Abstract
The signal recognition particle (SRP), which mediates cotranslational protein targeting to cellular membranes, is universally conserved and essential for bacterial and mammalian cells. However, the current understanding of the role of SRP in cell physiology and pathology is still poor, and the reasons behind its essential role in cell survival remain unclear. Here, we systematically analyzed the consequences of SRP loss in E. coli using time-resolved quantitative proteomic analyses. A series of snapshots of the steady-state and newly synthesized proteome unveiled three stages of cellular responses to SRP depletion, and demonstrated essential roles of SRP in metabolism, membrane potential, and protein and energy homeostasis in both the membrane and cytoplasm. We also identified a group of periplasmic proteins, including key molecular chaperones, whose localization was impaired by the loss of SRP; this and additional results showed that SRP is crucial for protein homeostasis in the bacterial envelope. These results reveal the extensive roles that SRP plays in bacterial physiology, emphasize the importance of proper membrane protein biogenesis, and demonstrate the ability of time-resolved quantitative proteomic analysis to provide new biological insights.
The Signal Recognition Particle (SRP)1 is a key cellular machinery that mediates the cotranslational targeting of secretory and membrane proteins to translocation machineries on the eukaryotic endoplasmic reticulum, or the bacterial plasma membrane (1). The functional core of SRP is highly conserved and comprises the SRP54 protein subunit (Ffh in bacteria) and domain IV of the SRP RNA. Many biochemical properties of SRP are conserved across the different kingdoms of life, and most notably, the bacterial SRP together with its receptor can replace their eukaryotic homologues to mediate the efficient targeting of mammalian proteins into endoplasmic reticulum microsomes (2). Consistent with its remarkable evolutionary conservation, the SRP is essential for the growth and survival of bacterial and mammalian cells (3).
Despite the importance of SRP, its role in the physiology and pathology of cells, especially bacteria, is not well understood. Many studies have attributed cellular defects upon SRP depletion to the accumulation of membrane and secretory proteins in the cytosol, whose aggregation and misfolding can be toxic to cells. In support of this notion, SRP depletion induces heat shock responses, and reduction of SRP is synthetically lethal with suppression of the heat shock response (4–8). Nevertheless, simple heat stress is not known to cause cell death (9). It is also generally recognized that depletion of SRP impairs the targeted delivery of bacterial inner membrane proteins (10). Nevertheless, in vivo analyses found that SRP deletion causes only a mild kinetic defect in protein targeting, and even verified SRP substrate proteins localize to the membrane after 2–5 min (7, 11, 12). Indeed, it appears that many proteins normally targeted by the SRP can utilize alternative pathways (8), and recent results further suggested that information in the mRNA itself could enable the localization of transcripts encoding membrane proteins to the bacterial plasma membrane (13, 14). These observations raise intriguing questions: to what extent does the SRP influence membrane protein biogenesis and cell physiology? Can the mild defects in protein targeting upon SRP depletion lead to severe consequences? How do alternative pathways and cellular adaptive responses cope with the loss of SRP? What contributes to the essential role of SRP in cell survival?
These questions are more pronounced given that a relatively small number of bona-fide SRP substrate proteins have been identified in bacteria, which to date includes 21 membrane- and seven periplasmic-proteins (15–21). It is generally thought that the bacterial SRP mediates the targeting of a subset of inner membrane proteins, whereas the majority of secretory and outer membrane proteins are delivered by the alternative SecA/B pathway (10, 17, 22). Nevertheless, the lack of a complete inventory of SRP-dependent protein substrates raises additional questions about the roles of SRP in cellular structure and function.
SRP, being an essential cellular machinery that mediates the proper localization of membrane and secretory proteins, also provides an excellent model system to probe the importance of proper membrane protein biogenesis for cell structure and function, and for the magnitude, pattern, and effectiveness of cellular adaptive responses to the stress caused by compromised protein biogenesis. An example of this is provided by genomic analysis of the consequences of SRP loss in yeast (23). This analysis showed that Saccharomyces cerevisiae adapts to the loss of SRP by up-regulating chaperones and proteases, which protect cells from mislocalized precursor proteins in the cytosol (23) and provide alternative pathways for protein export (4, 24, 25). In addition, yeast cells down-regulate the synthesis of ribosomal components to reduce protein synthesis, which helps reduce the load on protein targeting and translocation machineries (23). Partly as a consequence of these adaptive responses, yeasts are the only organisms that survive the loss of SRP. Whether and how bacteria respond differently to the loss of SRP and how such differences contribute to cell death remain to be explored.
Regulation of cells in response to stress or signaling cues occurs at various stages, from transcription, translation, to protein degradation. DNA microarrays have been the most widely used tools for global analysis of gene expression patterns. Nevertheless, the correlation between mRNA and protein abundance is poor (26). Much less is known about how cells respond to cellular stress signals at the proteome level, as changes in protein expression are often masked by the steady-state proteome.
Stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture (SILAC) provides a simple and powerful approach that allows quantitative analysis of steady-state proteome changes in cells (27, 28). Recently, an extension of this technique, pulsed SILAC (pSILAC), further allows for quantitative comparison of translation rates on a proteome-wide scale (29). pSILAC directly measures the difference in the level of newly synthesized proteome between two cell samples by pulse labeling with two different stable isotopes (29). Here, we used a combination of SILAC and pSILAC to analyze changes in the steady-state and newly synthesized proteome upon depletion of SRP, and to identify additional proteins whose localization is dependent on the SRP. These studies revealed distinct stages of cellular stress responses to the loss of SRP, and demonstrated the essential roles that SRP plays in a variety of cellular processes.
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
Cell Growth
E. coli strain HDB51 (WAM113 secB+ zic-4901::Tn10), in which the expression of genomic Ffh is under the control of an arabinose-inducible promoter (11), were grown in M9 medium containing 0.2% arabinose. Overnight culture was washed and diluted into fresh M9 containing either 0.2% arabinose or glucose to generate SRP+ and SRP– cells, respectively. Cells were replenished with fresh media whenever they reached late log-phase. Control experiments examining the effects of medium shift used wild-type DH5a cells, which were grown under the same conditions as with HDB51 and analyzed seven generations after shift to glucose-containing media.
SILAC and pSILAC Experiments
All the isotopically labeled amino acids are from the Cambridge Isotope Lab, with purity of 97–99%. For SILAC, two parallel HDB51 cultures were grown in M9 media containing 0.2% arabinose, one containing heavy (H) amino acids (13C6-l-arginine and 13C6-l-lysine) and one containing light (L) amino acids (12C6-l-arginine and 12C6-l-lysine), for at least seven generations to allow full incorporation of the isotope label. After seven cell generations, ∼95% of the proteins are labeled with heavy amino acids (supplemental Fig. S2). Cells grown in the heavy media were washed and incubated in glucose instead of arabinose to generate SRP- cells. At different times after the depletion of SRP (supplemental Fig. S1A, black arrows), the two types of cells were mixed in 1:1 ratio, processed, and analyzed by liquid chromatography-tandem MS (LC-MS/MS) (Fig. 1A). For pSILAC, SRP– and SRP+ cells were initially grown in light media. At specified times after SRP depletion (supplemental Fig. S1A, black arrows), SRP– and SRP+ cells were pulse labeled with heavy (H) (13C6,15N4-l-arginine and 13C6,15N2-l-lysine) and medium-heavy (M) (13C6-l-arginine and D4-l-lysine) amino acids, respectively, for 20 min (Fig. 1B). The two types of cells were mixed in 1:1 ratio and analyzed by LC-MS/MS (Fig. 1B). Two to four biological replicates were carried out for each experiment.
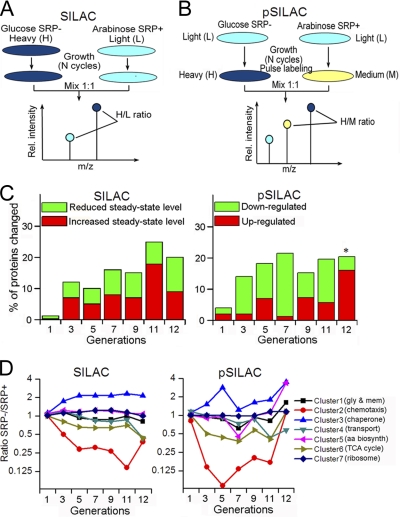
Fig. 1.
