Abstract
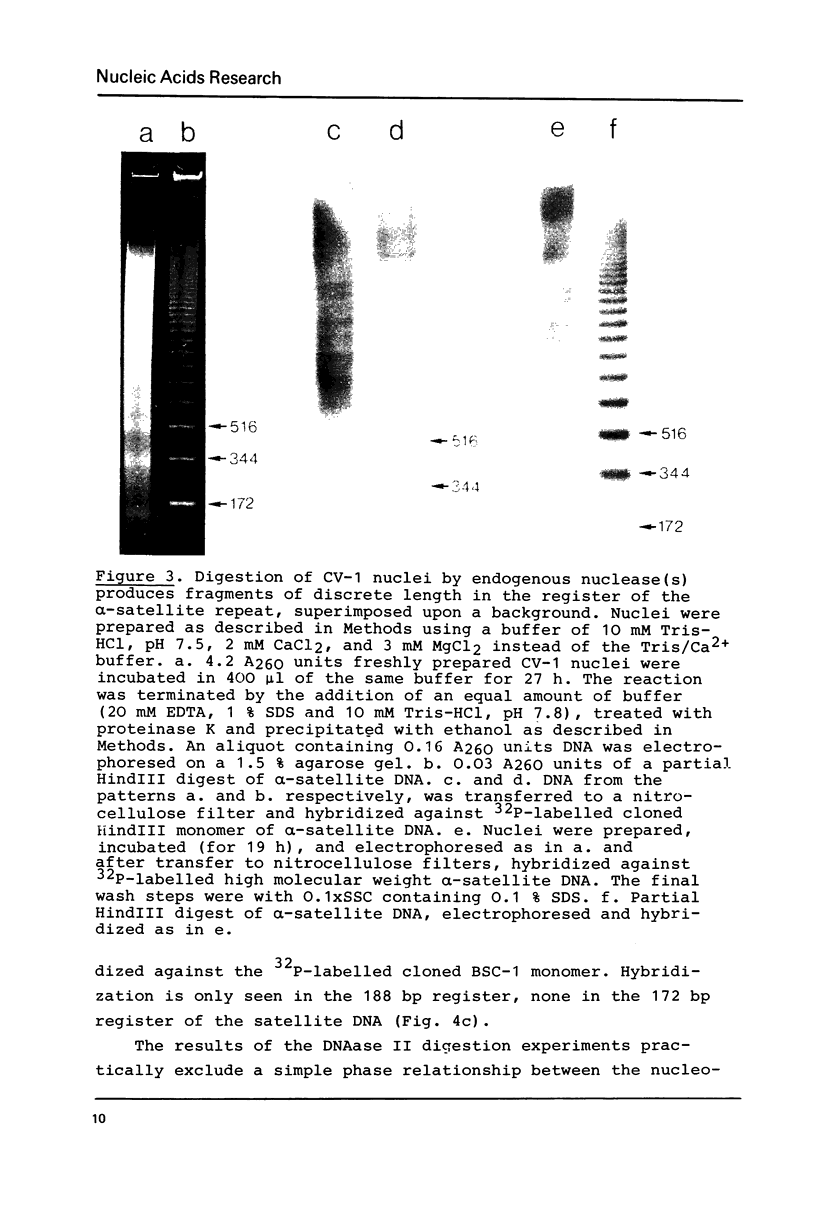
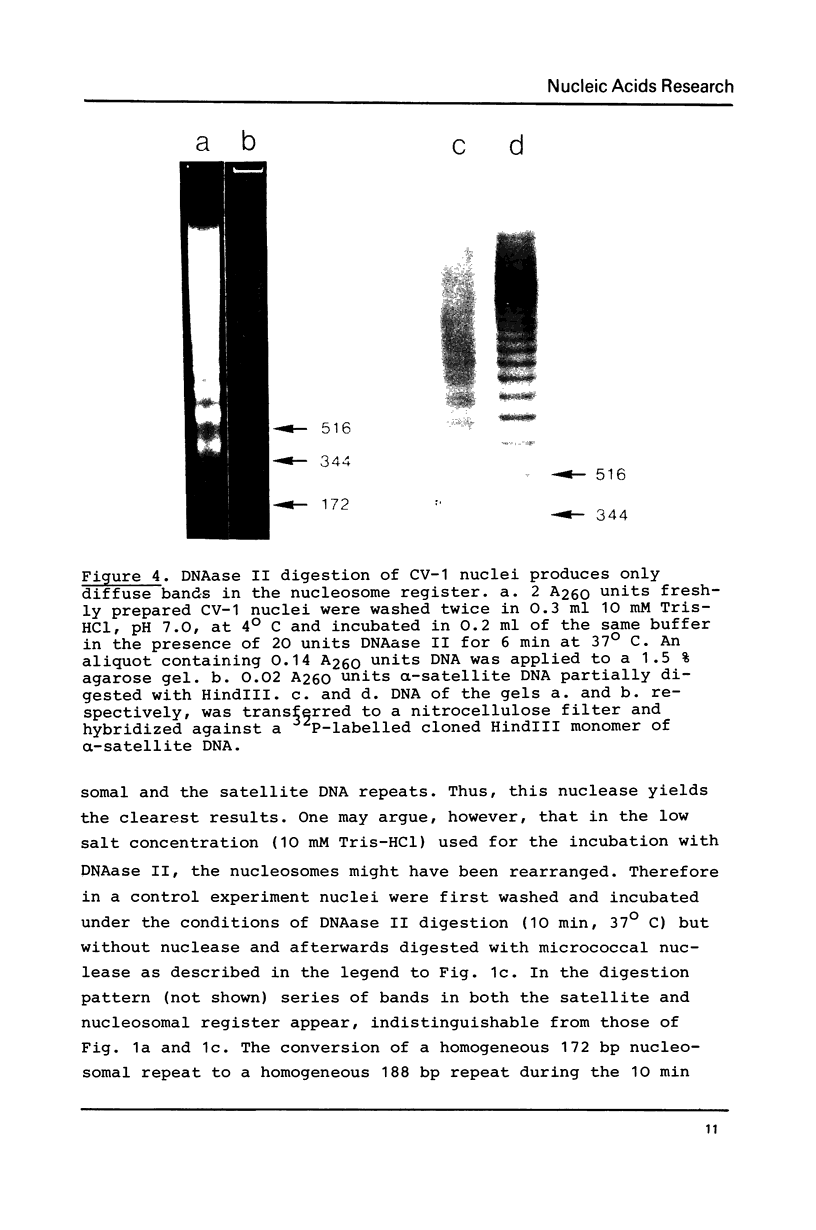
alpha-Satellite DNA containing chromatin from African green monkey cells (CV-1 cells) has been used to study the question whether or not nucleosomes are arranged in phase with the 172 bp repeat unit of the satellite DNA. Digestion experiments with DNAase II led us to exclude a simple phase relationship between the nucleosomal and the satellite DNA repeats. Digestion of CV-1 nuclei with micrococcal nuclease and endogenous nuclease (s) produced a series of sharp bands in the satellite DNA register over a background of heterogeneous length fragments. This observation is explained by a preferential cleavage of certain nucleotide sequences by these nucleases and is not in contradiction to our conclusion that a simple phase relationship does not exist.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altenburger W., Hörz W., Zachau H. G. Nuclease cleavage of chromatin at 100-nucleotide pair intervals. Nature. 1976 Dec 9;264(5586):517–522. doi: 10.1038/264517a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown F. L., Musich P. R., Maio J. J. Cae I: an endonuclease isolated from the African green monkey with properties indicating site-specific cleavage of homologous and heterologous mammalian DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Apr;5(4):1093–1107. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.4.1093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao M. V., Gralla J., Martinson H. G. DNA sequence directs placement of histone cores on restriction fragments during nucleosome formation. Biochemistry. 1979 Mar 20;18(6):1068–1074. doi: 10.1021/bi00573a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton J. L., Bellard M., Chambon P. Biochemical evidence of variability in the DNA repeat length in the chromatin of higher eukaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4382–4386. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crémisi C., Pignatti P. F., Yaniv M. Random location and absence of movement of the nucleosomes on SV 40 nucleoprotein complex isolated from infected cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Dec 6;73(3):548–554. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90845-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingman C. W., Peacock A. C. Analytical studies on nuclear ribonucleic acid using polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1968 Feb;7(2):659–668. doi: 10.1021/bi00842a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fittler F. Analysis of the alpha-satellite DNA from African green monkey cells by restriction nucleases. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Apr 1;74(2):343–352. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11399.