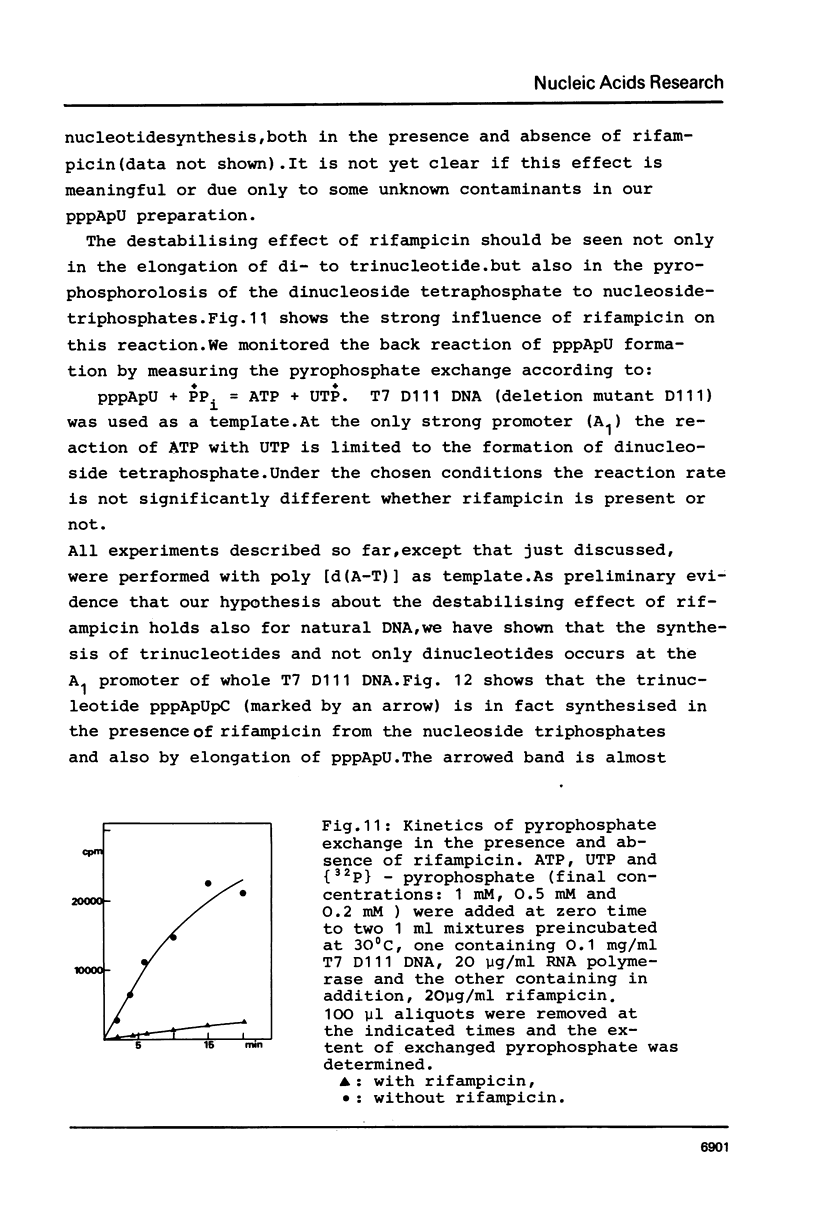
Although the antibiotic rifampicin inhibits the transcription of poly[d(A-T)] by E.coli RNA polymerase, a series of short oligonucleotides is produced. It is claimed that the overall inhibition of RNA synthesis by rifampicin is caused by a destabilising effect on the binding of the intermediate oligonucleotides to the active enzyme-DNA complex. Rifampicin itself can only interact specifically with RNA polymerase if the enzyme is free or in a binary complex with DNA. However, the enzyme is not susceptible in a ternary complex, even if the "RNA" is as short as a trinucleotide.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- APOSHIAN H. V., KORNBERG A. Enzymatic synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid. IX. The polymerase formed after T2 bacteriophage infection of Escherichia coli: a new enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1962 Feb;237:519–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Inhibition of rifampicin-resistant RNA synthesis by rifampicin-RNA polymerase complexes. FEBS Lett. 1974 Sep 1;45(1):259–262. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80857-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpousis A. J., Gralla J. D. Cycling of ribonucleic acid polymerase to produce oligonucleotides during initiation in vitro at the lac UV5 promoter. Biochemistry. 1980 Jul 8;19(14):3245–3253. doi: 10.1021/bi00555a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen U. M., McClure W. R. A noncycling activity assay for the omega subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):5713–5717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Kaya K. M., Chamberlin M. J. Escherichia coli RNA polymerase-rifampicin complexes bound at promoter sites block RNA chain elongation by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and T7-specific RNA polymerase. Biochemistry. 1978 Dec 26;17(26):5798–5804. doi: 10.1021/bi00619a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure W. R., Cech C. L., Johnston D. E. A steady state assay for the RNA polymerase initiation reaction. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):8941–8948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure W. R., Cech C. L. On the mechanism of rifampicin inhibition of RNA synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):8949–8956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sippel A., Hartmann G. Mode of action of rafamycin on the RNA polymerase reaction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Mar 18;157(1):218–219. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90286-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smagowicz W. J., Scheit K. H. Primed abortive initiation of RNA synthesis by E. coli RNA polymerase on T7 DNA. Steady state kinetic studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jun;5(6):1919–1932. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.6.1919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So A. G., Downey K. M. Studies on the mechanism of ribonucleic acid synthesis. II. Stabilization of the deoxyribonucleic acid-ribonucleic acid polymerase complex by the formation of a single phosphodiester bond. Biochemistry. 1970 Nov 24;9(24):4788–4793. doi: 10.1021/bi00826a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sylvester J. E., Cashel M. Stable RNA-DNA-RNA polymerase complexes can accompany formation of a single phosphodiester bond. Biochemistry. 1980 Mar 18;19(6):1069–1074. doi: 10.1021/bi00547a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zillig W., Zechel K., Halbwachs H. J. A new method of large scale preparation of highly purified DNA-dependent RNA-polymerase from E. coli. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1970 Feb;351(2):221–224. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1970.351.1.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]