Outline of proteomic methods and global analysis of the proteomic data. (A, B,) Overview of the SILAC (A) and pSILAC (B) procedures, as described in the text and in the Experimental Procedures. C, Overview of the number of proteins whose expression (pSILAC) and steady-state (SILAC) levels changed over twofold after SRP depletion. Asterisk denotes that at the 12th generation, only the proteins whose expression (normalized ratio in pSILAC) is up-regulated over fourfold were considered; this was done to correct for potential overnormalization during MaxQuant analysis of the data at this generation, as explained in the Experimental Procedures. D, Protein clusters were generated based on different patterns of changes upon SRP depletion, as described in the Experimental Procedures. The proteins enriched in each cluster are denoted in the parenthesis and listed in supplemental Table S1B. Gly and mem, glycolysis and membrane proteins; aa biosynth, amino acid biosynthesis. Cluster 1 includes proteins that were unchanged in SILAC but slightly downregulated in the seventh generation and/or altered in the 12th generation in pSILAC. Cluster 2 includes proteins significantly and immediately down-regulated in both SILAC and pSILAC. Cluster 3 includes proteins that exhibited two spikes of induction in the fifth and 11–12th generations in pSILAC. Cluster 4 includes proteins that were specifically downregulated at the 11–12th generations. Cluster 5 includes proteins that exhibited qualitatively similar pattern but a greater extent of changes than those in cluster 1. Cluster 6 includes proteins that exhibited qualitatively similar patterns of changes as those in cluster 2, but the extent of changes is smaller. Cluster 7 includes proteins that were not significantly changed upon SRP depletion.
MS Sample Preparation
Samples were processed following the Filter Aided Sample procedure (30). Briefly, cells were heated at 95 °C for 5 min in lysis buffer (4% w/v SDS, 100 mm Tris/HCl pH 7.6, 100 mm dithiothreitol), sonicated for 10 min and clarified by centrifugation at 16,000 × g for 5 min. Thirty microliters of the cell extract were added to 200 μl of UA (8 m urea in 100 mm Tris/HCl, pH 8.5) in 10-kDa Amicon filtration devices (Millipore) and centrifuged at 14,000 × g for 30 min. The concentrates were diluted in the filter device with 200 μl of UA and centrifuged again. 100 μl of 50 mm iodoacetamide in UA was added to the concentrated lysate and incubated in dark at room temperature for 5 min, followed by centrifugation at 14,000 × g for 40 min. The concentrate was then diluted with 100 μl of UB (8 m urea in 100 mm Tris/HCl, pH 8.0) and centrifuged again at 14,000 × g in Amicon filtration devices for 40 min. This step was repeated twice. 40 μl of UB containing Lys-C (enzyme to protein ratio 1:50) was added to the concentrate and incubated overnight at 37 °C. 120 μl of trypsin (enzyme to protein ratio 1:100) in 50 mm NH4HCO3 was added to the concentrate and incubated for 4 h at room temperate. The resulting peptides were collected by centrifugation using the Amicon devices for 40 min at 14,000 × g, followed by addition of 50 μl of 500 mm NaCl and centrifugation at 14,000 × g for 20 min. The peptide sample was acidified with TFA (trifluoroacetic acid) and desalted using 3 ml MILI-SPE extraction disk cartridges (C18-S.D.).
Strong Anion Exchange Fractionation
Desalted peptides were fractionated on “in-house ” built strong anion exchangers, which were assembled based on the StageTip protocol (31) by stacking six layers of a 3 m Empore Anion Exchange disk (Varian) into a 200 μl pipet tip. Equilibration and elution of fractions was as described previously (32) using the Britton and Robinson buffer (20 mm acetic acid, 20 mm phosphoric acid, 20 mm boric acid titrated with NaOH to pH 11, 8, 6, 5, 4, and 3). Peptides were loaded at pH 11, the flow-through was captured on a StageTip (31) containing three layers of C18 membrane. Fractions were subsequently eluted from the strong anion exchangers with buffer solutions of pH 8, 6, 5, 4, and 3, respectively. These peptide fractions were also captured on C18 StageTips, eluted with 80% acetonitrile, 0.5% acetic acid, lyophilized and stored at −80 °C prior to mass spectrometry analysis.
Mass Spectrometry
All mass spectrometry experiments were performed on an EASY-nLC connected to either a hybrid LTQ-Orbitrap Classic (Thermo Fisher Scientific) or LTQ-FT Ultra (Thermo Fisher Scientific) equipped with a nano-electrospray ion source (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Peptide fractionation was carried out on a 15 cm reversed phase analytical column (75 μm ID) packed in-house with 3 μm C18 beads (ReproSil-Pur C18-AQ medium; Dr. Maisch GmbH), using a 160-min gradient of 5–35% acetonitrile in 0.2% formic acid at a flow rate of 350 nL/minute.
The mass spectrometers were operated in data-dependent mode automatically switching between full-scan MS and tandem MS acquisition. Survey full scan mass spectra were acquired after accumulation of 500,000 ions, with a resolution of 60,000 (in the Orbitrap) and 50,000 (in the LTQ-FT) at 400 m/z. The top ten (in the Orbitrap) and top seven (in the LTQ-FT) most intense ions from the survey scan were isolated and, after the accumulation of 5000 ions, fragmented in the linear ion trap by collisionally induced dissociation. Preview scan mode was enabled in the Orbitrap but not in the LTQ-FT. Precursor ion charge state screening was enabled and all singly charged and unassigned charge states were rejected. The dynamic exclusion list was enabled with a relative mass window of 10 ppm and with early expiration turned on.
MS Data Analysis
Raw data files were analyzed using MaxQuant (33) (version 1.0.13.13) and Mascot (version 2.2.06, www.matrixscience.com). All files were searched against Uniprot E. coli MG1655 entries (34, 35) (downloaded on 1/21/2009, 4252 sequences) and contaminant entries (262 sequences) using a target/decoy approach as described (33). Mass tolerances of 7 ppm for precursor ions and 0.5 Da for fragment ions were used. Variable modifications included carbamylation of peptide N terminus, oxidation of methionine, and acetylation of protein N terminus in addition to the SILAC modifications. Carboxyamidomethylation of cysteine was a fixed modification. Trypsin was specified as the digestion enzyme and up to two missed cleavages were allowed. Peptide and protein false discovery rates were fixed at 1%. All other parameters were set at default. In analysis of the proteome changes in the different subcellular fractions and in the sugar control experiments, at least two peptides were required for protein identification. For the purposes of quantitation, peptides belonging to more than one protein group were assigned to the protein group with the most unique peptides. Proteins ratios were quantified using MaxQuant (33). At least two ratios were required for protein quantitation. Protein ratio statistical significance was calculated by MaxQuant (33).
At the 12th generation, there was a global reduction in protein synthesis (see the Results). As a result, the normalization process in the MaxQuant algorithm, which sets the medium of all the observed protein ratios as 1 to generate normalized protein ratios, could have resulted in over-correction and raised the apparent ratios of some proteins by up to twofold. For this reason, only the proteins whose level increased fourfold or more at the 12th generation are discussed in the text.
Clustering of protein groups by their ratios was performed using unsupervised k-means clustering using an in-house script written in python (www.python.org) with SciPy (http://www.scipy.org) and Matplotlib. Gene ontology analysis was performed using DAVID (36, 37) and in-house scripts. Groups of functionally related proteins enriched in each cluster are listed in supplemental Table S1B.
Subcellular Fractionation
Cells containing pJH29 encoding AcrB-MBP (11) were grown to an optical density of OD600 = 0.6. Cells were lysed in Lysis buffer (100 mm Tris, pH 8.0, 20% sucrose, 1 mm CaCl2, 0.5 mm EDTA, and 50 μg/ml lysozyme) at room temperature for 10 min before centrifugation at 8000 rpm for 10 min at 4 °C. The resulting supernatant and pellet were used as periplasmic and spheroplast fractions, respectively. Remaining periplasmic contents in the spheroplast fraction was released by an additional incubation in 10 ml of Lysis buffer at room temperature for 80 min. MgCl2 was added to a final concentration of 20 mm to stabilize the spheroplasts, which was washed two more times and resuspended in 15 ml phosphate-buffered saline with 1 mm phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride. The cells were broken by french pressing at 20,000 pSi, and the lysate was ultracentrifuged at 320,000 × g for 3 h at 4 °C. The resulting supernatant and pellet were used as cytoplasmic and membrane fractions, respectively. For Western blotting analysis of the quality of cell fractionation, all the fractions were precipitated with trichloroacetic acid (TCA). For mass spec analyses, SRP+ and SRP- cells were used for fractionation following the same procedures. Two biological replicates were carried out for this experiment.
Measurement of Membrane Potential (ΔΨ)
Cells from 1 ml of culture (OD600 ∼ 0.8) were collected and resuspended in 1 ml of permeabilization buffer (10 mm Tris, pH 7.5, 1 mm EDTA, 10 mm glucose). Two microliters of 5 mg/ml JC-1 (Sigma) were added for 30 min at room temperature. Cells were collected and resuspended in 500 μl of permeabilization buffer. Fluorescent bacteria were imaged using a Fascol confocal microscope equipped with an argon laser using excitation wavelengths of 488 and 543 nm (38). The F530/F590 ratio was calculated from the number of cells that emit green or red fluorescence.