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesfeld J. M., Melton D. A. The length of nucleosome-associated DNA is the same in both transcribed and nontranscribed regions of chromatin. Nature. 1978 May 25;273(5660):317–319. doi: 10.1038/273317a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf H., Fittler F., Zachau H. G. Studies on the organization of the alpha-satellite DNA from African green monkey cells using restriction nucleases and molecular cloning. Gene. 1979 Feb;5(2):93–110. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90096-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruss P., Sauer G. Repetitive primate DNA containing the recognition sequences for two restriction endonucleases which generate cohesive ends. FEBS Lett. 1975 Dec 1;60(1):85–88. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80424-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewish D. R., Burgoyne L. A. Chromatin sub-structure. The digestion of chromatin DNA at regularly spaced sites by a nuclear deoxyribonuclease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 May 15;52(2):504–510. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90740-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörz W., Igo-Kemenes T., Pfeiffer W., Zachau H. G. Specific cleavage of chromatin by restriction nucleases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Nov;3(11):3213–3226. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.11.3213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Flavell R. A. A physical map of the DNA regions flanking the rabbit beta-globin gene. Cell. 1977 Oct;12(2):429–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90119-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D. Structure of chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:931–954. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.004435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurnit D. M., Maio J. J. Subnuclear redistribution of DNA species in confluent and growing mammalian cells. Chromosoma. 1973 May 14;42(1):23–36. doi: 10.1007/BF00326328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loening U. E. The determination of the molecular weight of ribonucleic acid by polyacrylamide-gel electrophresis. The effects of changes in conformation. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(1):131–138. doi: 10.1042/bj1130131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maio J. J. DNA strand reassociation and polyribonucleotide binding in the African green monkey, Cercopithecus aethiops. J Mol Biol. 1971 Mar 28;56(3):579–595. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90403-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musich P. R., Maio J. J., Brown F. L. Subunit structure of chromatin and the organization of eukaryotic highly repetitive DNA: indications of a phase relation between restriction sites and chromatin subunits in African green monkey and calf nuclei. J Mol Biol. 1977 Dec 15;117(3):657–677. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90063-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polisky B., McCarthy B. Location of histones on simian virus 40 DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):2895–2899. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.2895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponder B. A., Crawford L. V. The arrangement of nucleosomes in nucleoprotein complexes from polyoma virus and SV40. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):35–49. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90315-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prunell A., Kornberg R. D. Relation of nucleosomes to nucleotide sequences in the rat. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1978 May 11;283(997):269–273. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1978.0023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTS W. K., DEKKER C. A., RUSHIZKY G. W., KNIGHT C. A. Studies on the mechanism of action of micrococcal nuclease. 1. Degradation of thymus deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 May 14;55:664–673. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90844-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg H., Singer M., Rosenberg M. Highly reiterated sequences of SIMIANSIMIANSIMIANSIMIANSIMIAN. Science. 1978 Apr 28;200(4340):394–402. doi: 10.1126/science.205944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott W. A., Wigmore D. J. Sites in simian virus 40 chromatin which are preferentially cleaved by endonucleases. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1511–1518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streeck R. E., Zachau H. G. A long-range and two short-range periodicities are superimposed in the 1.706-g/cm3 satellite DNA from calf thymus. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Aug 15;89(1):267–279. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb20923.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. J., Sundin O., Bohn M. A stretch of "late" SV40 viral DNA about 400 bp long which includes the origin of replication is specifically exposed in SV40 minichromosomes. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):453–466. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldeck W., Föhring B., Chowdhury K., Gruss P., Sauer G. Origin of DNA replication in papovavirus chromatin is recognized by endogenous endonuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5964–5968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]