Ribosomal Profiling
Wild-type and SRP- cells were grown at 37 °C in M9 medium to an OD600 of 0.5, rapidly chilled on ice, and harvested in the presence of 34 μg/ml chloramphenicol to stabilize translating ribosomes. Preparation of cell extract was performed by French pressing in lysis buffer (20 mm KHEPES, pH 7.5, 40 mm KCl, 10 mm MgCl2, 34 μg/ml chloramphenicol, 1 mm dithiothreitol, 1 mm phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, and protease inhibitor mixture). Equivalent amounts of clarified cell lysate from each sample were loaded onto a 10–50% sucrose gradient in lysis buffer, and ultracentrifuged for 20 h at 20,000 rpm at 4 °C (39). Gradients were fractionated with a density gradient fractionator and A254 was monitored to detect the cytosolic fraction and different populations of ribosomes.
ArcA/B Activation Assay
Strain WAM121 (40) carrying the pLpZ1 (41) was grown in M9 medium with or without arabinose to generate SRP+ and SRP- cells. For the β-galactosidase activity assay, the medium was supplemented with 0.1 m MOPS (morpholinepropanesulfonic acid) (pH 7.4), 20 mm d-xylose, and 20 mm l-lactate. β-Galactosidase activity was assayed and expressed in Miller units (41).
Permeability Assays
Permeability of the cellular envelope to SDS and vancomycin was analyzed in liquid medium as described previously (42). Briefly, cells grown to an A600 of ∼0.5 in M9 medium were incubated with varying concentrations of SDS/0.5 mm EDTA for 10 min, or vancomycin for 180 min, and cell lysis was analyzed based on turbidity changes. The concentration of SDS or vancomycin necessary to produce a 50% reduction in turbidity was quantified and reported.
Additional experimental methods are provided in Supplemental Text and Figures.
RESULTS
Experimental Design
E. coli strain HDB51, in which the expression of genomic Ffh is under the control of an arabinose-inducible promoter (11), was used in this study. In the presence of arabinose or glucose, HDB51 cells present the SRP+ or SRP- genotypes, respectively (11). As indicated by proteomic analysis, the synthesis of Ffh was shut off as early as the first generation after the shift of growth media; the steady-state level of Ffh was reduced to ∼5% of that of the SRP+ cells three generations after the media shift and remained in the range of 8.6 ± 4.7% during subsequent generations (supplemental Fig. S1C).
To minimize other sources of stress such as saturation and nutrient depletion, we continuously replenished the culture with fresh media when cells reached late log phase (see Methods). Under these conditions, the growth of SRP- cells was indistinguishable from that of wild type bacteria up to 10 generations after SRP depletion (supplemental Fig. S1A). After the 10th generation, SRP- cells began to exhibit growth defects: cell growth was ∼twofold slower than SRP+ cells at the 12th generation, and stopped altogether afterwards (supplemental Fig. S1A), consistent with the notion that SRP is essential for cell viability. The growth defect of SRP- cells could be reversed by restoring SRP expression prior to the 12th generation, but less efficient rescue was observed with cells at the 12th generation (supplemental Fig. 1B), suggesting that severe cellular damage has occurred 12 generations after SRP depletion.
To test the consequence of SRP depletion on the steady-state proteome, SILAC was used to label the SRP+ and SRP- cells with light (L) and heavy (H) amino acids, respectively (Fig. 1A and supplemental Fig. S2). At specified times after SRP depletion (supplemental Fig. S1A, black arrows), equal amounts of SRP+ and SRP- cells were mixed and subjected to LC-MS/MS analysis (Fig. 1A). All the quantified proteins from each SILAC experiments can be found in supplemental Tables S2–S4. Proteins identified with only a single peptide sequence are described in supplemental Tables S5–S6.
In parallel, we used pSILAC to analyze changes in protein expression (Fig. 1B). In these experiments, cells were initially grown in light media. At specified times after SRP depletion (supplemental Fig. S1A, black arrows), SRP– and SRP+ cells were labeled with a 20 min pulse of heavy (H) and medium-heavy (M) amino acids, respectively (Fig. 1B). Pulse-labeled cells were mixed and analyzed by LC-MS/MS for quantitative comparison of the newly synthesized proteome (Fig. 1B). In general, 1000–1300 proteins were identified in each pSILAC experiment (supplemental Table S1A; for complete information on the pSILAC experiments, see supplemental Tables S7–S11). These proteins were distributed over all the major categories of Gene Ontology terms (43), similar to that of the E. coli proteome (supplemental Fig. S3). Thus pSILAC provides a simple, efficient, and unbiased method to identify the newly synthesized proteome irrespective of protein size, function, and localization.
Proteome Changes upon SRP Depletion
We analyzed proteins whose normalized levels changed over twofold in any of the generations in pSILAC or SILAC experiments. The kinetics of proteome changes in the pSILAC data suggested different stages of cellular responses to the loss of SRP. Immediately after SRP depletion, the synthesis of a significant fraction of the proteome was down-regulated; these changes peaked at seven generations after SRP depletion (Fig. 1C, right). At later stages, however, up-regulation of the synthesis of a large number of proteins was observed despite a global reduction of protein synthesis at the late stage (see section below) (Fig. 1C, right). Changes in the steady-state proteome, as reported by SILAC, followed a qualitatively similar trend but were not as pronounced as those in pSILAC (Fig. 1C, left), demonstrating the advantage of pSILAC in delineating cellular responses to stress signals.
The proteome changes were further analyzed by an unsupervised clustering algorithm, which yielded seven clusters of proteins that exhibit distinct patterns of changes either in pSILAC or SILAC (Fig. 1D). Importantly, the proteins from each cluster are enriched in different cellular pathways (supplemental Table S1B), such as chemotaxis (cluster 2), chaperones (cluster 3), transporters (cluster 4), metabolism (cluster 6), protein synthesis (cluster 7), membrane proteins and glycolysis (cluster 1). These changes are described in more detail below.
Down-regulation of Motility
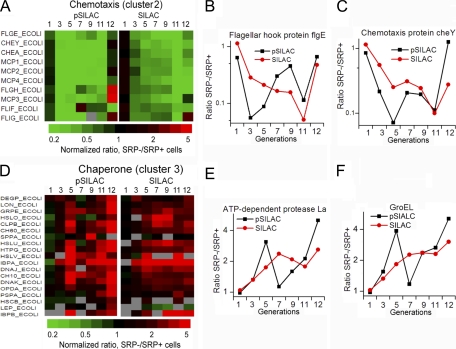
One of the most pronounced responses to SRP depletion was the down-regulation of proteins involved in bacterial motility (Figs. 2A–2C). These included components of the flagellar motor (FlgE, FlgH, FliF, FliG) and the signaling pathway that controls chemotaxis (CheY, CheA, and MCP1–4) (Figs. 2A–2C and supplemental Table S12A). Reduced synthesis of these proteins occurred immediately after SRP depletion, whereas changes in their steady-state level lagged behind the changes in protein expression by 1 to 2 generations (Figs. 2A–2C). Although glucose is known to down-regulate chemotaxis (44), control experiments showed that shifting cells from arabinose to glucose-containing media altered the expression of only a handful of proteins (supplemental Tables 1C and S13–S15). The effect of SRP depletion on the chemotaxis pathway was much more extensive and pronounced. As discussed later, down-regulation of motility is likely an adaptive response to compromised membrane potential.
Fig. 2.
Effects of SRP depletion on chemotaxis pathway components and chaperones. A–C, Changes in the expression (pSILAC) and steady-state (SILAC) levels of proteins involved in chemotaxis and bacteria motility. D–F, Changes in the expression (pSILAC) and steady-state (SILAC) levels of chaperones and proteases.
Induction of Chaperones and Proteases
Consistent with previous findings (4–8), chaperones and proteases were induced upon SRP depletion (Figs. 2D–2F and supplemental Table S12B). Analysis of the time course of proteome changes further revealed three phases of this response and suggested distinct origins of the induction at different stages. The first phase was characterized by an induction of cytoplasmic chaperones and proteases that peaked at the ∼fifth generation after SRP depletion (Figs. 2D–2F). This can be attributed to the heat shock response as previously suggested (4, 6, 7), as multiple sigma factors were also induced at this stage (supplemental Table S12I). An adaptation phase followed during seven to nine generations, in which new chaperone/protease synthesis returned to normal rates and their steady-state concentrations were maintained at slightly elevated levels (Figs. 2D–2F). After the ninth generation, a new spike of chaperone/protease induction occurred (Figs. 2D–2F). Although heat shock could still play a role, the induction of the phage shock protein PspA and the ArcA/B signaling pathway at this stage (Figs. 2D and 4 below) strongly suggested that the phage shock response, triggered by stress at the membrane (45, 46), contributed significantly to the second spike of chaperone and protease induction.
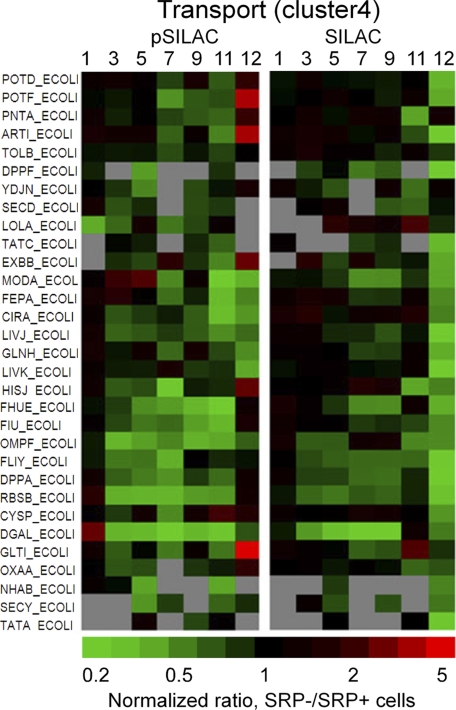
Fig. 4.
Changes in the expression (pSILAC) and steady-state (SILAC) levels of proteins involved in ion and amino acid transport after the depletion of SRP. Gray, not detected or quantifiable.
Impaired Metabolism
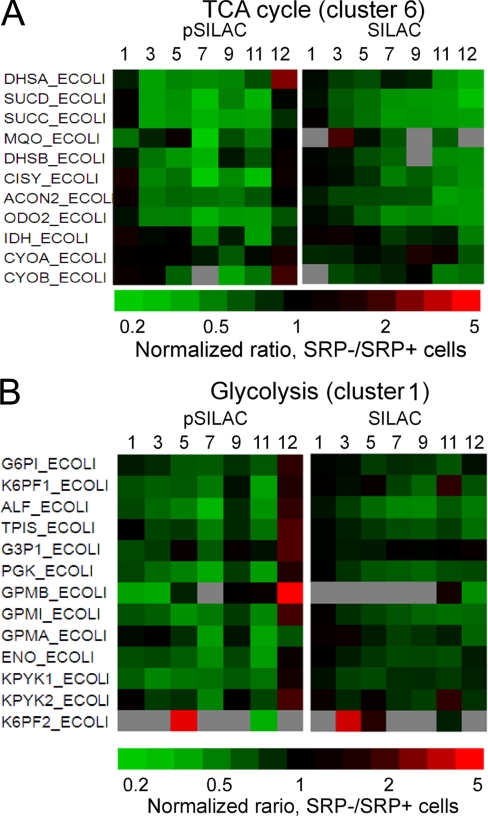
SRP depletion also caused significant down-regulation of the TCA cycle (Fig. 3A and supplemental Table S12C), which began immediately after SRP depletion and continued through the 11th generation. The steady-state level of TCA cycle enzymes was also reduced but lagged behind the reduction in their synthesis by two to four generations, reaching the lowest level at 11–12 generations (Fig. 3A). Similar changes were observed for components of the respiratory chain complex, such as succinate dehydrogenase flavoprotein subunit (DhsA), succinate dehydrogenase iron-sulfur subunit (DhsB), and cytochrome bo3 oxidase subunits (CyoA & CyoB) (Fig. 3A and supplemental Table S12C). These data are consistent with a recent analysis which detected reduced steady-state level and activity of respiratory chain complex four hours after SRP depletion (6, 7), but further showed that these reductions most likely arise from a cellular adaptive response that reduces the synthesis of these enzymes. Components of the glycolysis pathway were also down-regulated (Fig. 3B and supplemental Table S12C), but to a much lesser extent than the TCA cycle enzymes. Thus, SRP depletion led to a global down-regulation of metabolism, with a stronger impairment in aerobic metabolism.
Fig. 3.
Changes in the expression (pSILAC) and steady-state (SILAC) levels of proteins involved in TCA cycle (A) and glycolysis (B) after the depletion of SRP. Gray, not detected or quantifiable.
Down-regulation of Transporters
Most membrane proteins exhibited little change upon SRP depletion (supplemental Fig. S4). Although this seems surprising as SRP is thought to primarily target inner membrane proteins, these results are consistent with previous observations that disruption of the SRP pathway led to mild kinetic defects in membrane protein localization that were restored quickly (7, 8, 11, 12). However, down-regulation of various transporters was observed as early as 3–5 generations after SRP depletion (Fig. 4 and supplemental Table S12D), including inner or outer membrane transporters for ions (FhuE, FiU, NhaB, CirA, OmpF) and peptides (DppF), as well as periplasmic and cytoplasmic proteins that assist in transport pathways (LivJ, GltI, HisJ, FliY, FeS, DppA, ArtI, GlnH, ModA). There were also slight reductions in the expression of components of protein translocation machineries at later stages (SecY, SecD, YidC, TatA/C; Fig. 4, supplemental Fig. S4 and supplemental Table S12D). Nevertheless, changes in the steady-state level of these machineries as well as most membrane proteins were surprisingly minor (Fig. 4, supplemental Fig. S4 and supplemental Table S12D).
Response of Ribosome to the Loss of SRP
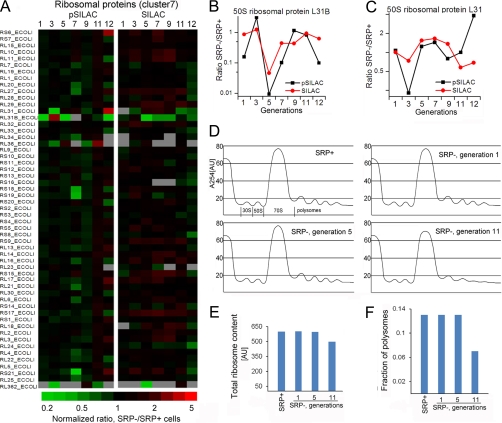
The expression and steady-state levels of most ribosomal proteins were not substantially affected by SRP depletion (Fig. 5A), in contrast to observations in S. cerevisiae and S. Mutans where a global transcriptional repression of ribosomal components occurred as an adaptive response to SRP depletion (6, 23). Only a handful of ribosomal proteins, most notably L31/L31B, were significantly down-regulated (Figs. 5B, 5C). The precise function of L31 is unclear, but its induction by σ32 has led to the suggestion that it represents a link between heat shock responses and translation (47). Additional suggestions of this link include the up-regulation of several enzymes essential for ribosome assembly at 11–12 generations after SRP depletion, including RluB and RrmJ that modify the 23S rRNA, and MiaA that stabilizes reading frames during protein synthesis (supplemental Table S12E). These enzymes are known to be up-regulated during heat shock (47), and their increased expression may reflect adaptive responses to maintain ribosome stability and translation in the face of stress.
Fig. 5.
Ribosomal proteins did not change significantly upon SRP depletion. A, Relative expression (pSILAC) and steady-state (SILAC) levels of ribosomal proteins, most of which were grouped in cluster 7. B, C, Changes in the expression (black) and steady-state (red) levels of 50S ribosomal protein L31B (B) and L31 (C). D, Analysis of ribosome profiles for SRP+ and SRP- cells at various times after SRP depletion, carried out as described under “Experimental Procedures”. E, F, Quantification of the total ribosome content (E) and the polysome fractions (F) from the data in part D.
To directly test whether the loss of SRP affected the abundance and activity of ribosomes, we compared the ribosomal profiles of SRP+ and SRP– cells by sucrose gradient ultracentrifugation. Loss of SRP did not significantly change the overall abundance of ribosomes, but reduced the polysome population after the 11th generation, suggesting reduced translation activity only at late stages of SRP depletion (Figs. 5D–5F).
Induction of Stress Responses at Late Stages
At 11–12 generations after SRP depletion, the synthesis of a large number of proteins (104, or 11% of total quantified proteins) was up-regulated (normalized ratio ≥5; supplemental Tables S12F, S12G) despite the global reduction in protein synthesis. These proteins are enriched in stress response pathways, including heat shock, phage shock, redox balance (NuoI, yhhX, IspB and FlaV), DNA repair (RecG), and cell volume regulation (CvrA). There was also significant up-regulation of proteins involved in filamentous bacteria and biofilm formation (supplemental Table S12F). Several proteins involved in DNA binding and chromosome segregation exhibited reduced expression or steady-state levels, including the DNA translocase FtsK required for chromosome resolution and septum formation during cell division (48), and the DNA binding proteins Rir4, DbhB, and NDK (supplemental Table S12G). Many of these effects likely reflect the consequences and cellular adaptive responses to cumulated stress generated by defective protein biogenesis at the membrane. The fact that SRP– cells exhibited filamentous morphology and defects in cell growth at this stage (supplemental Fig. S5A; (5)) suggest that many of these responses, though less directly connected to the SRP, reflect cellular stress and defects that are intimately linked to the eventual cell death.
SRP Depletion Causes Dissipation of Membrane Potential
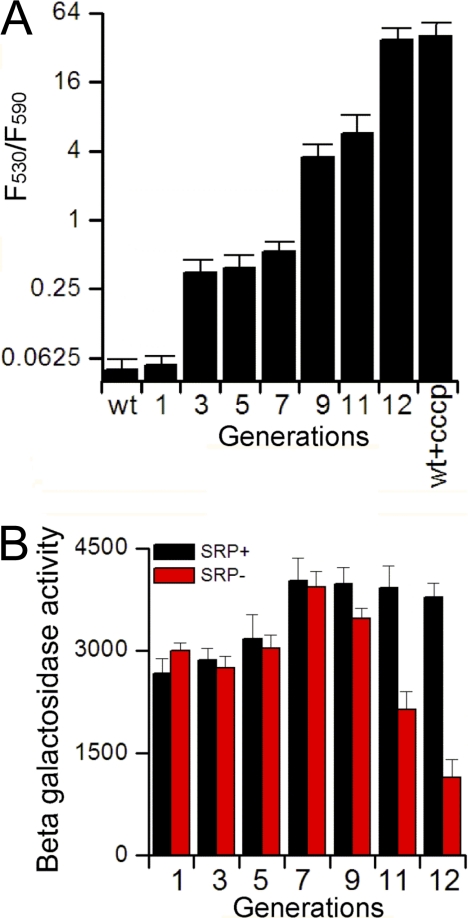
The down-regulation of motility and induction of the phage shock protein, both of which are sensitive to the membrane potential, led us to hypothesize that SRP depletion impairs the proton motive force (pmf). To directly test this hypothesis, we used fluorescence imaging with JC-1 to compare the ΔΨ component of pmf in wild type and SRP depleted cells. JC-1 is a pmf sensitive dye that exists as a green fluorescent monomer at low membrane potential, but forms red fluorescent aggregates at high membrane potential. These experiments showed that pmf was compromised immediately after SRP depletion, and that this defect exacerbated with prolonged loss of SRP (Fig. 6A and supplemental Fig. 5B). At the 12th generation after SRP depletion, the loss of pmf is similar to that in cells treated with the ionophore CCCP (Fig. 6A).
Fig. 6.
SRP depletion dissipates the membrane potential. A, Measurement of pmf using fluorescence imaging with JC-1, as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The number of cells that exhibit green (530 nm; low pmf) or red (590 nm; high pmf) fluorescence was quantified and their ratio was plotted for each generation after SRP depletion. For representative images, see data in supplemental Fig. S5B. B, The ArcA/B phosphorylation/signaling pathway was activated at late stages of SRP depletion. ArcA/B activity was measured using a β-Gal reporter for SRP+ (black) and SRP- (red) cells, as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The data represent the average of three experiments, and error bars denote standard deviation.
Phosphorylation of ArcB/A is a key pathway that senses defects in the electron transport chain and redox homeostasis at the membrane, which are critical for maintaining the pmf. To test whether SRP depletion activates the ArcB/A signaling pathway, we measured the expression of reporter genes placed under the control of lctPRD operon (41), which is repressed upon phosphorylation and activation of ArcB/A. Indeed, ArcB/A was significantly activated after 9 generations of SRP depletion (Fig. 6B), providing additional evidence for severe defects in membrane potential upon the loss of SRP.
SRP Depletion Compromises the Bacterial Envelope
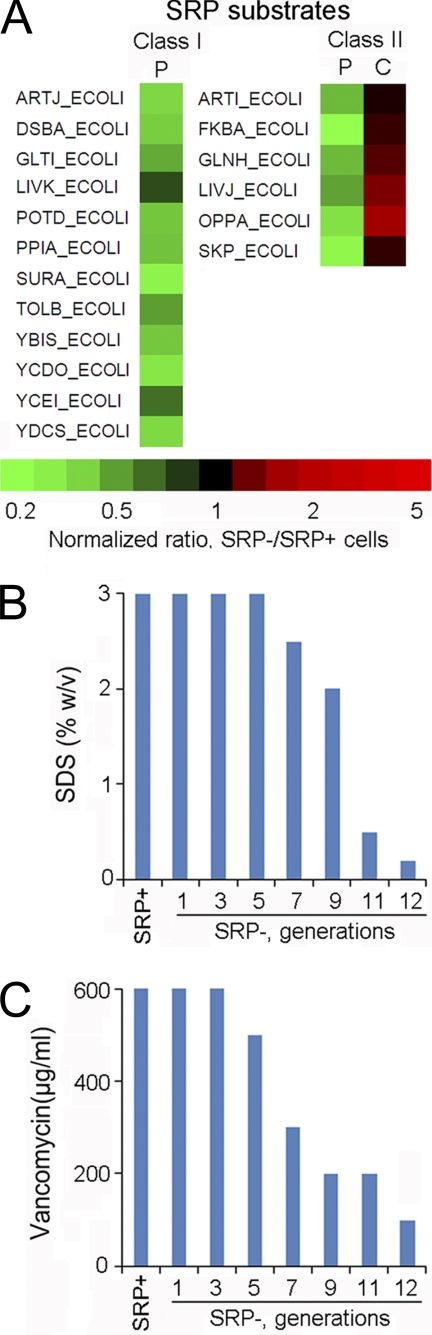
We next asked how the localization of proteins could be altered by the depletion of SRP, which would result in their reduction in the target compartment (e.g. membrane or periplasm) and possibly accumulation in the cytoplasm. To this end, we fractionated equal amounts of SRP+ and SRP– cells from the ninth generation into the cytoplasmic, periplasmic, and membrane fractions (supplemental Fig. S6), and compared the protein levels of SRP- versus SRP+ cells in each fraction using SILAC. A recent work (7) indicated that the steady-state distribution of most membrane proteins was not significantly affected by SRP depletion, and our preliminary analysis reached similar conclusions. We therefore focused our analyses on the periplasmic proteome. We identified 18 proteins that exhibited substantially reduced levels in the periplasm (Fig. 7A); among them, six proteins also accumulated slightly in the cytoplasm (Fig. 7A, Class II and supplemental Tables S12H, S16–S21). The pSILAC and SILAC results showed that neither the expression nor steady-state level of these proteins was altered by the SRP depletion at this stage, ruling out artifacts caused by cellular adaptive responses. Among these proteins were two verified SRP substrates, DsbA and TolB (18), supporting the validity of this strategy in identifying proteins whose proper localization is SRP-dependent.
Fig. 7.
SRP depletion compromises the bacterial envelope. A, Impaired localization of periplasmic proteins at the ninth generation after SRP depletion. P, periplasm; C, cytoplasm. Class I and II are distinguished by whether the proteins also exhibited cytoplasmic accumulation. B, C, Analysis of the permeability of SRP+ and SRP- cells to SDS (B) and vancomycin (C) at various generations after SRP depletion. The concentrations of SDS or vancomycin required to produce a 50% reduction in cell trubidity were reported. The data represent average values from duplicate experiments.
Interestingly, many of these proteins were molecular chaperones (FkbA, Skp, SurA, PPiA, DsbA) essential for protein folding in the periplasm and for the export of outer membrane proteins, suggesting that SRP is also important for the integrity and homeostasis of the bacterial envelope. To directly test this idea, we investigated whether the bacterial envelope is compromised in SRP- cells based on their sensitivity to minimal doses of vancomycin and SDS. These reagents are impermeable to intact bacterial outer membrane in wild type cells, but become toxic to cells with compromised envelope. Indeed, SRP- cells exhibited increased sensitivity to these reagents after five generations of SRP depletion, and the defect exacerbated with continued loss of SRP (Figs. 7B, 7C). This provided direct evidence that the loss of SRP also causes severe defects in the bacterial envelope.
DISSCUSSION
pSILAC as a Powerful Tool to Identify Newly Synthesized Proteome
Cells constantly sense and respond to intracellular or environmental cues by reprogramming their gene expression. The selective identification of newly synthesized proteome provides an important means to understand such responses. Using the SRP pathway as a model system, we demonstrate here that pSILAC, pioneered by the Selbach group (29), provides a simple and powerful method to quantitatively identify changes in protein expression in response to cellular stress or signaling cues. The combination of pSILAC with SILAC allowed us to pinpoint cellular reprogramming and proteome changes in response to SRP depletion, and provided new insights into the roles of SRP in cell physiology and pathology. Compared with previously described approaches that enrich and identify the newly synthesized proteome using chemical tags (49, 50), pSILAC is simple in design and execution as it bypasses the chemical tagging and purification steps. Further, although methods using chemical tagging have yielded, in general, ∼200–500 newly synthesized protein identifications (49, 50), the pSILAC procedure in this study yielded ∼1000–1400 protein identifications in each experiment, of which ∼700–1300 are quantifiable, indicating that it is also highly efficient. Finally, comparison of the pSILAC and SILAC data could, in principle, yield information about protein stability (29). In this study, reductions in the steady-state level of proteins generally lagged behind the reductions in their expression, yet different proteins exhibited different durations of such “lags.” This information could be used to provide rough estimates of the relative turnover rates of these proteins in vivo.
Cellular Reprogramming and Proteome Changes in Response to Loss of SRP
SRP is essential for the survival of most bacterial and mammalian cells. Previous work has identified two major consequences of SRP depletion: cytoplasmic accumulation of SRP substrates, which induces the heat shock response, and a kinetic defect in the localization of inner membrane proteins (7, 8, 11, 12). Down-regulation of the synthesis of ribosomal components has been observed as an adaptive response to the loss of SRP in yeast cells and in S. mutans (6, 23). Recent studies also found that the steady-state level of metabolic proteins was reduced upon SRP depletion (7). Here, time-resolved proteomic analysis enriched the previous findings, demonstrated more extensive roles of SRP in bacterial physiology, identified additional proteins whose localization is dependent on SRP, and emphasized the importance of proper membrane protein biogenesis. This work also provided a case study for cellular adaptive responses to the stress caused by protein localization and biogenesis defects. We note here that because of the use of 10 kDa cutoff filters during sample preparation, a number of small proteins associated with stress responses (51) may have escaped detection in this work; the extent of cellular stress response to protein biogenesis defects could be more extensive than described here.
Immediate Cellular Responses to the Loss of SRP
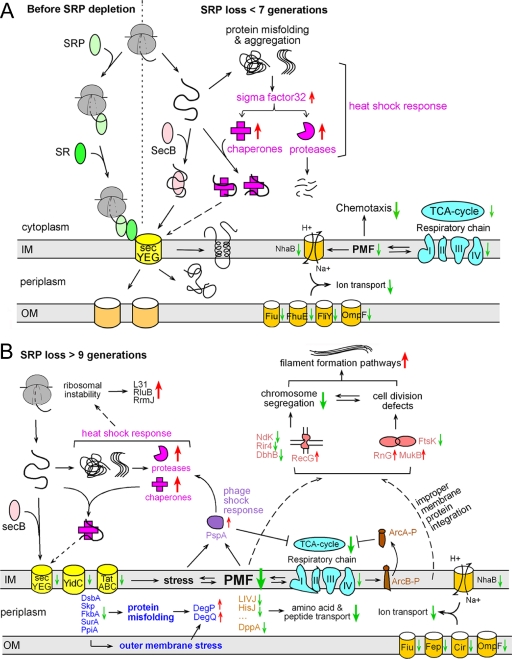
Two major cellular adaptive responses occurred at early stages of SRP depletion (Fig. 8A). First, there was an induction of cytoplasmic chaperones and proteases. As suggested previously (4, 6, 7), this likely arises from the heat shock response (Fig. 8A, magenta). Heat shock proteins protect cells against the accumulation of mislocalized proteins in the cytoplasm; they might also provide alternative pathways to deliver proteins to the membrane, although this role has not been demonstrated in bacteria (Fig. 8A, dashed arrow). Second, there were global reductions in the expression and steady-state levels of enzymes in the TCA cycle and respiratory chain complex (Fig. 8A, cyan). As the electron transport chain is primarily responsible for generating the pmf, its down-regulation is intimately linked to the reduction of membrane potential upon the loss of SRP (Fig. 8A). The extensive down-regulation of cell motility observed concurrently is likely an adaptive response to the impaired membrane potential, as bacterial motility is a pmf-consuming process. Likewise, the reduced synthesis of ion, amino acid, and peptide transporters (Fig. 8A, orange) most likely reflect adaptive responses to reduced membrane potential, as most of these transporters are driven by the pmf (52, 53). Together, these results demonstrate a previously under-appreciated role of SRP in intracellular metabolism and the maintenance of membrane potential.
Fig. 8.
Model for the consequences and cellular adaptive responses at various stages of SRP depletion in bacteria. A, Immediate cellular responses to SRP depletion (<7 generations), which primarily involves the heat shock response (magenta), down-regulation of TCA cycle and the respiratory chain (cyan), coupled with compromised pmf which likely leads to down-regulation of chemotaxis/motility and reduced expression of pmf-dependent transporters. B, Cellular stress responses and proteome changes at late stages of SRP depletion (≥9 generations), including: reduced levels of TCA cycle and respiratory chain components (cyan) coupled with severe dissipation of the pmf, which leads to activation of ArcB/A signaling (brown) and induction of the phage shock response (purple); a second spike of cytoplasmic chaperones and protease induction (magenta); reduced levels of transporters (orange and yellow); impaired localization of periplasmic chaperones that leads to envelope stress and the induction of DegP and DegQ (dark blue); defects in chromosome segregation and cell division that leads to filamentous morphology (coral).
How the loss of SRP leads to down-regulation of metabolism and the dissipation of pmf remains to be determined. Several possibilities could be envisioned. The proper biogenesis of key enzymes in the respiratory chain complex could be highly SRP-dependent, whose defective biogenesis could induce the cells to down-regulate their expression. In support of this notion, cytochrome-d oxidases (CydA/B) have been suggested to be SRP substrates from a genetic screen (17). Alternatively or in addition, the kinetic defects in the biogenesis of numerous proteins on the bacterial inner membrane (7, 11, 12), though mild, could compromise the quality of membrane and signal the cells to down-regulate metabolism. The identification of a more complete set of SRP substrates, higher resolution methods to investigate the quality of the cytoplasmic membrane, and advances in the understanding of signaling pathways that regulate cellular metabolism will be crucial to distinguish between these models.
A Transient “Adapted” Phase
During seven to nine generations after the loss of SRP, cells appear to enter a relatively “adapted ” phase, during which the synthesis of heat shock proteins returned to “normal ” rates, and cells maintained a new steady-state level of these proteins. The proteins involved in motility and metabolism remained at a new steady-state level. Up until this stage, SRP-depleted cells maintained similar growth rates and morphology as wild-type cells. This demonstrates the effectiveness of cellular adaptive responses in overcoming the stress caused by protein biogenesis defects, and argues against the cytoplasmic accumulation of SRP substrates and heat shock as the major source of toxicity upon SRP depletion.
Stress Responses After Prolonged SRP Depletion
At late stages of SRP depletion (>9 generations), another wave of cellular reprogramming occurred that was more extensive than the earlier response (Fig. 8B). Despite the complexity of these responses, many of them could be attributed to two closely interconnected phenomena: the severe reductions in the level of TCA cycle/respiratory chain components (Fig. 8B, cyan) and the dissipation of pmf (Fig. 8). For example, both the activation of the ArcB/A signaling pathway (Fig. 8B, brown) and the induction of PspA (Fig. 8B, purple) at this stage are consistent with the roles of these pathways in sensing and rescuing redox imbalances in the respiratory chain and defects in pmf. The phage shock response, in addition to the heat shock response, is likely responsible for the second spike of chaperone and protease induction (Fig. 8B, magenta). It is not clear what caused the slight reductions in the expression of protein translocation machineries (SecY, YidC, and TatAC; Fig. 8B, yellow) after the ninth generation. These reductions, though minor, could further exacerbate the stress at the membrane and defects in protein homeostasis of the cell.
In addition, stress pathways were induced that reflect defects in DNA metabolism and cell division (Fig. 8B, coral), including reduced levels of the DNA translocase FtsK and DNA binding proteins (Rir4, DbhB, NDK), and induction of the DNA repair protein RecG and cell volume regulator CvrA. Although many possibilities exist, these defects have been reported to arise from the dissipation of pmf, which causes delocalization or defective biogenesis of membrane proteins involved in cell division and chromosome segregation (48). Thus these defects, though less directly connected to the SRP pathway, reflect the link between protein homeostasis and genome stability; they are likely responsible for the changes in cell morphology, the induction of pathways involved in filamentous bacteria and biofilm formation (Fig. 8B), and eventually cell death.
Loss of SRP Compromises Bacterial Envelope
SRP depletion also impairs the proper localization of a group of periplasmic proteins, including several key chaperones in the periplasmic space (Fig. 8B, dark blue). As these chaperones are essential for the folding, export and biogenesis of many periplasmic and outer membrane proteins, this suggests that SRP depletion not only affects events at the inner membrane, but also profoundly impairs protein homeostasis in the entire bacterial envelope (Fig. 8B, dark blue). In support of this model, SRP- cells exhibit impaired outer membrane integrity and becomes hypersensitive to minimal doses of drugs that are normally impermeable to an intact bacterial envelope. Further, the DegP and DegQ proteases, which are often induced by protein misfolding in the periplasm and outer membrane (54, 55), are induced at late stages of SRP depletion (Fig. 8B, dark blue).
Comparison of Cellular Adaptive Responses to the Loss of SRP
It is intriguing to compare the cellular reprogramming and adaptive responses upon SRP depletion in E. coli to those in S. cerevisiae and S. Mutans, which can survive the loss of SRP (6, 23, 56). In all cases, cells up-regulate the expression of chaperones and proteases to cope with the accumulation of mislocalized membrane and secretory proteins. A significant difference is that yeast cells as well as S. Mutans also down-regulate the synthesis of ribosomal components and thus reduce global protein synthesis (6, 23). In contrast, active down-regulation of protein synthesis was not observed in E. coli. The modest reduction in protein synthesis, observed only at late stages of SRP depletion ((7) and this work), is most consistent with destabilization of the ribosome in the face of protein homeostasis imbalances, and cellular responses to maintain ribosome stability in the face of this stress were observed instead. Another notable difference is that chaperones such as Hsp70 provide efficient alternative pathways for protein secretion in yeast cells (24); conceivably, the up-regulation of Hsp70 proteins upon SRP depletion could effectively help yeast cells cope with the loss of SRP. The ability of the bacterial Hsp70 homologue, DnaK, to help rescue protein targeting has not been established. Notably, the expression and steady state levels of SecA and SecB, which together provide an alternative pathway for the targeting of membrane and secretory proteins in bacteria (Fig. 8, pink), remain unchanged upon SRP depletion. The absence of down-regulation in protein synthesis, which reduces the load on protein targeting and translocation machineries (23), as well as up-regulation of effective alternative protein targeting pathways may account, at least in part, for the inability of E. coli to survive the loss of SRP compared with yeast cells.
Summary and Perspective
The combination of pSILAC and SILAC allowed us to distinguish cellular adaptive responses from changes in protein level caused by their mislocalization and degradation. The results revealed new roles of SRP in membrane potential, metabolism and energy status, and protein homeostasis in almost all the cellular compartments. These results also suggest that, aside from the cytoplasmic accumulation of mislocalized proteins, other deleterious consequences of SRP depletion may ultimately cause cell death. These include the collapse in metabolism and membrane potential, defects in envelope integrity, and genome instability.
Intriguingly, the results here and from previous work present two opposing sets of observations. On the one hand, previous work showed that SRP depletion causes only a mild kinetic defect in the localization of inner membrane proteins (7, 8, 11, 12); we also found here that the steady-state level or distribution of most inner membrane proteins was not significantly altered by SRP depletion. On the other hand, the numerous cellular stress responses upon the loss of SRP observed here indicate stress and compromised integrity of the membrane. These observations led us to speculate that cotranslational protein targeting by the SRP is important not only for the localization of inner membrane proteins, but also for their proper folding, integration, or assembly. Alternative pathways could help rescue their localization, but might not restore their proper biogenesis and function. The immediate reduction of pmf upon SRP depletion suggests that such folding/assembly defects occurred as a direct consequence of the loss of SRP. At late stages of SRP depletion, these defects could be further exacerbated by the impaired pmf, which is crucial for the proper orientation of many membrane proteins (57). The link between protein targeting pathways and the subsequent folding/assembly of proteins has been documented in a number of cases (10, 58, 59), and will remain an important subject for future investigations.
Acknowledgments
We thank H. Bernstein for strain HDB51 and plasmid pJH29, G. Phillips for strain WAM121, U. Hartl for antibodies, O. Kwon for plasmid pLpZ1, S. Sweeney for help with fluorescence imaging, G. Smith for help with mass spectrometry, A. Typas and D. Newman for insightful discussions and suggestions, and S. Mazmanian, D. Tirrell, A. Varshavsky, N. Pierce, X. Zhang and members of the Shan group for helpful comments on the manuscript.
Footnotes
* This work was supported by National Institutes of Health grant GM078024 to S.S. S.S. was supported by career awards from the Burroughs Welcome Foundation, a Beckman Young Investigator award, a Packard and Lucile award in science and engineering, and a Henry Dreyfus teacher-scholar award. S. H., R. L. J. G. and M. S. were supported by the Betty and Gordon Moore Foundation and the Beckman Institute.
 This article contains Supplemental Text, supplemental Figs. S1 to S6 and Tables S1 to S21.
This article contains Supplemental Text, supplemental Figs. S1 to S6 and Tables S1 to S21.
1 The abbreviations used are:
- SRP
- signal recognition particle
- SILAC
- stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture
- pSILAC
- pulsed SILAC
- pmf
- proton motive force.
REFERENCES
- 1. Keenan R. J., Freymann D. M., Stroud R. M., Walter P. (2001) The signal recognition particle. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 70, 755–775 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Powers T., Walter P. (1997) Co-translational protein targeting catalyzed by the Escherichia coli signal recognition particle and its receptor. EMBO J. 16, 4880–4886 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Walter P., Johnson A. E. (1994) Signal sequence recognition and protein targeting to the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 10, 87–119 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Bernstein H. D., Hyndman J. B. (2001) Physiological basis for conservation of the signal recognition particle targeting pathway in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 183, 2187–2197 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Park S. K., Jiang F., Dalbey R. E., Phillips G. J. (2002) Functional analysis of the signal recognition particle in Escherichia coli by characterization of a temperature-sensitive ffh mutant. J. Bacteriol. 184, 2642–2653 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Hasona A., Zuobi-Hasona K., Crowley P. J., Abranches J., Ruelf M. A., Bleiweis A. S., Brady L. J. (2007) Membrane composition changes and physiological adaptation by Streptococcus mutans signal recognition particle pathway mutants. J. Bacteriol. 189, 1219–1230 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Wickström D., Wagner S., Baars L., Ytterberg A. J., Klepsch M., van Wijk K. J., Luirink J., de Gier J. W. (2011) Consequences of Depletion of the Signal Recognition Particle in Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 4598–4609 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Newitt J. A., Ulbrandt N. D., Bernstein H. D. (1999) The structure of multiple polypeptide domains determines the signal recognition particle targeting requirement of Escherichia coli inner membrane proteins. J. Bacteriol. 181, 4561–4567 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Han K. Y., Park J. S., Seo H. S., Ahn K. Y., Lee J. (2008) Multiple stressor-induced proteome responses of Escherichia coli BL21(DE3). J. Proteome Res. 7, 1891–1903 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Cross B. C., Sinning I., Luirink J., High S. (2009) Delivering proteins for export from the cytosol. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 10, 255–264 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Lee H. C., Bernstein H. D. (2001) The targeting pathway of Escherichia coli presecretory and integral membrane proteins is specified by the hydrophobicity of the targeting signal. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 98, 3471–3476 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Peterson J. H., Woolhead C. A., Bernstein H. D. (2003) Basic amino acids in a distinct subset of signal peptides promote interaction with the signal recognition particle. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 46155–46162 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Prilusky J., Bibi E. (2009) Studying membrane proteins through the eyes of the genetic code revealed a strong uracil bias in their coding mRNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106, 6662–6666 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Nevo-Dinur K., Nussbaum-Shochat A., Ben-Yehuda S., Amster-Choder O. (2011) Translation-independent localization of mRNA in E. coli. Science 331, 1081–1084 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Koch H. G., Hengelage T., Neumann-Haefelin C., MacFarlane J., Hoffschulte H. K., Schimz K. L., Mechler B., Müller M. (1999) In vitro studies with purified components reveal signal recognition particle (SRP) and SecA/SecB as constituents of two independent protein-targeting pathways of Escherichia coli. Mol. Biol. Cell 10, 2163–2173 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Koch H. G., Moser M., Schimz K. L., Muller M. (2002) The integration of YidC into the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli requires the signal recognition particle, SecA and SecYEG. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 5715–5718 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Ulbrandt N. D., Newitt J. A., Bernstein H. D. (1997) The E. coli signal recognition particle is required for the insertion of a subset of inner membrane proteins. Cell 88, 187–196 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Huber D., Boyd D., Xia Y., Olma M. H., Gerstein M., Beckwith J. (2005) Use of thioredoxin as a reporter to identify a subset of Escherichia coli signal sequences that promote signal recognition particle-dependent translocation. J. Bacteriol. 187, 2983–2991 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Sijbrandi R., Urbanus M. L., ten Hagen-Jongman C. M., Bernstein H. D., Oudega B., Otto B. R., Luirink J. (2003) Signal recognition particle (SRP)-mediated targeting and Sec-dependent translocation of an extracellular Escherichia coli protein. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 4654–4659 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Macfarlane J., Müller M. (1995) The functional integration of a polytopic membrane protein of Escherichia coli is dependent on the bacterial signal-recognition particle. Eur. J. Biochem. 233, 766–771 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Neumann-Haefelin C., Schäfer U., Müller M., Koch H. G. (2000) SRP-dependent co-translational targeting and SecA-dependent translocation analyzed as individual steps in the export of a bacterial protein. EMBO J. 19, 6419–6426 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Kumamoto C. A., Beckwith J. (1985) Evidence for specificity at an early step in protein export in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 163, 267–274 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Mutka S. C., Walter P. (2001) Multifaceted physiological response allows yeast to adapt to the loss of the signal recognition particle-dependent protein-targeting pathway. Mol. Biol. Cell 12, 577–588 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Deshaies R. J., Koch B. D., Werner-Washburne M., Craig E. A., Schekman R. (1988) A subfamily of stress proteins facilitates translocation of secretory and mitochondrial precursor polypeptides. Nature 332, 800–805 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Driessen A. J., Nouwen N. (2008) Protein translocation across the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 77, 643–667 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Ideker T., Thorsson V., Ranish J. A., Christmas R., Buhler J., Eng J. K., Bumgarner R., Goodlett D. R., Aebersold R., Hood L. (2001) Integrated genomic and proteomic analyses of a systematically perturbed metabolic network. Science 292, 929–934 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Ong S. E., Mann M. (2006) A practical recipe for stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture (SILAC). Nat. Protoc. 1, 2650–2660 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. de Godoy L. M., Olsen J. V., Cox J., Nielsen M. L., Hubner N. C., Fröhlich F., Walther T. C., Mann M. (2008) Comprehensive mass-spectrometry-based proteome quantification of haploid versus diploid yeast. Nature 455, 1251–1254 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Schwanhäusser B., Gossen M., Dittmar G., Selbach M. (2009) Global analysis of cellular protein translation by pulsed SILAC. Proteomics 9, 205–209 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Wiśniewski J. R., Zougman A., Nagaraj N., Mann M. (2009) Universal sample preparation method for proteome analysis. Nat. Methods 6, 359–362 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Rappsilber J., Ishihama Y., Mann M. (2003) Stop and Go Extraction Tips for Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization, Nanoelectrospray, and LC/MS Sample Pretreatment in Proteomics. Anal. Chem. 75, 663–670 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Wiśniewski J. R., Zougman A., Mann M. (2009) Combination of FASP and StageTip-Based Fractionation Allows In-Depth Analysis of the Hippocampal Membrane Proteome. J. Proteome Res. 8, 5674–5678 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Cox J., Mann M. (2008) MaxQuant enables high peptide identification rates, individualized p.p.b.-range mass accuracies and proteome-wide protein quantification. Nat. Biotechnol. 26, 1367–1372 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.(2010) The Universal Protein Resource (UniProt) in 2010. Nucleic Acids Res. 38, D142–148 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Jain E., Bairoch A., Duvaud S., Phan I., Redaschi N., Suzek B. E., Martin M. J., McGarvey P., Gasteiger E. (2009) Infrastructure for the life sciences: design and implementation of the UniProt website. BMC Bioinformatics 10, 136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Huang da W., Sherman B. T., Lempicki R. A. (2009) Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat. Protoc. 4, 44–57 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Dennis G., Jr., Sherman B. T., Hosack D. A., Yang J., Gao W., Lane H. C., Lempicki R. A. (2003) DAVID: Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery. Genome Biol. 4, P3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Becker L. A., Bang I. S., Crouch M. L., Fang F. C. (2005) Compensatory role of PspA, a member of the phage shock protein operon, in rpoE mutant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Mol. Microbiol. 56, 1004–1016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Schaffitzel C., Ban N. (2007) Reprint of “Generation of ribosome nascent chain complexes for structural and functional studies” [J. Struct. Biol. 158 463–471]. (2007) J. Struct. Biol. 159, 302–310 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. de Gier J. W., Mansournia P., Valent Q. A., Phillips G. J., Luirink J., von Heijne G. (1996) Assembly of a cytoplasmic membrane protein in Escherichia coli is dependent on the signal recognition particle. FEBS Lett. 399, 307–309 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Kwon O., Georgellis D., Lynch A. S., Boyd D., Lin E. C. (2000) The ArcB sensor kinase of Escherichia coli: genetic exploration of the transmembrane region. J. Bacteriol. 182, 2960–2966 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Cascales E., Gavioli M., Sturgis J. N., Lloubès R. (2000) Proton motive force drives the interaction of the inner membrane TolA and outer membrane pal proteins in Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 38, 904–915 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Zeeberg B. R., Feng W., Wang G., Wang M. D., Fojo A. T., Sunshine M., Narasimhan S., Kane D. W., Reinhold W. C., Lababidi S., Bussey K. J., Riss J., Barrett J. C., Weinstein J. N. (2003) GoMiner: a resource for biological interpretation of genomic and proteomic data. Genome Biol. 4, R28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Adler J., Hazelbauer G. L., Dahl M. M. (1973) Chemotaxis toward sugars in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 115, 824–847 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Jovanovic G., Lloyd L. J., Stumpf M. P., Mayhew A. J., Buck M. (2006) Induction and function of the phage shock protein extracytoplasmic stress response in Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 21147–21161 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Wagner S., Baars L., Ytterberg A. J., Klussmeier A., Wagner C. S., Nord O., Nygren P. A., van Wijk K. J., de Gier J. W. (2007) Consequences of membrane protein overexpression in Escherichia coli. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 6, 1527–1550 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Rasouly A., Ron E. Z. (2009) Interplay between the heat shock response and translation in Escherichia coli. Res. Microbiol. 160, 288–296 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Draper G. C., Gober J. W. (2002) Bacterial chromosome segregation. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 56, 567–597 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Dieterich D. C., Link A. J., Graumann J., Tirrell D. A., Schuman E. M. (2006) Selective identification of newly synthesized proteins in mammalian cells using bioorthogonal noncanonical amino acid tagging (BONCAT). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103, 9482–9487 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Kramer G., Sprenger R. R., Back J., Dekker H. L., Nessen M. A., van Maarseveen J. H., de Koning L. J., Hellingwerf K. J., de Jong L., de Koster C. G. (2009) Identification and quantitation of newly synthesized proteins in Escherichia coli by enrichment of azidohomoalanine-labeled peptides with diagonal chromatography. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 8, 1599–1611 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Hemm M. R., Paul B. J., Miranda-Rios J., Zhang A., Soltanzad N., Storz G. Small stress response proteins in Escherichia coli: proteins missed by classical proteomic studies. J. Bacteriol. 192, 46–58 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Braun V. (1995) Energy-coupled transport and signal transduction through the gram-negative outer membrane via TonB-ExbB-ExbD-dependent receptor proteins. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 16, 295–307 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Braun V., Braun M. (2002) Iron transport and signaling in Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 529, 78–85 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Raivio T. L., Silhavy T. J. (2001) Periplasmic stress and ECF sigma factors. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 55, 591–624 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Waller P. R., Sauer R. T. (1996) Characterization of degQ and degS, Escherichia coli genes encoding homologs of the DegP protease. J. Bacteriol. 178, 1146–1153 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Hasona A., Crowley P. J., Levesque C. M., Mair R. W., Cvitkovitch D. G., Bleiweis A. S., Brady L. J. (2005) Streptococcal viability and diminished stress tolerance in mutants lacking the signal recognition particle pathway or YidC2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 102, 17466–17471 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Schuenemann T. A., Delgado-Nixon V. M., Dalbey R. E. (1999) Direct evidence that the proton motive force inhibits membrane translocation of positively charged residues within membrane proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 6855–6864 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. du Plessis D. J., Nouwen N., Driessen A. J. (2011) The Sec translocase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1808, 851–865 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Kadokura H., Beckwith J. (2009) Detecting folding intermediates of a protein as it passes through the bacterial translocation channel. Cell 138, 1164–1173 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]